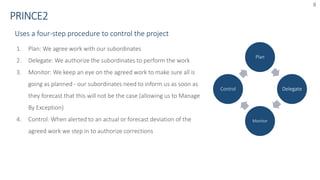
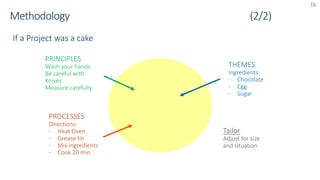
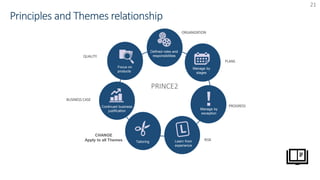
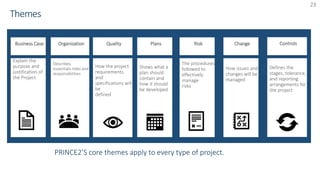
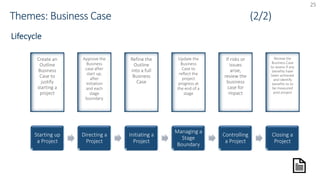
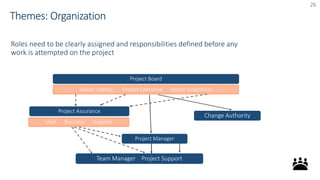
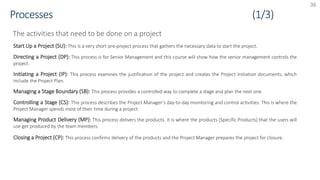
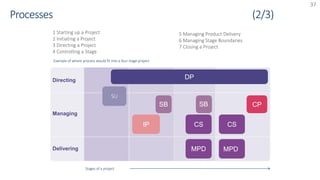
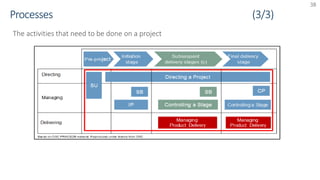
The document provides an overview of PRINCE2 project management methodology. It discusses the key components of PRINCE2 including the 7 themes, 7 principles, and 7 processes. The 7 processes are starting up a project, directing a project, initiating a project, controlling a stage, managing a stage boundary, managing product delivery, and closing a project. PRINCE2 provides a standardized approach to project management focused on delivering projects on time, on budget, and meeting quality standards.