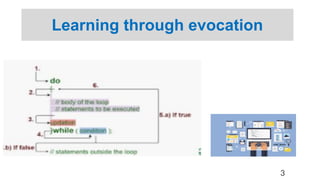
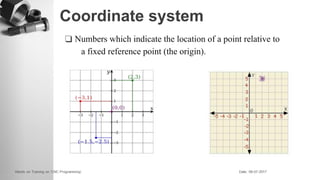
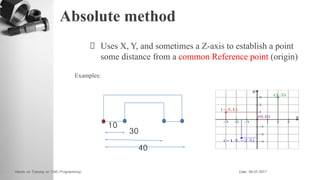
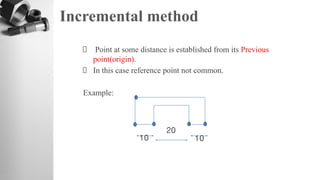
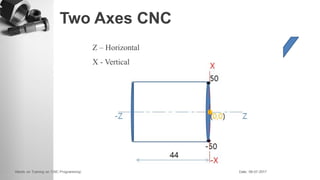
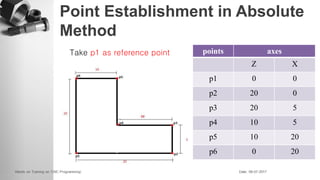
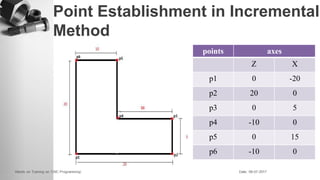
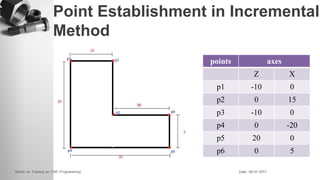
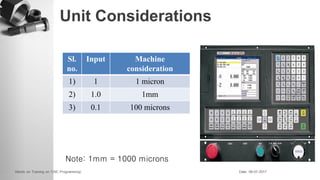
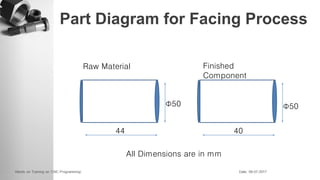
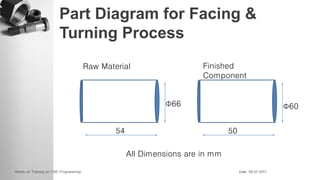
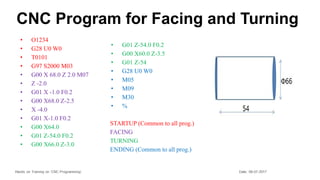
The document provides information on a training session on CNC programming including the objectives, topics covered, example programs, and sample parts. The session covered coordinate systems, address characters, offsets, G-codes and M-codes. Example programs were provided for facing and turning processes. Formative assessments and a practice program were also included to help students learn CNC programming.