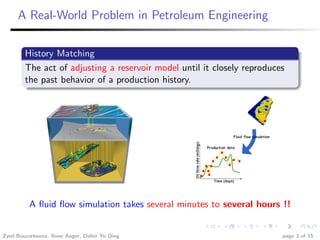
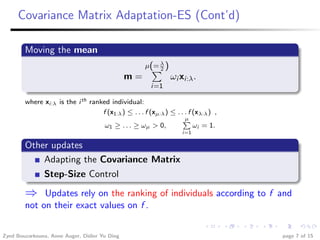
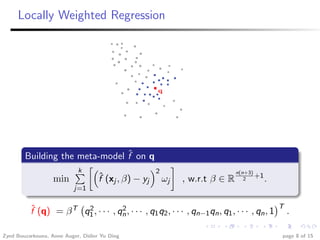
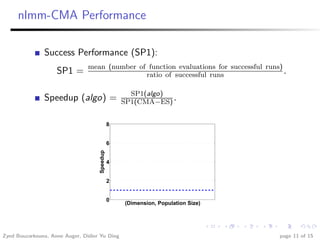
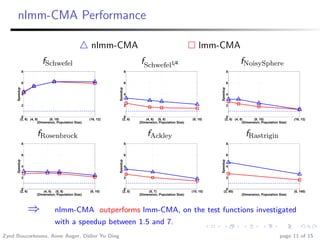
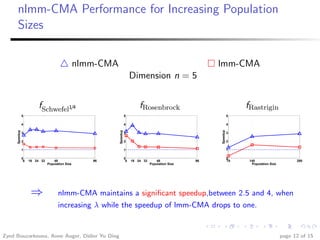
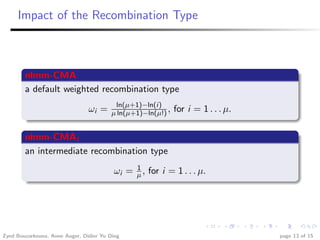
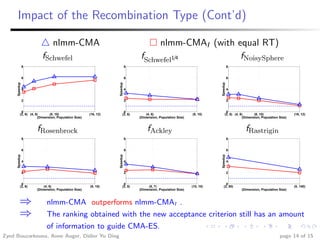
This document summarizes research investigating the use of local meta-models within the CMA-ES optimization algorithm for large population sizes. It introduces CMA-ES, describes how local meta-models can be used to build surrogate models of the objective function to reduce evaluations, and presents a new variant called nlmm-CMA that uses a more flexible acceptance criterion for the meta-model. Experimental results show nlmm-CMA achieves speedups over lmm-CMA, the prior local meta-model approach for CMA-ES, on benchmark optimization problems.