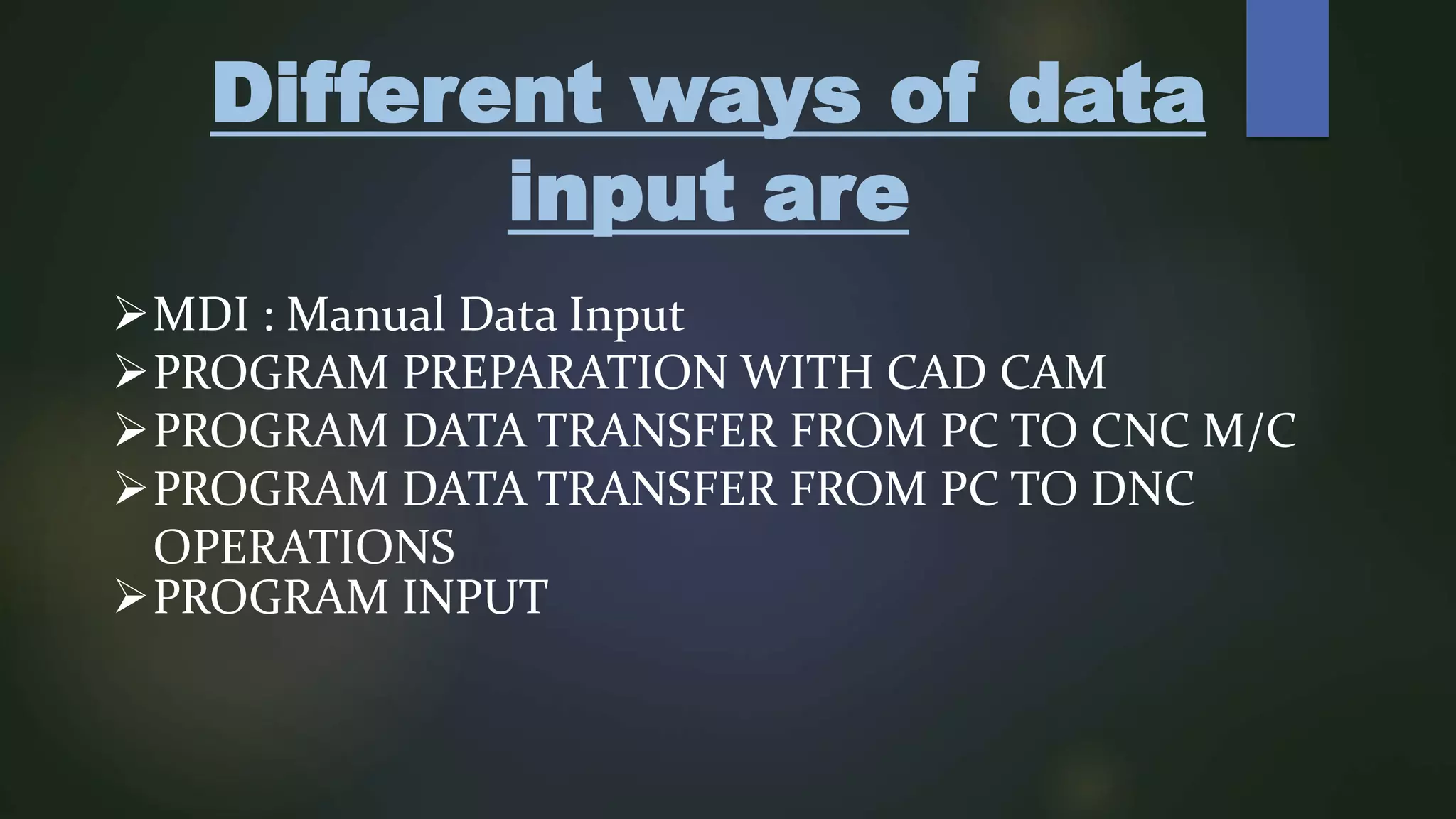
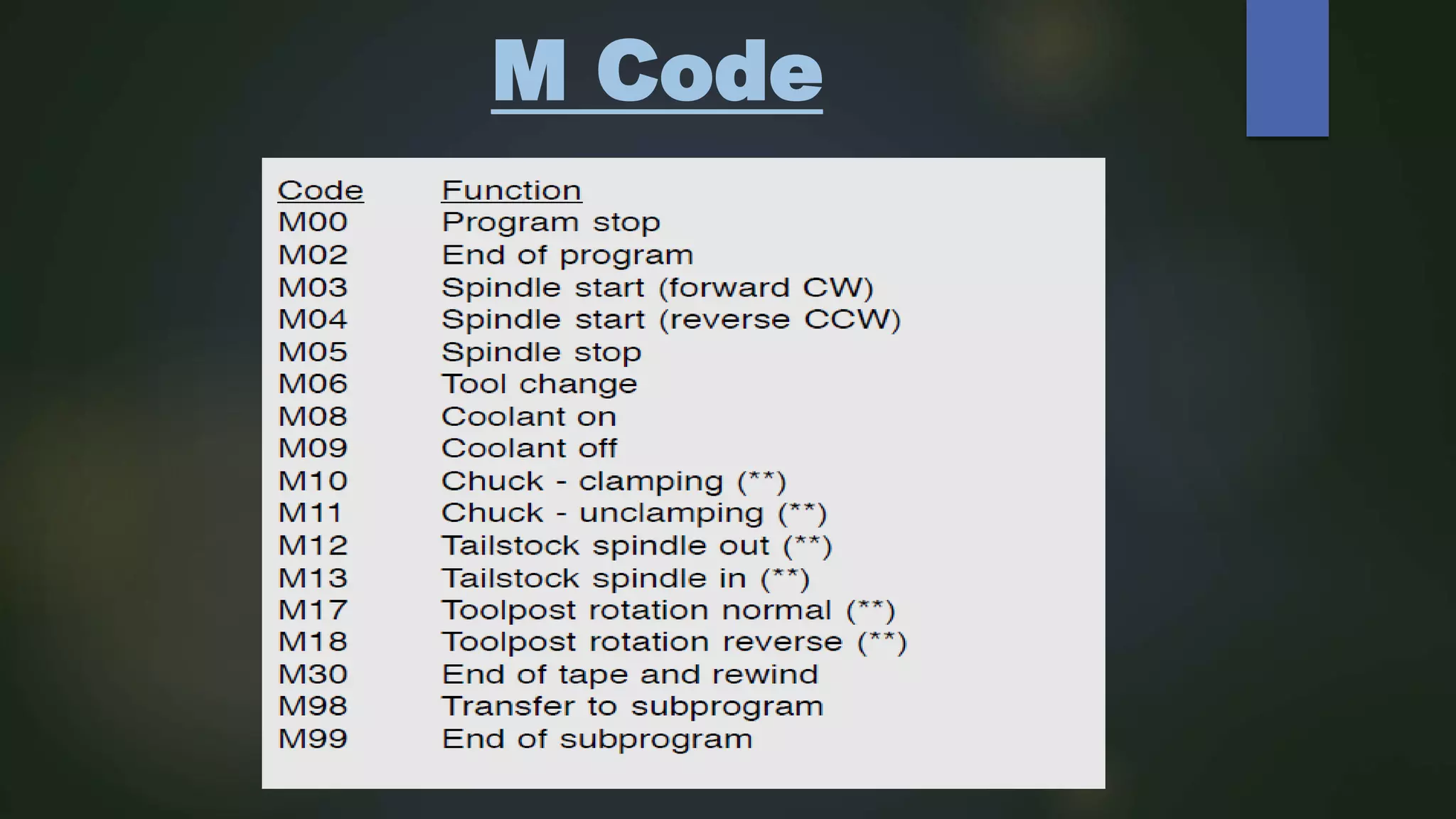
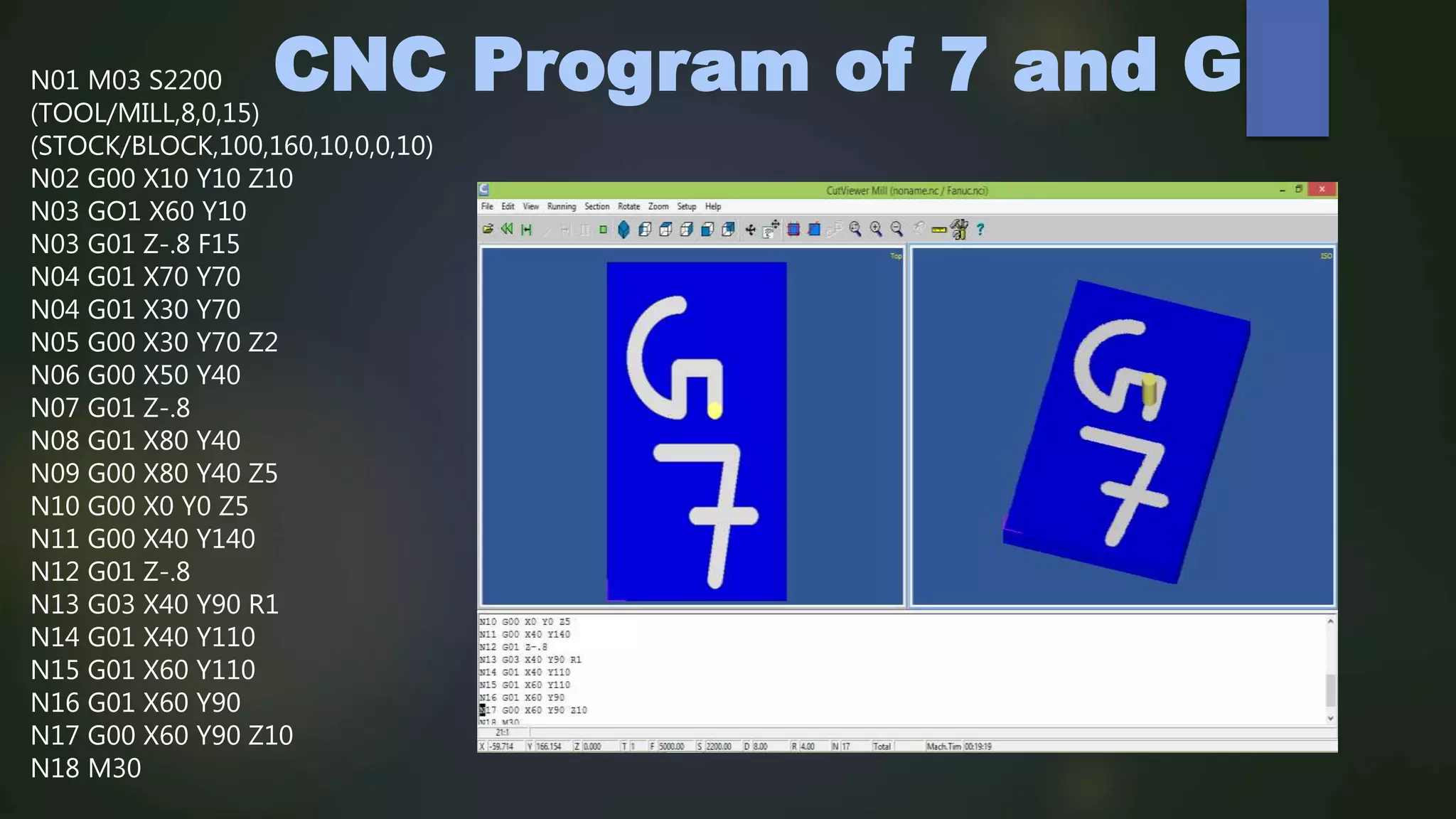
This document describes a CNC milling machine training program presented by Gitanshu Kumar. It includes sections on the evolution of NC machines, types of CNC machines and controls, data input methods, operational features of CNC machines, features of CNC milling, tools used, cut viewer software, programming letters and codes, and an example CNC program. Advantages of CNC machines include high repeatability, precision, and productivity while disadvantages include high setup costs and needing skilled operators.