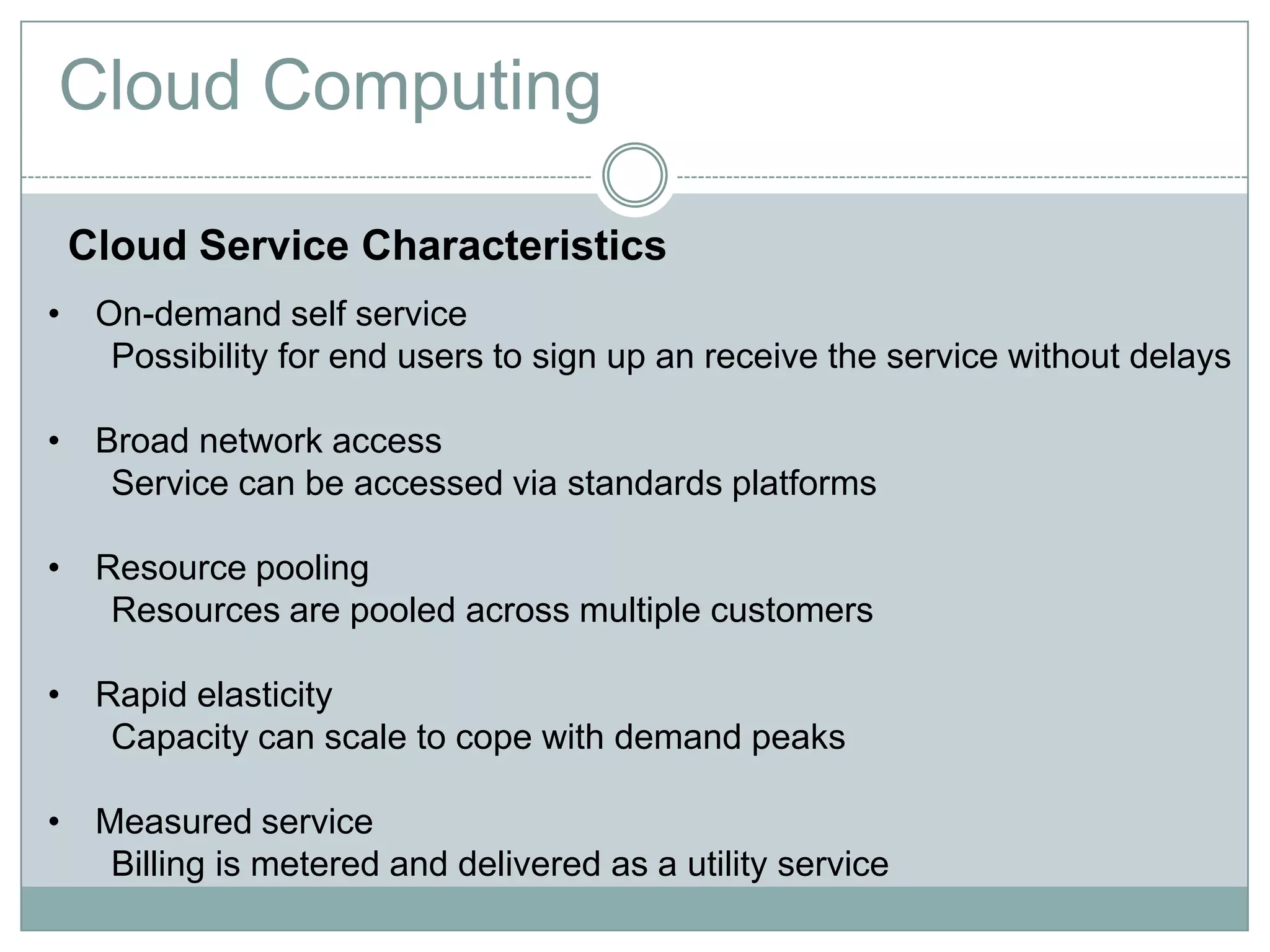
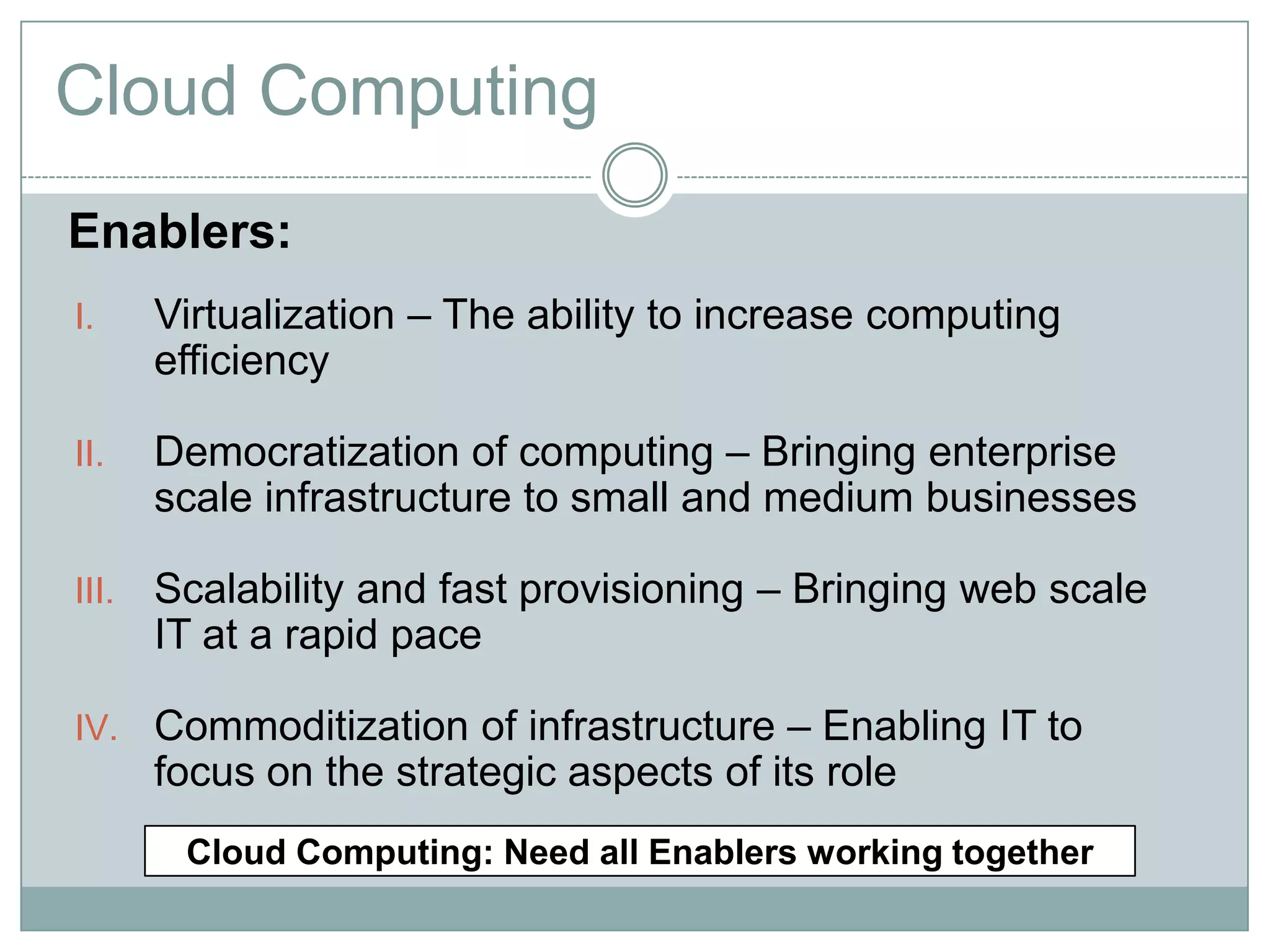
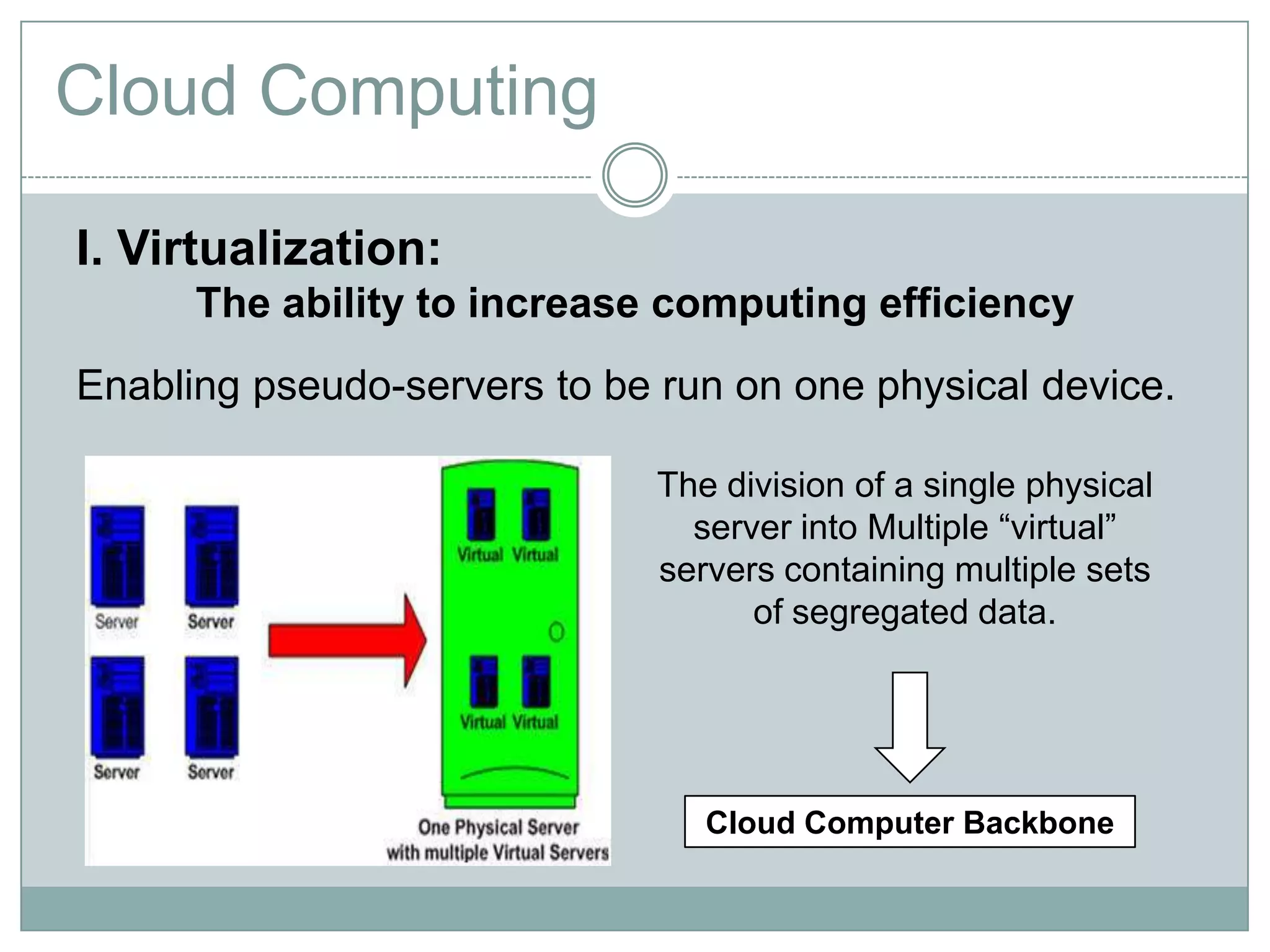
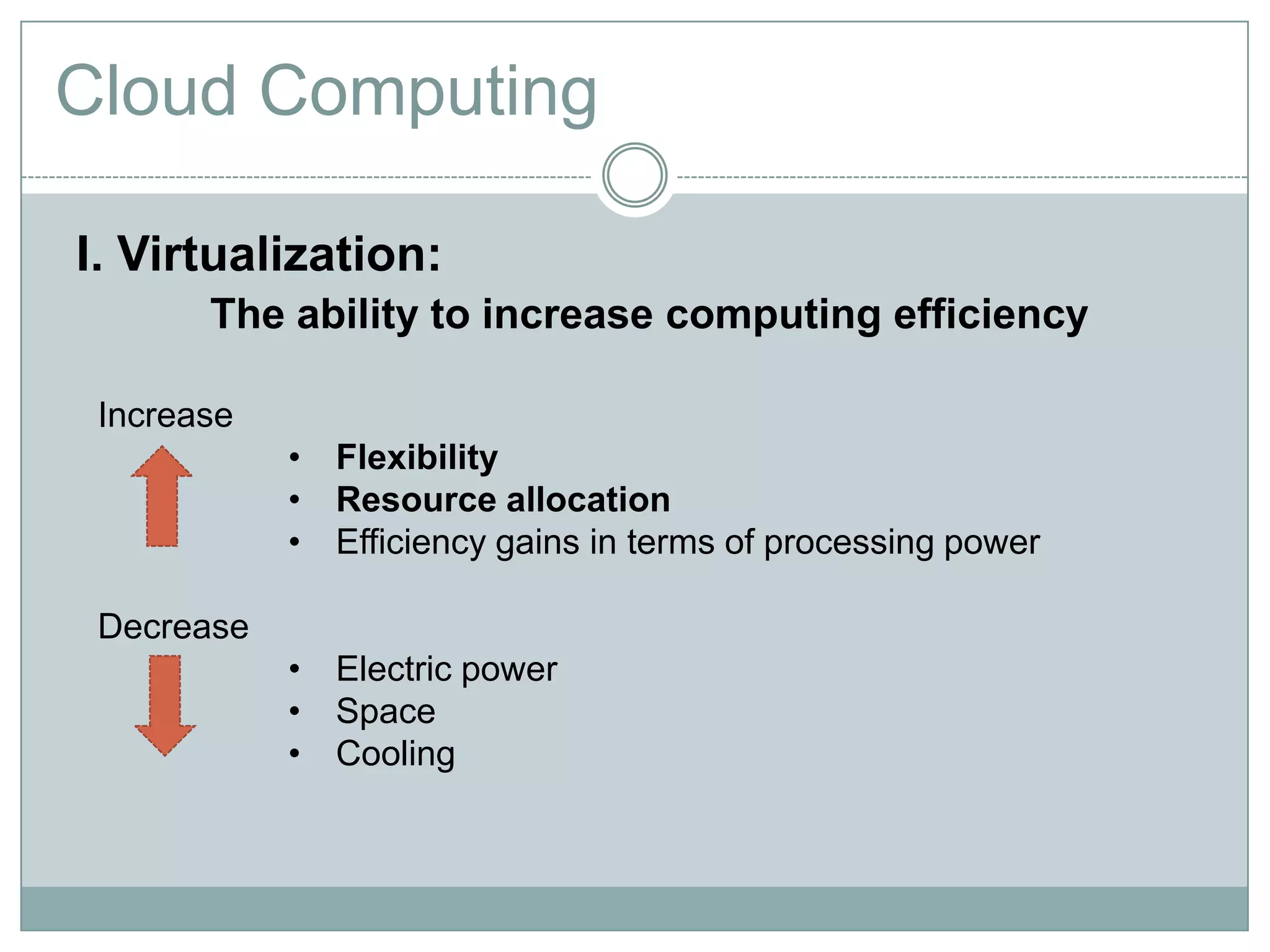
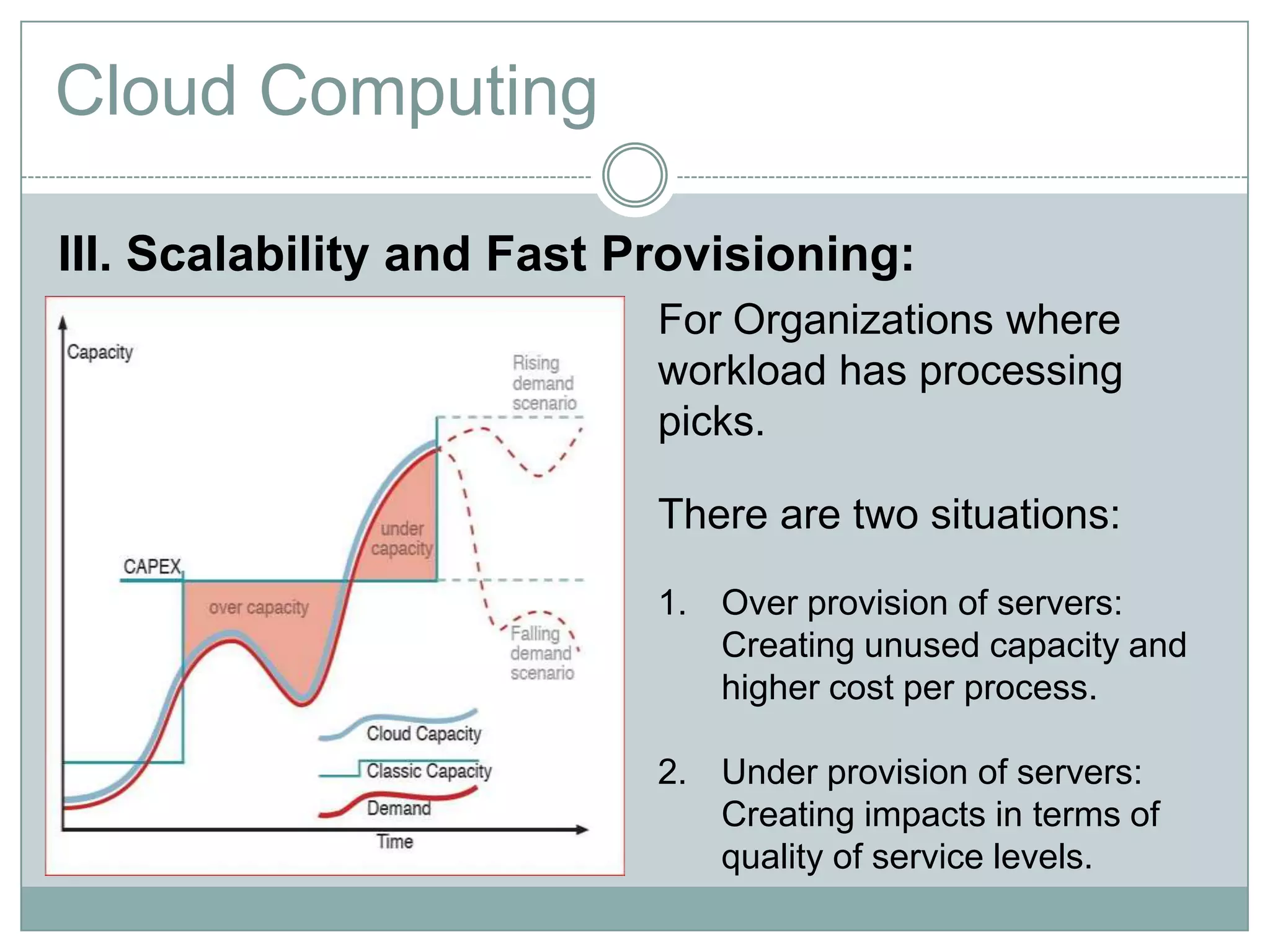
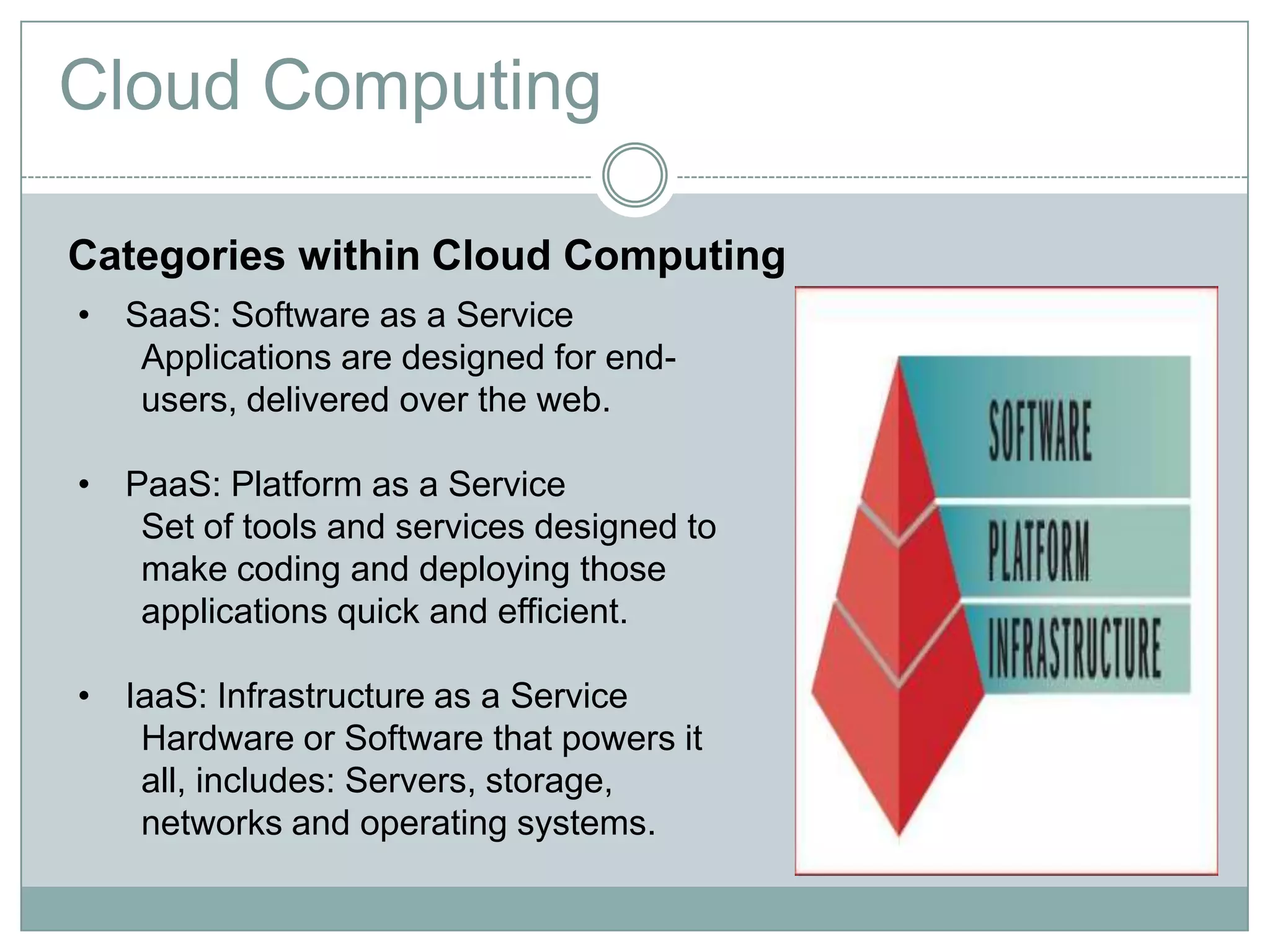
Cloud computing is a model that provides on-demand access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources like networks, servers, storage, applications and services. It has characteristics like on-demand self-service, broad network access, resource pooling, rapid elasticity and measured service. Key enablers of cloud computing include virtualization, democratization of computing through scalable infrastructure, fast provisioning, and commoditization of infrastructure. Common categories are SaaS, PaaS and IaaS.