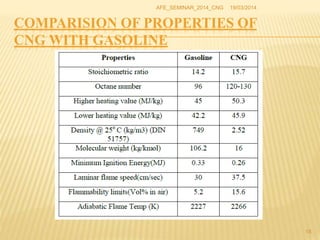
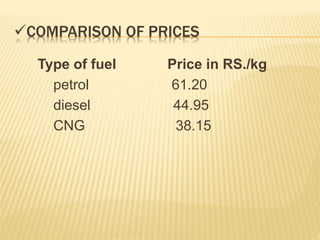
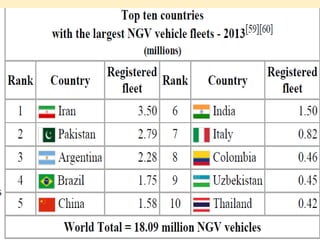
Compressed natural gas (CNG) is made by compressing natural gas (mostly methane) to less than 1% of its volume at standard atmospheric pressure. It is an environmentally friendly alternative to gasoline and diesel fuel that is used in vehicles. CNG produces fewer emissions and is cheaper than gasoline or diesel. While CNG vehicles require a high-pressure storage tank that takes up space, manufacturers are developing solutions like roof and underbody storage to address this disadvantage. CNG is also safer and more readily available than liquefied natural gas (LNG), making it more suitable for powering vehicles.