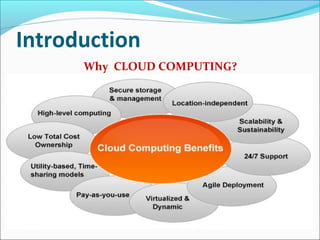
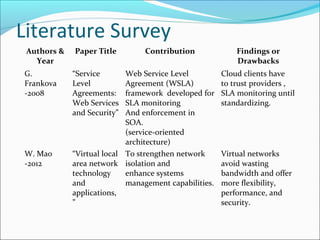
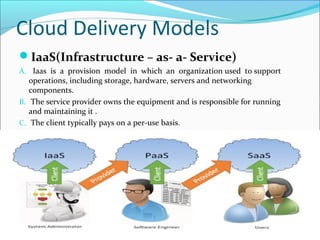
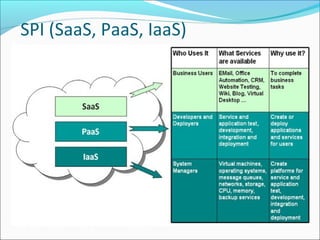
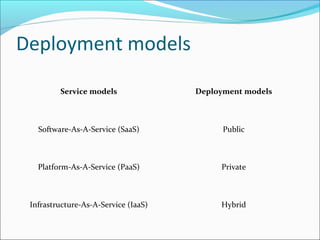
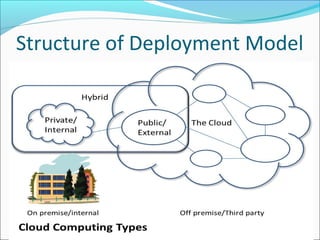
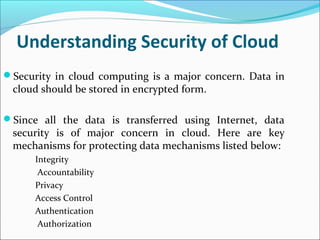
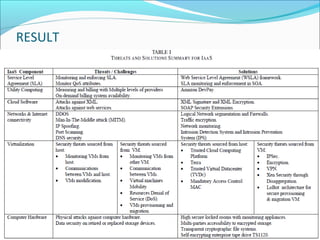
This document summarizes a technical seminar presentation on security issues in cloud computing infrastructure as a service (IaaS). The presentation covers IaaS components and security drawbacks, literature reviewing approaches to monitoring service level agreements and strengthening network isolation, and the conclusions that each IaaS component poses security risks, cloud requires balancing cost, security and privacy, and changes in trust increase challenges.