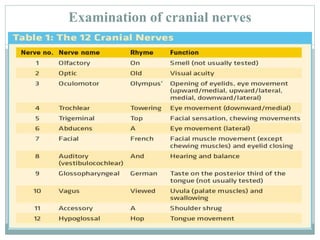
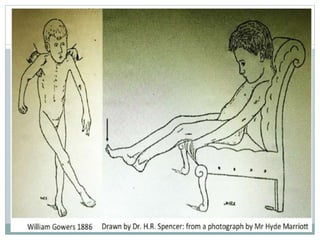
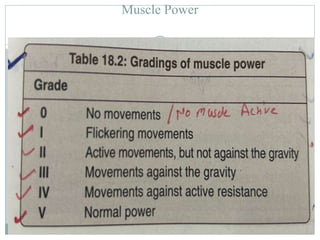
The document discusses examination of the central nervous system. It covers assessment of higher functions like behavior, memory and orientation. It also discusses signs of meningeal irritation like nuchal rigidity and Kernig's sign. The cranial nerves, motor system, sensation and localizing signs are examined. The motor system examination includes gait, posture and muscle tone, power and reflexes. Sensory examination involves tests of pain, touch and temperature. Localizing signs help identify abnormalities in specific areas of the brain or spinal cord.