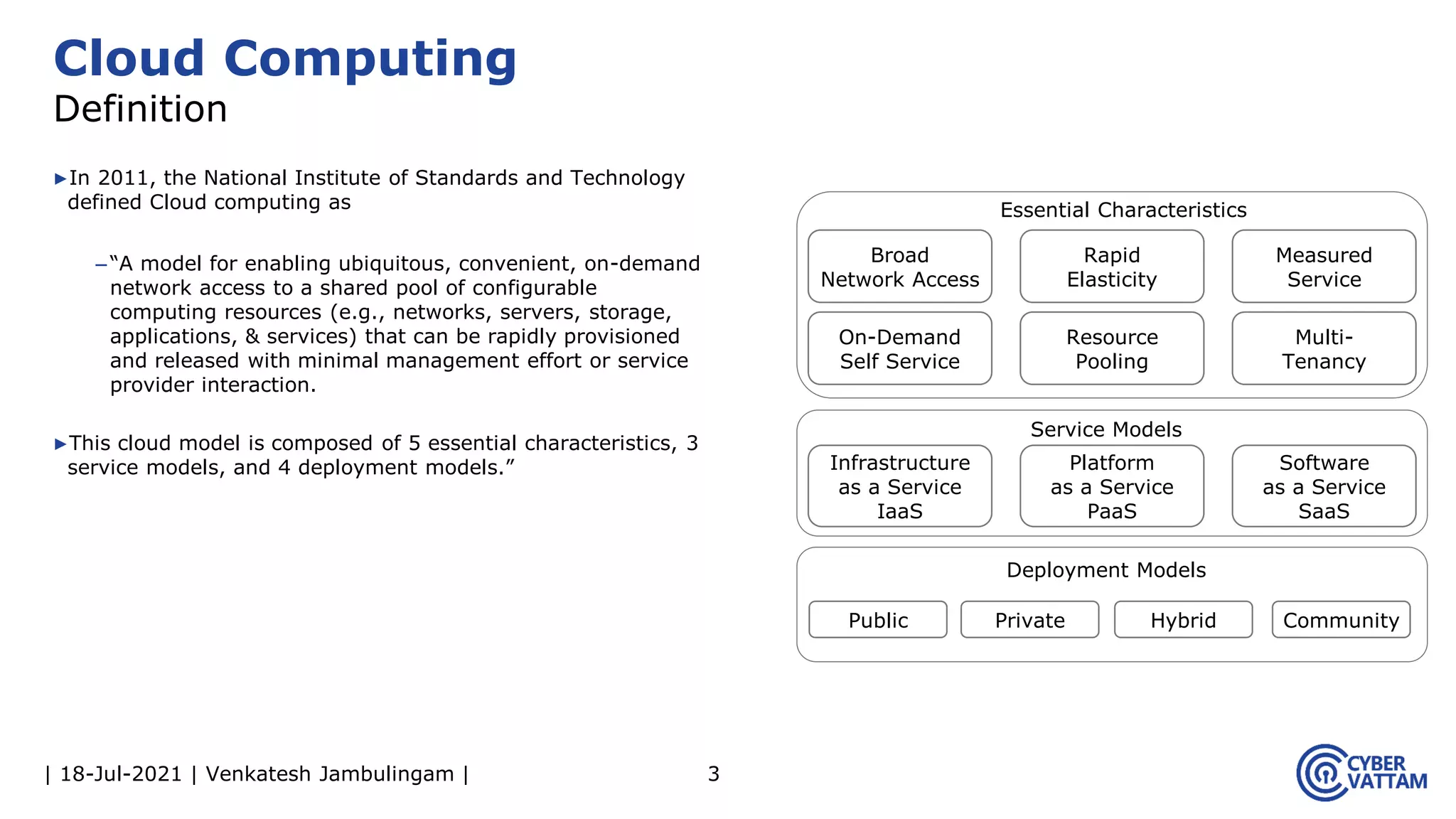
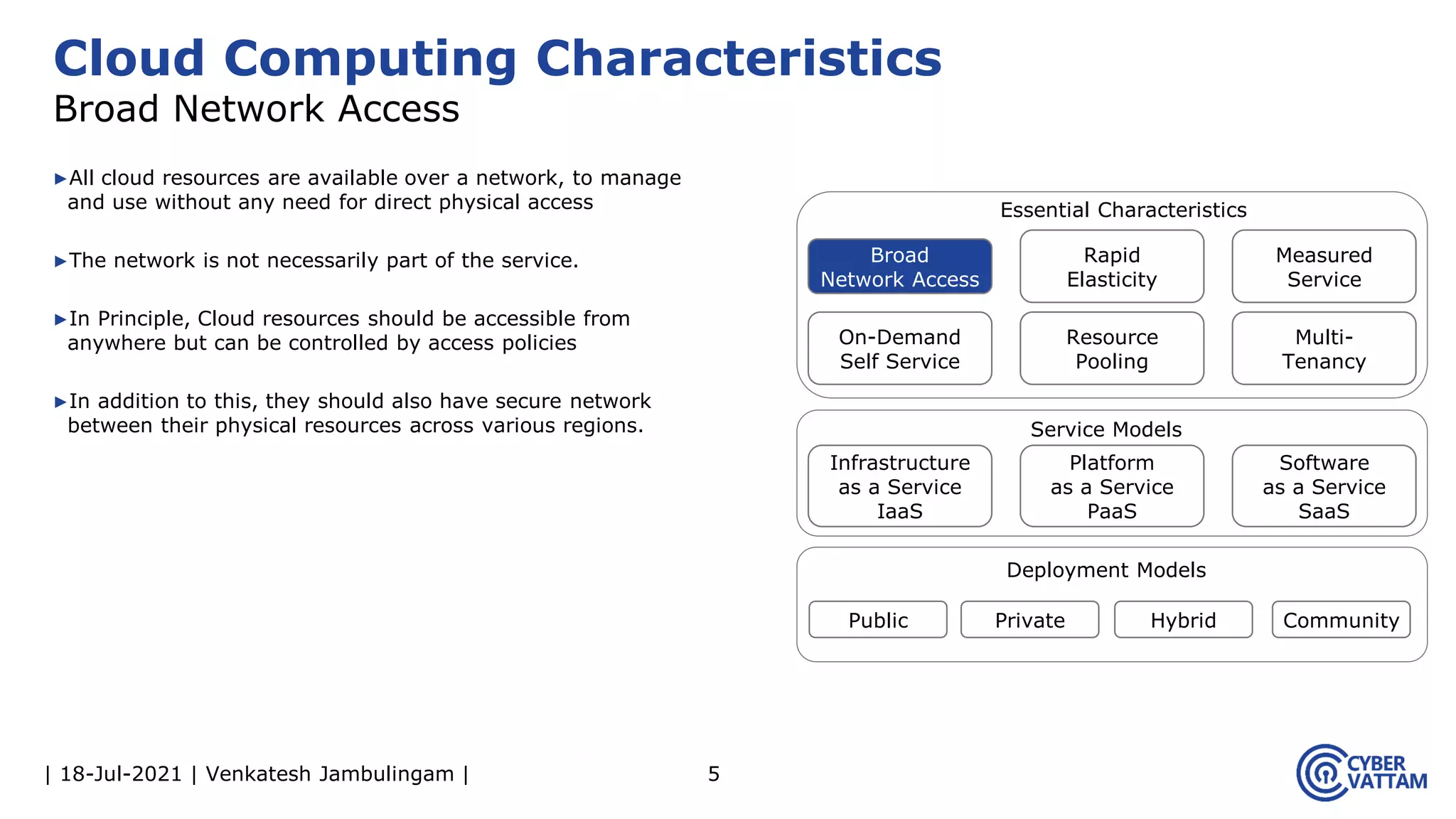
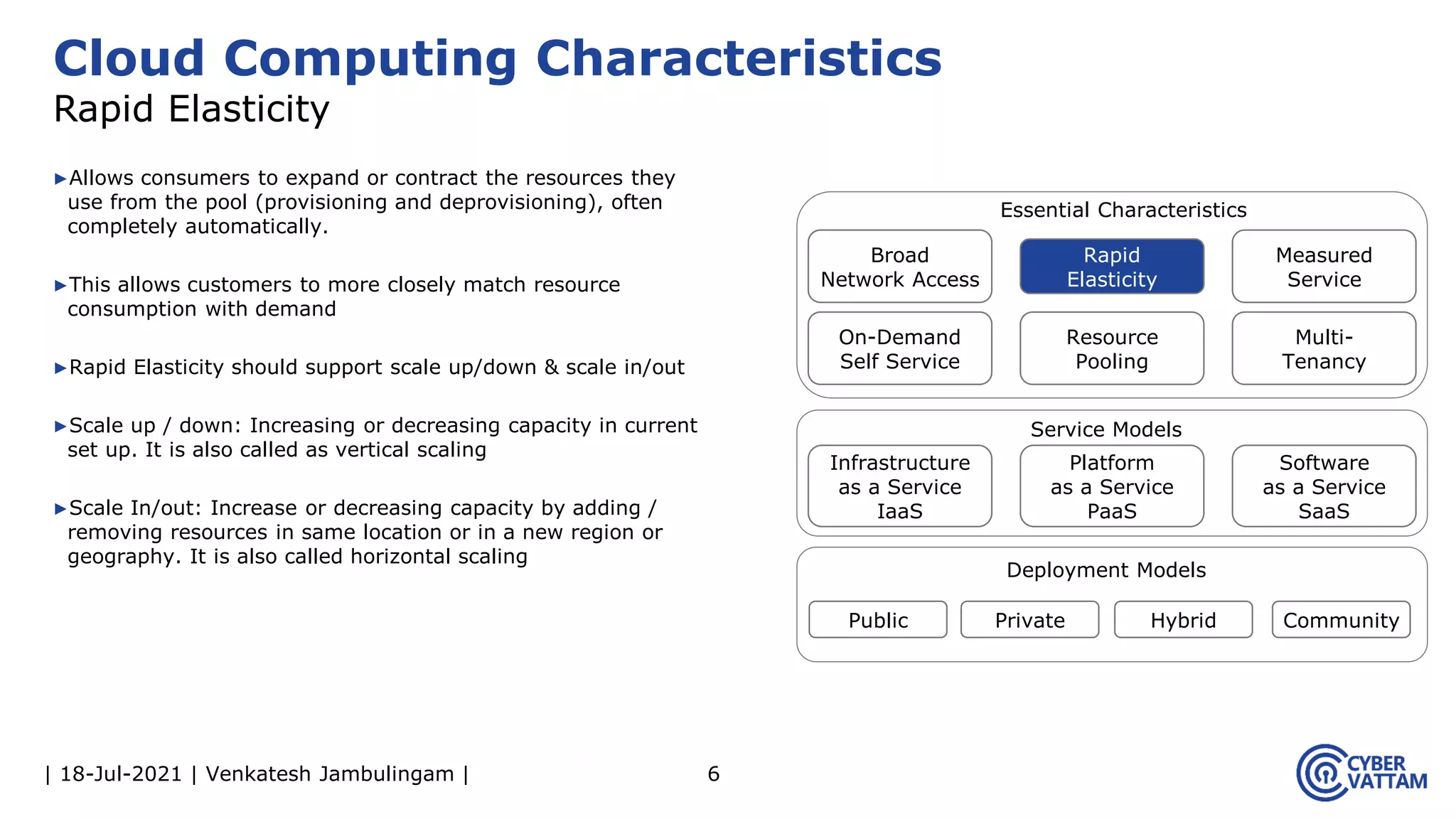
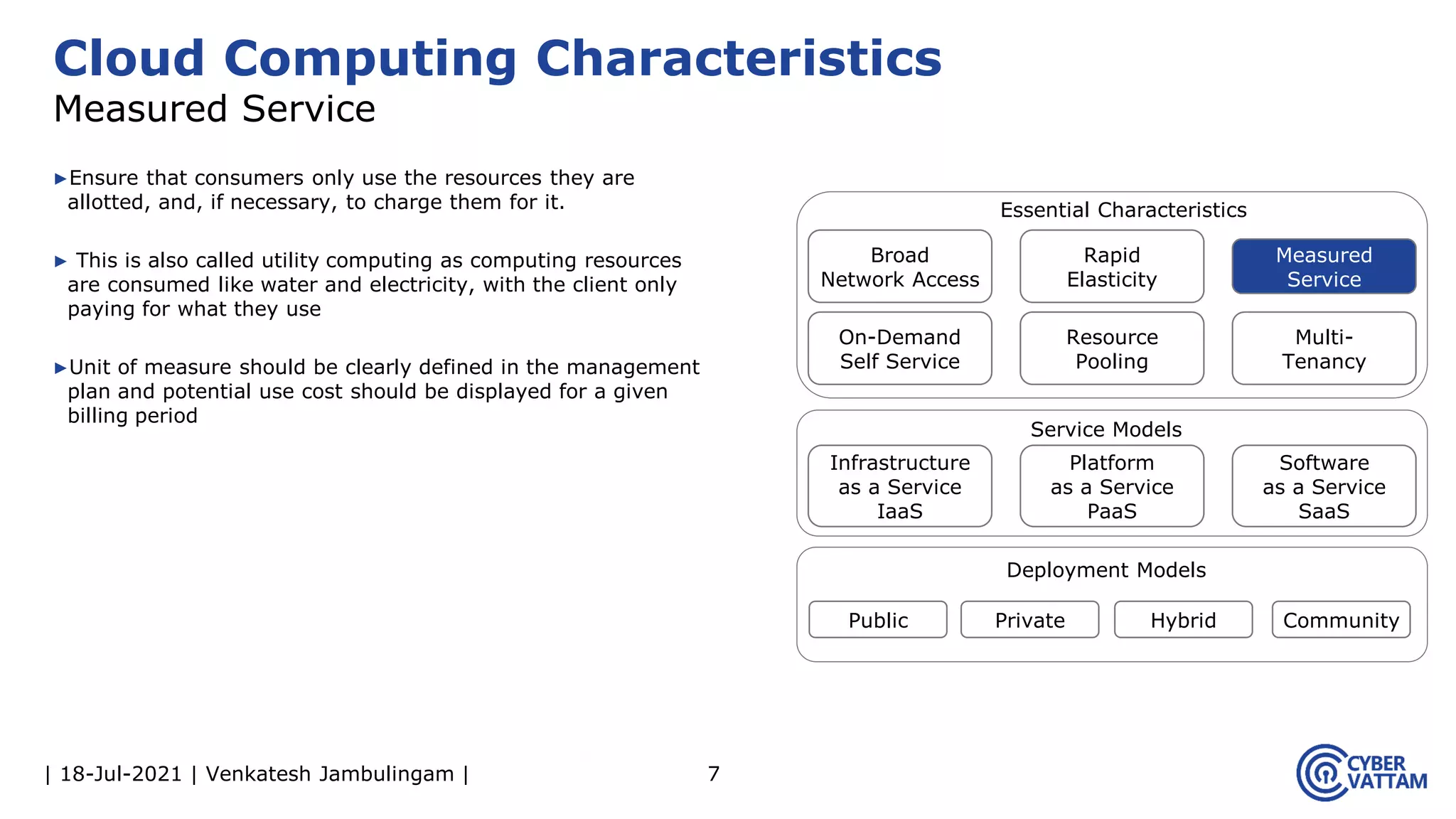
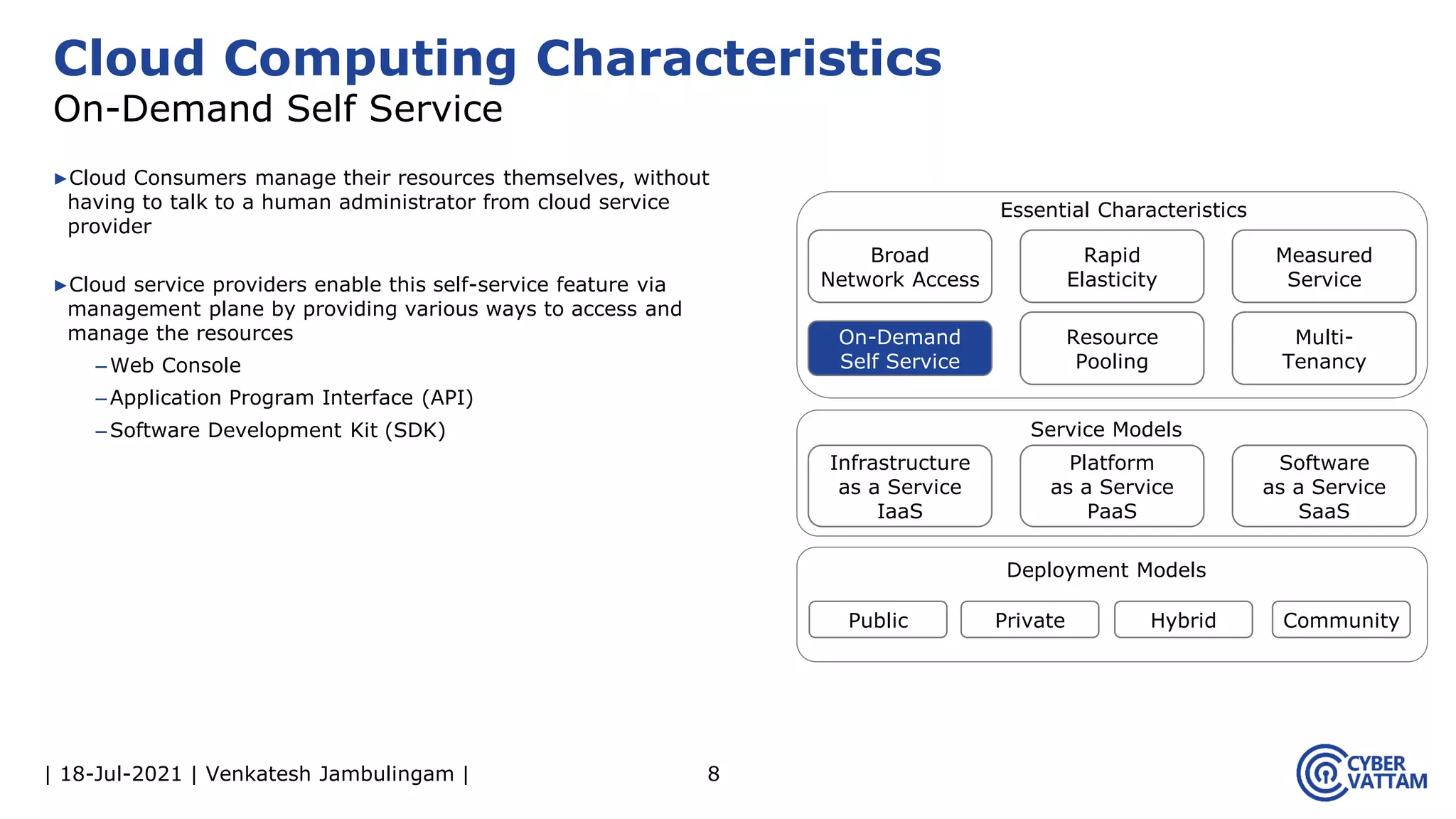
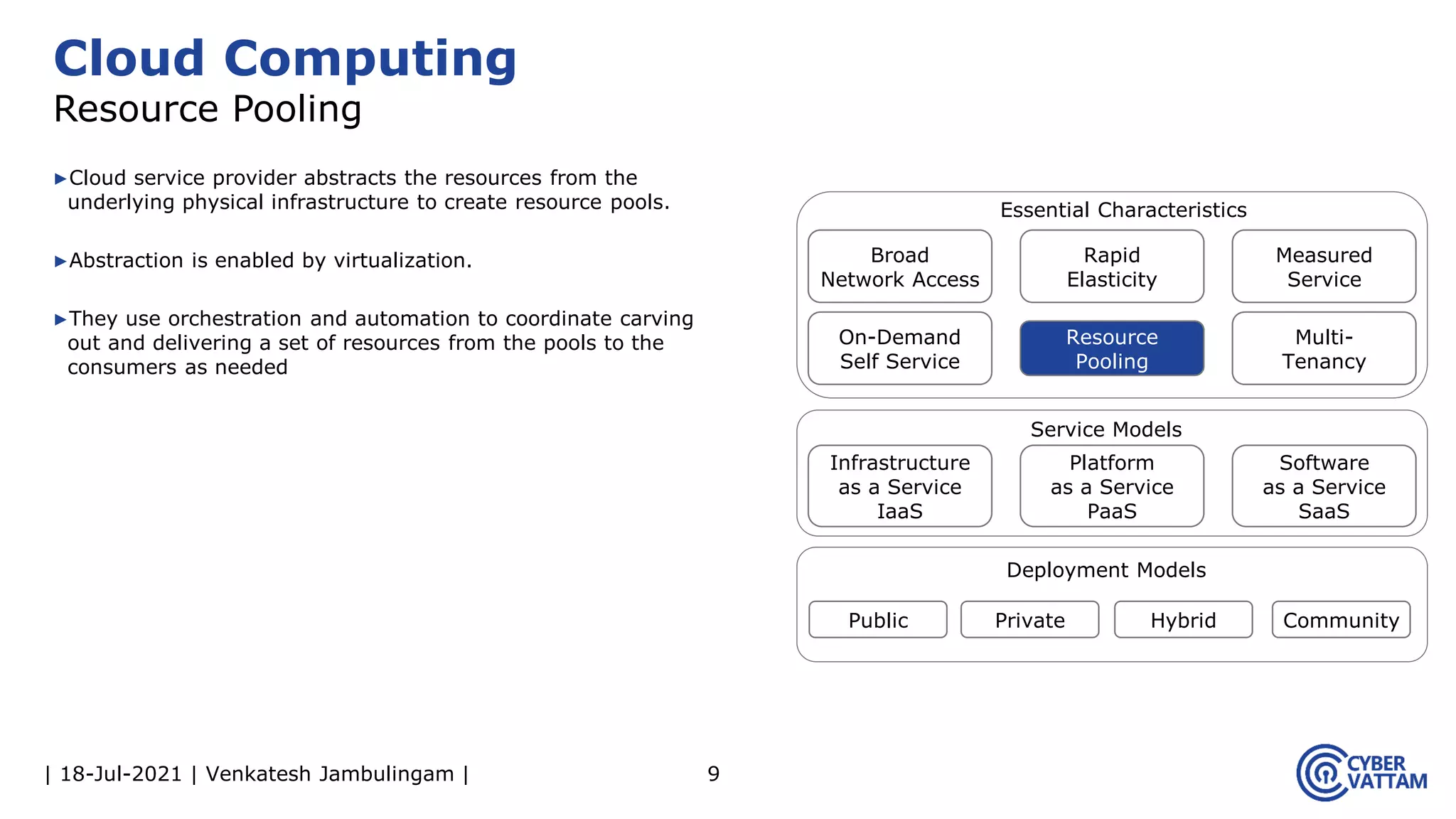
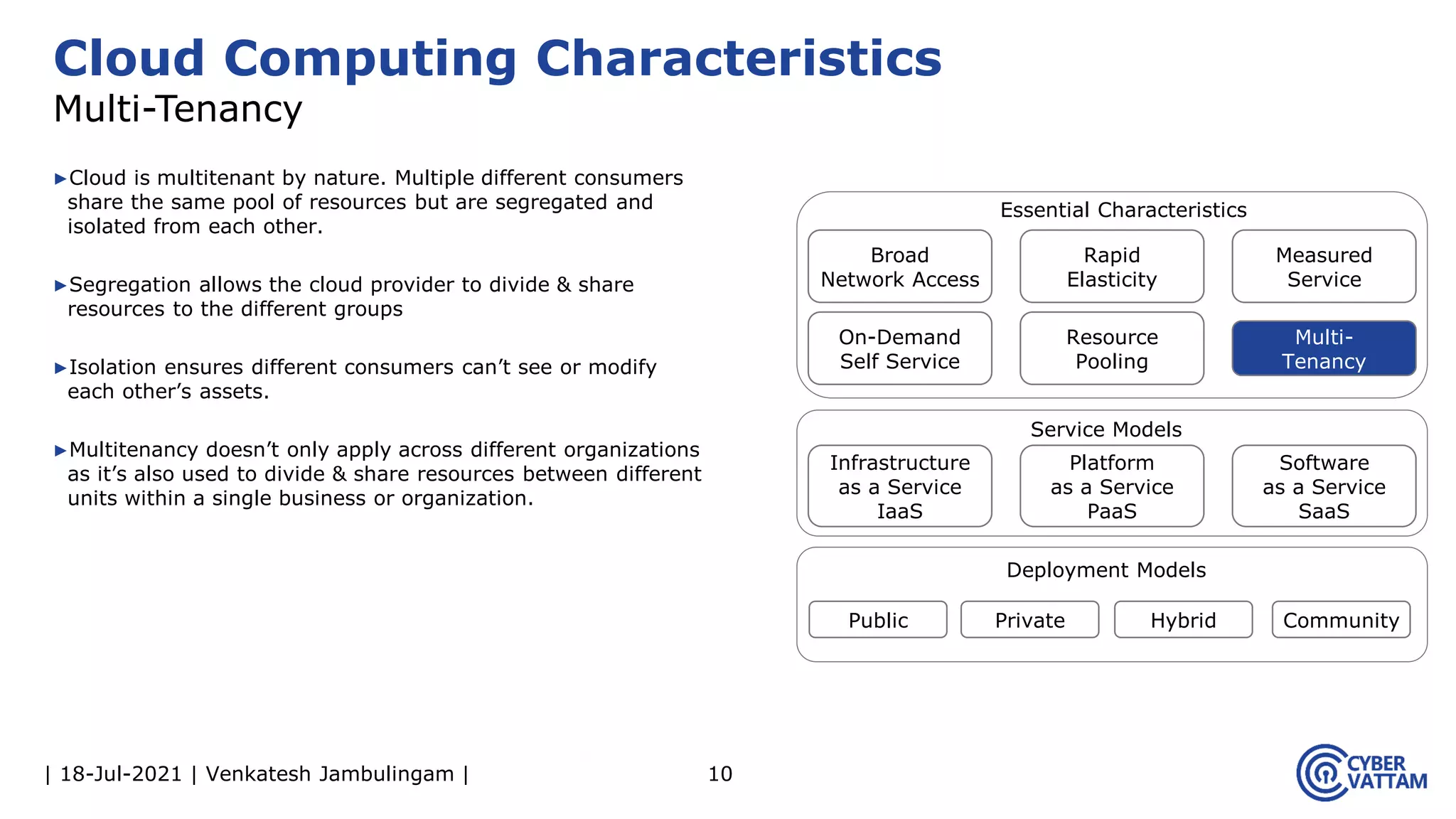
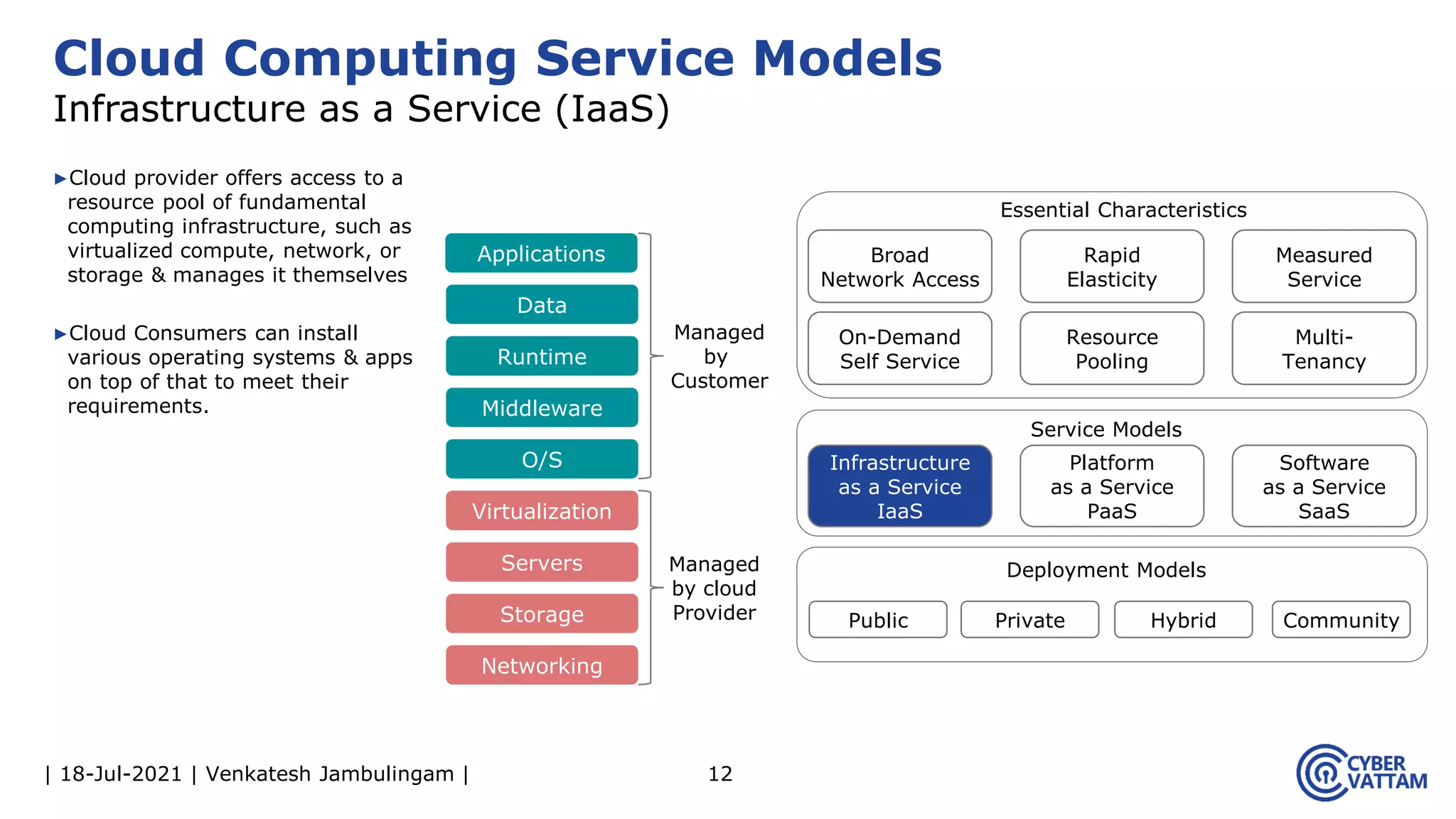
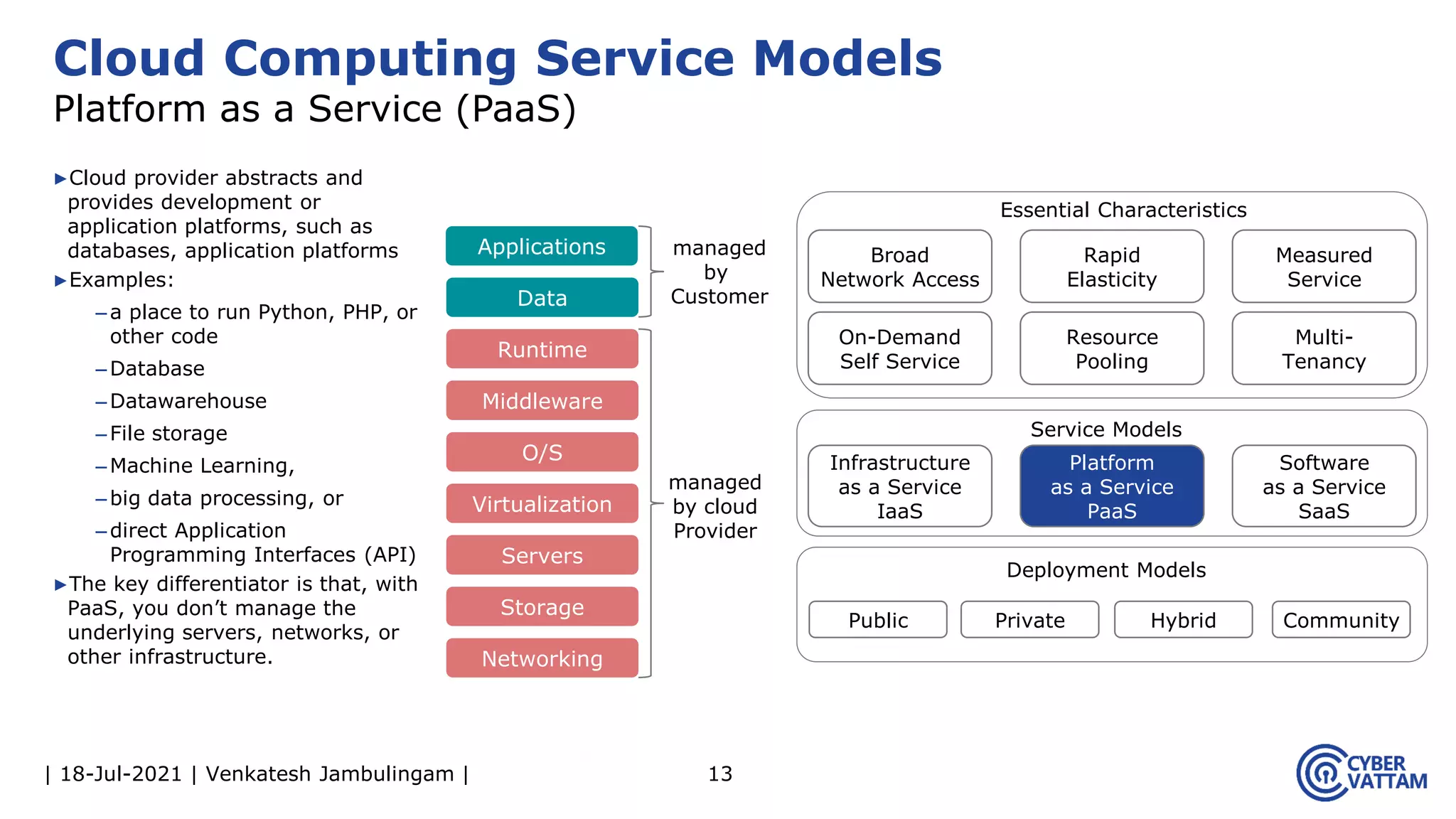
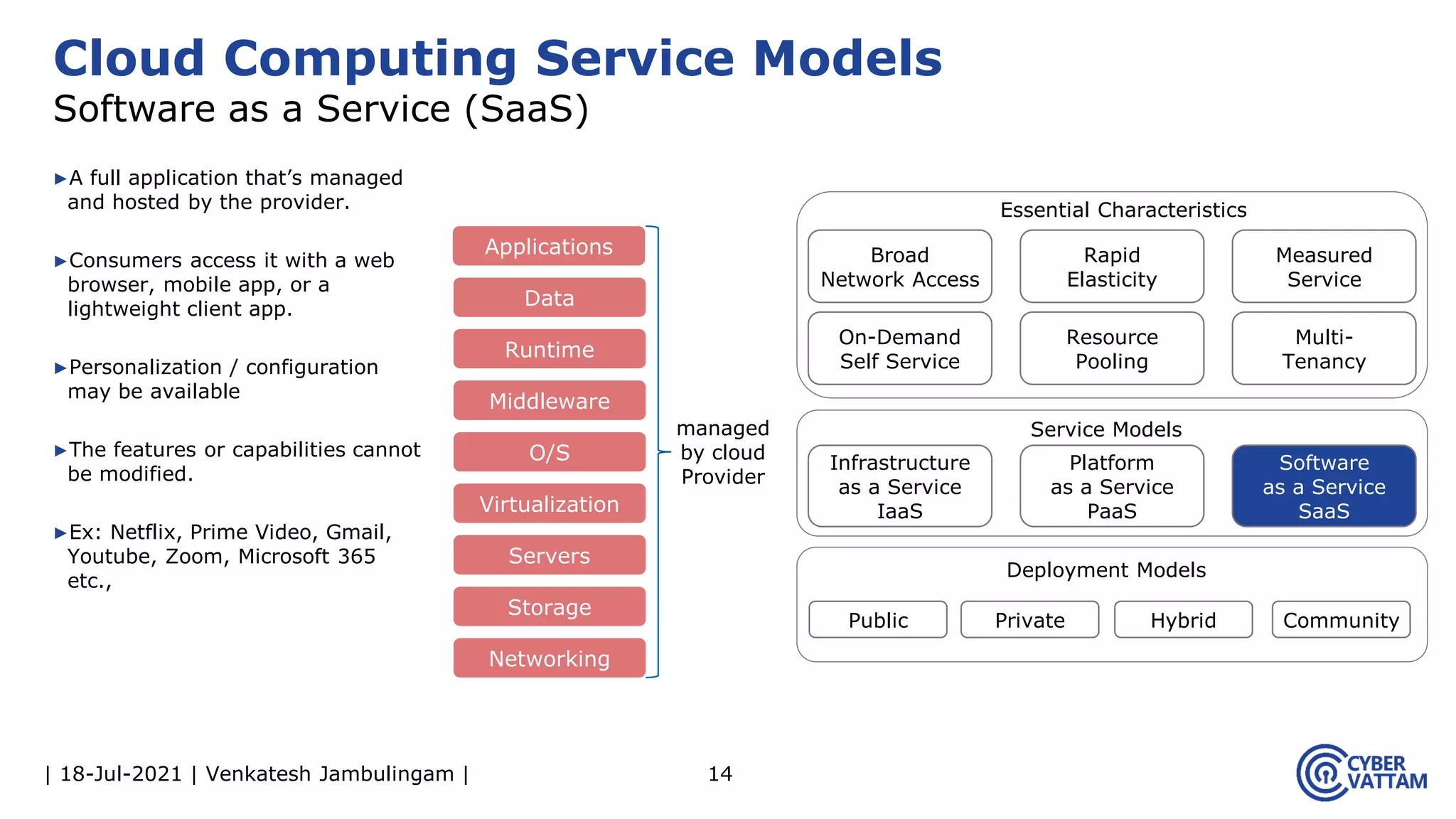
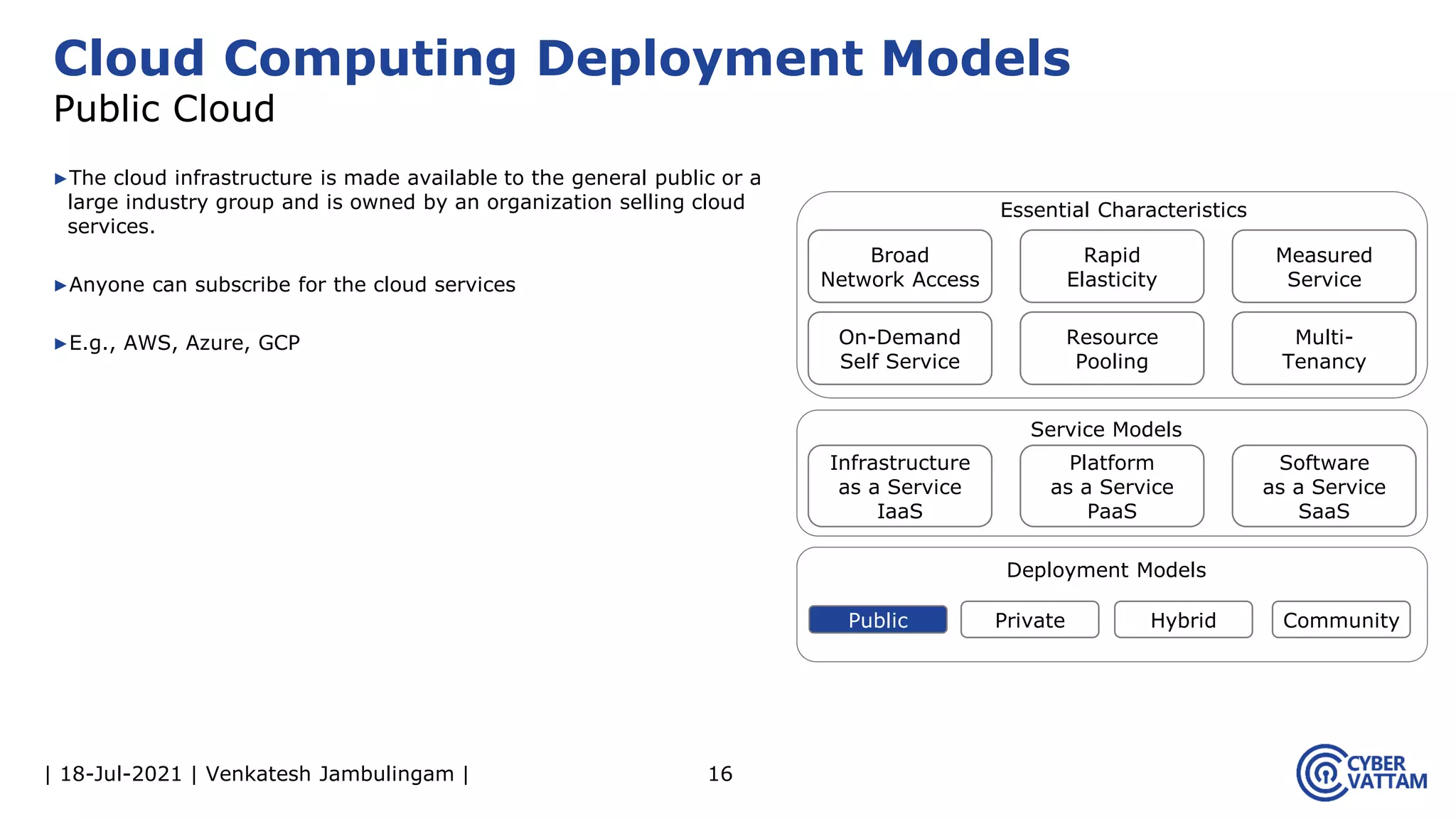
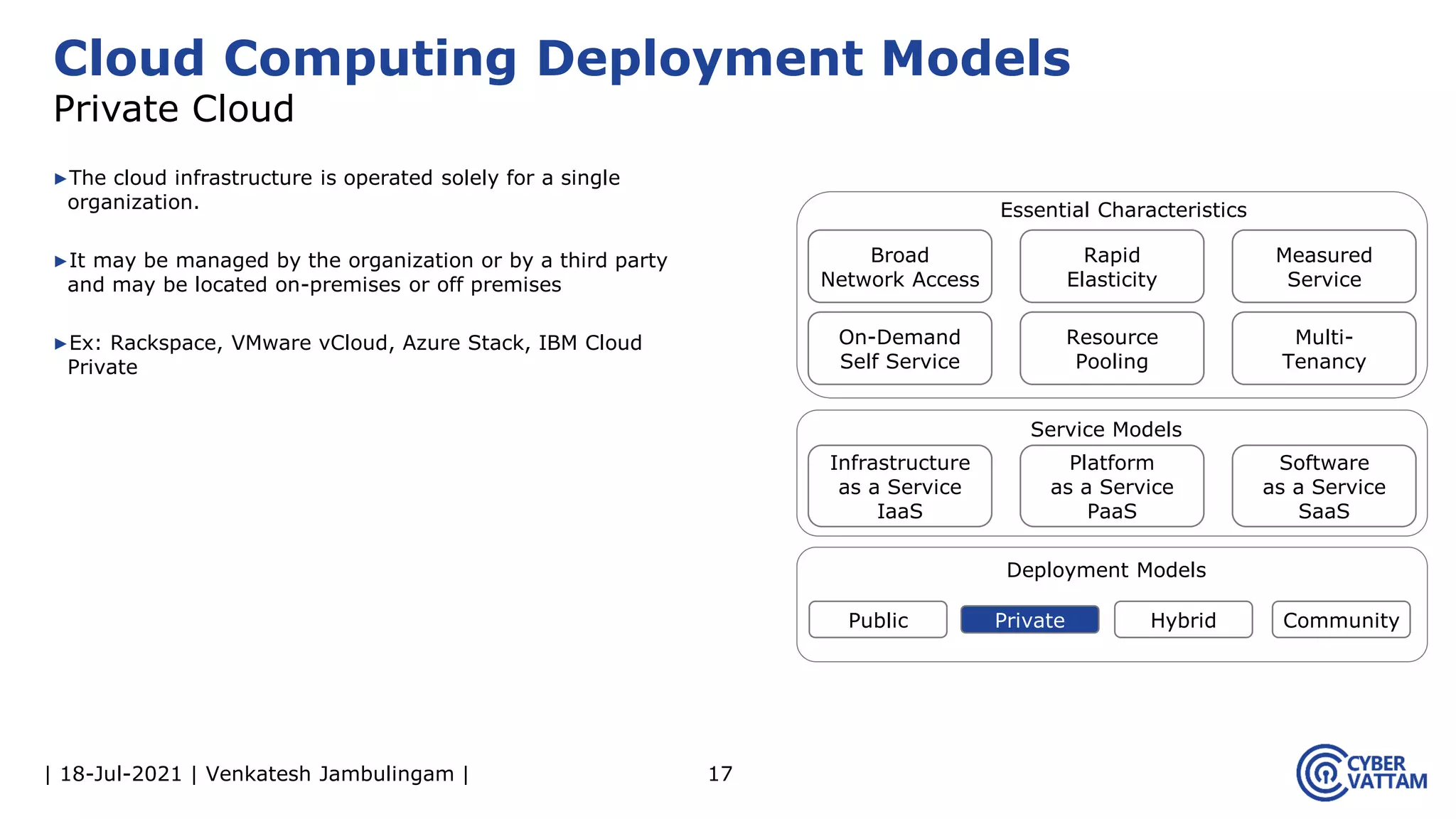
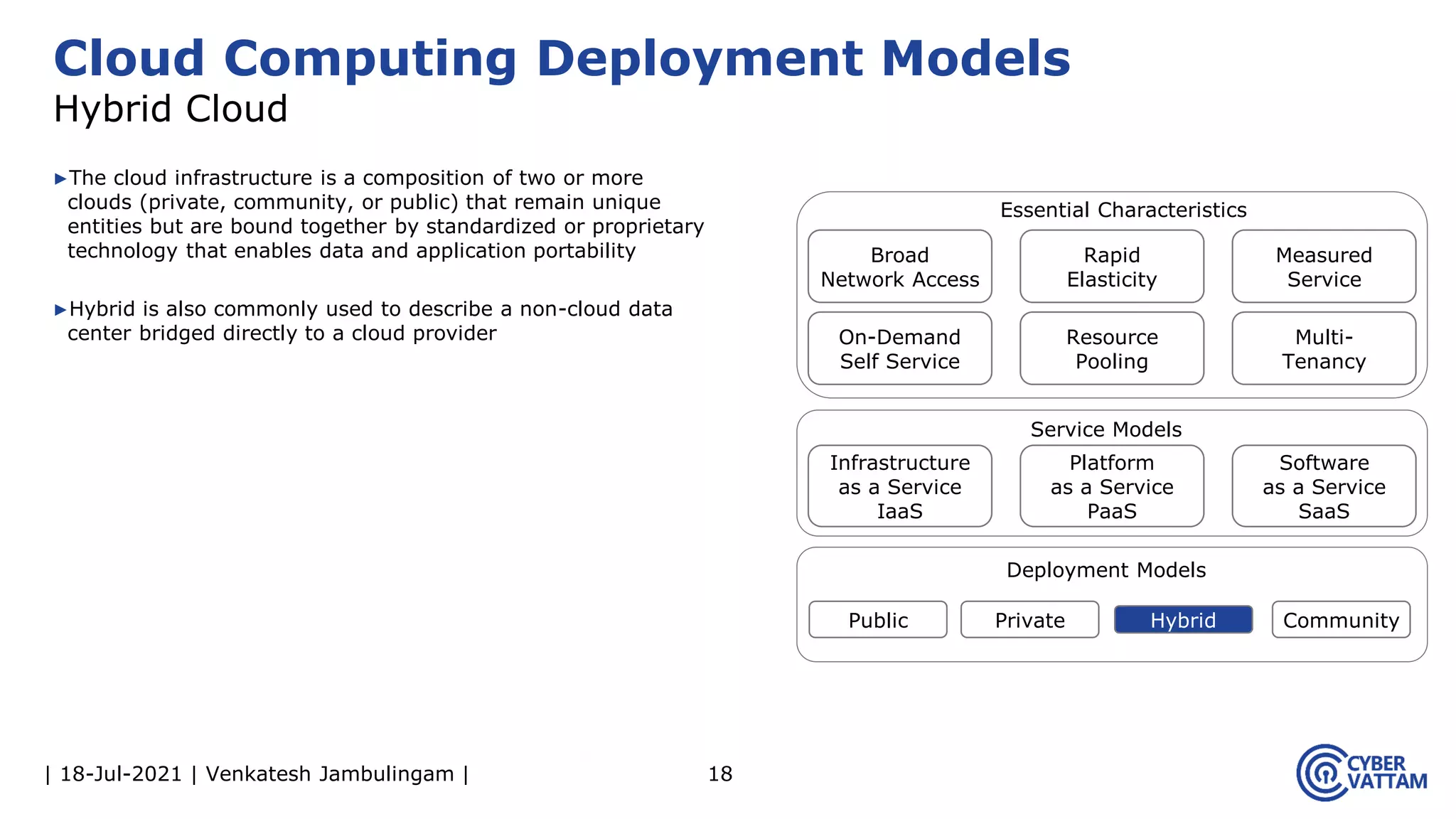
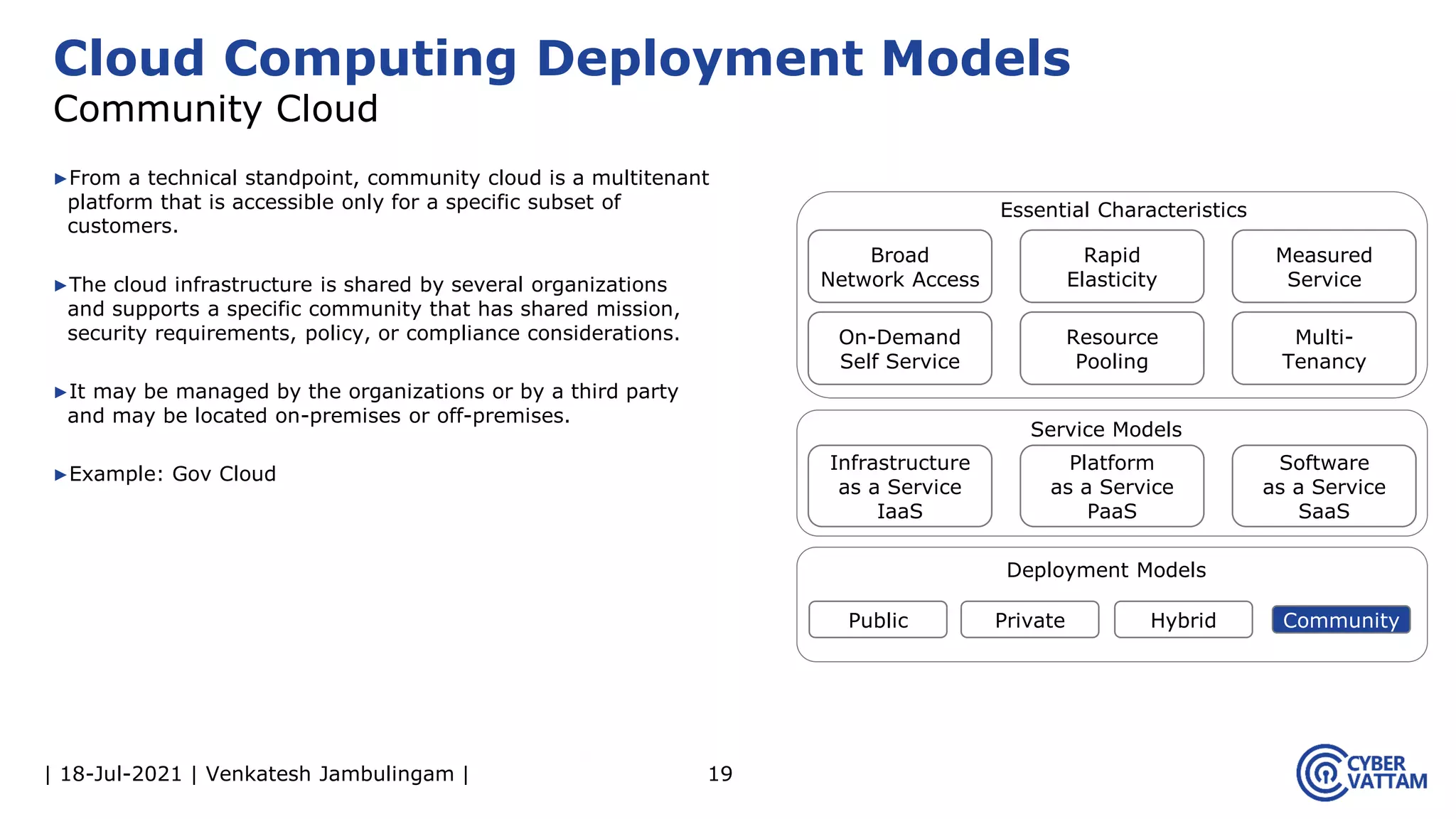
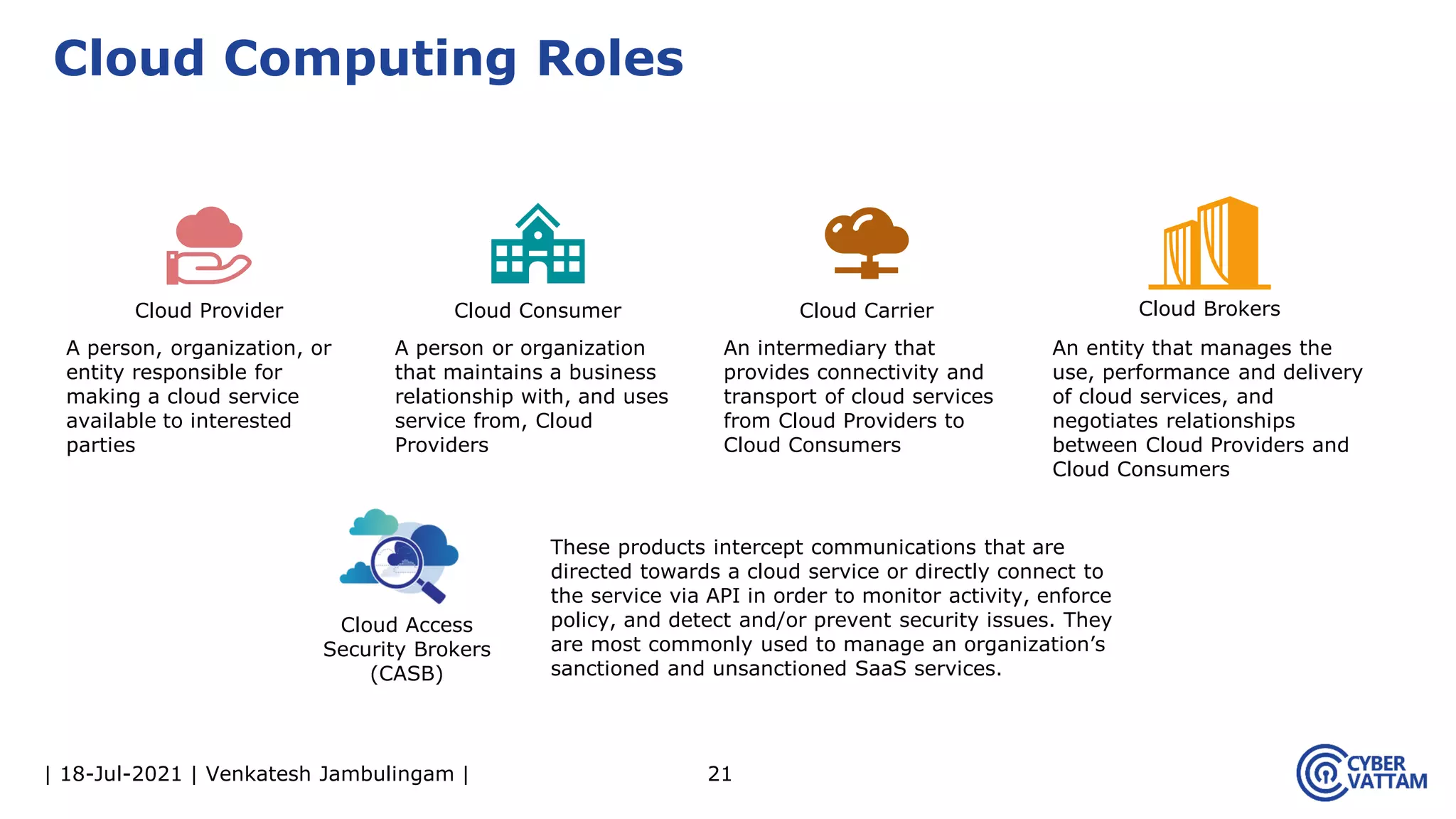
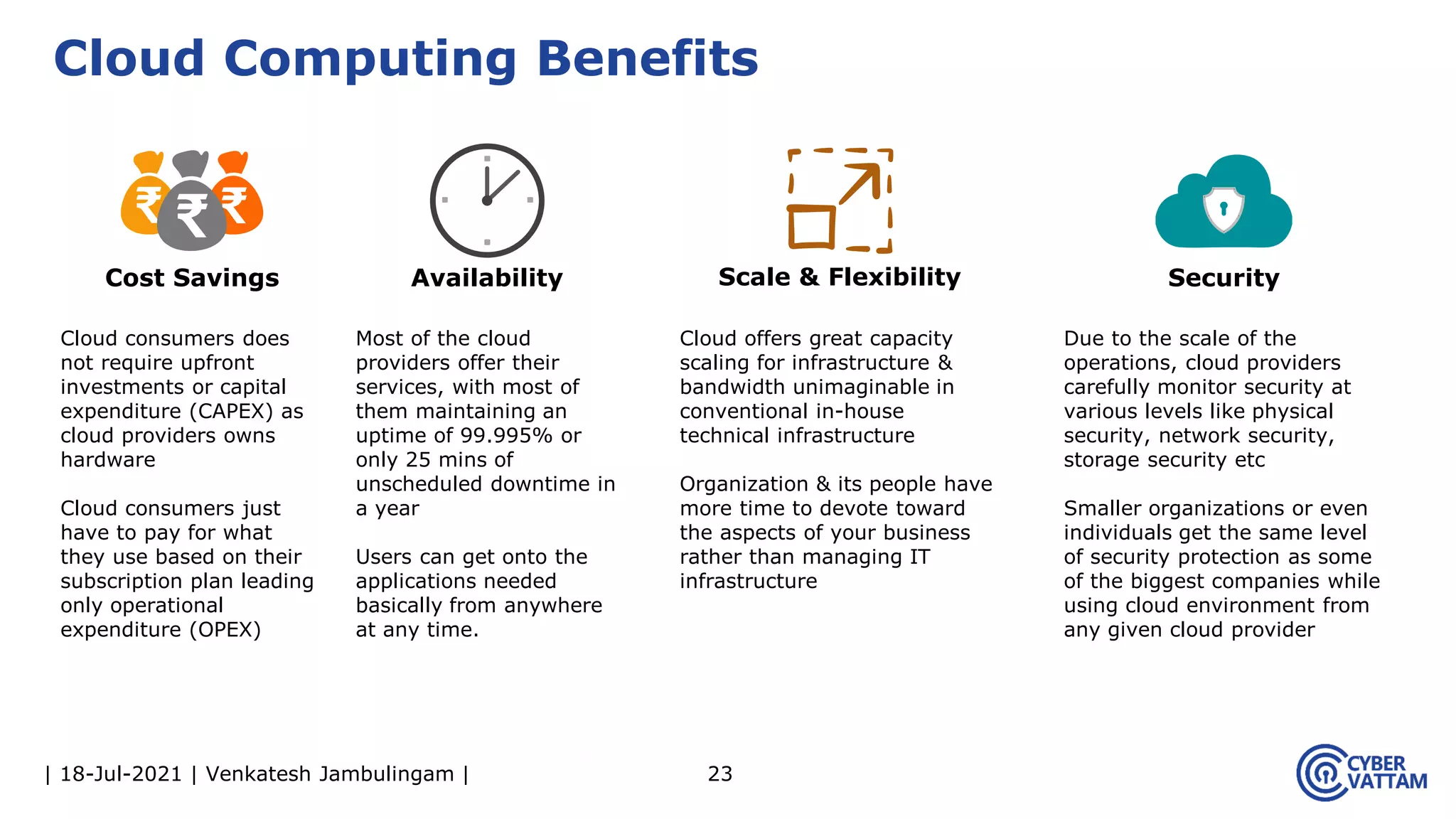
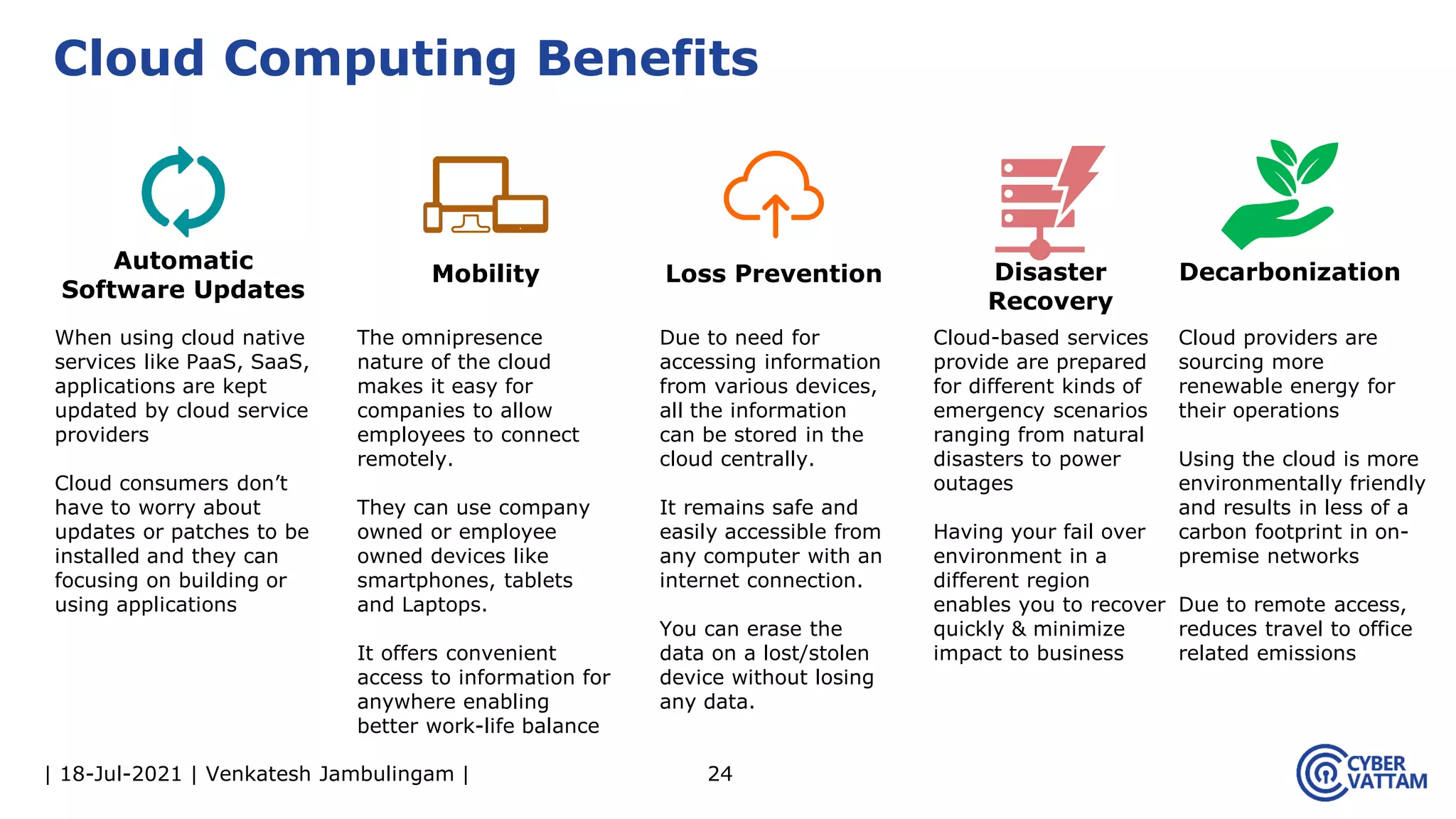
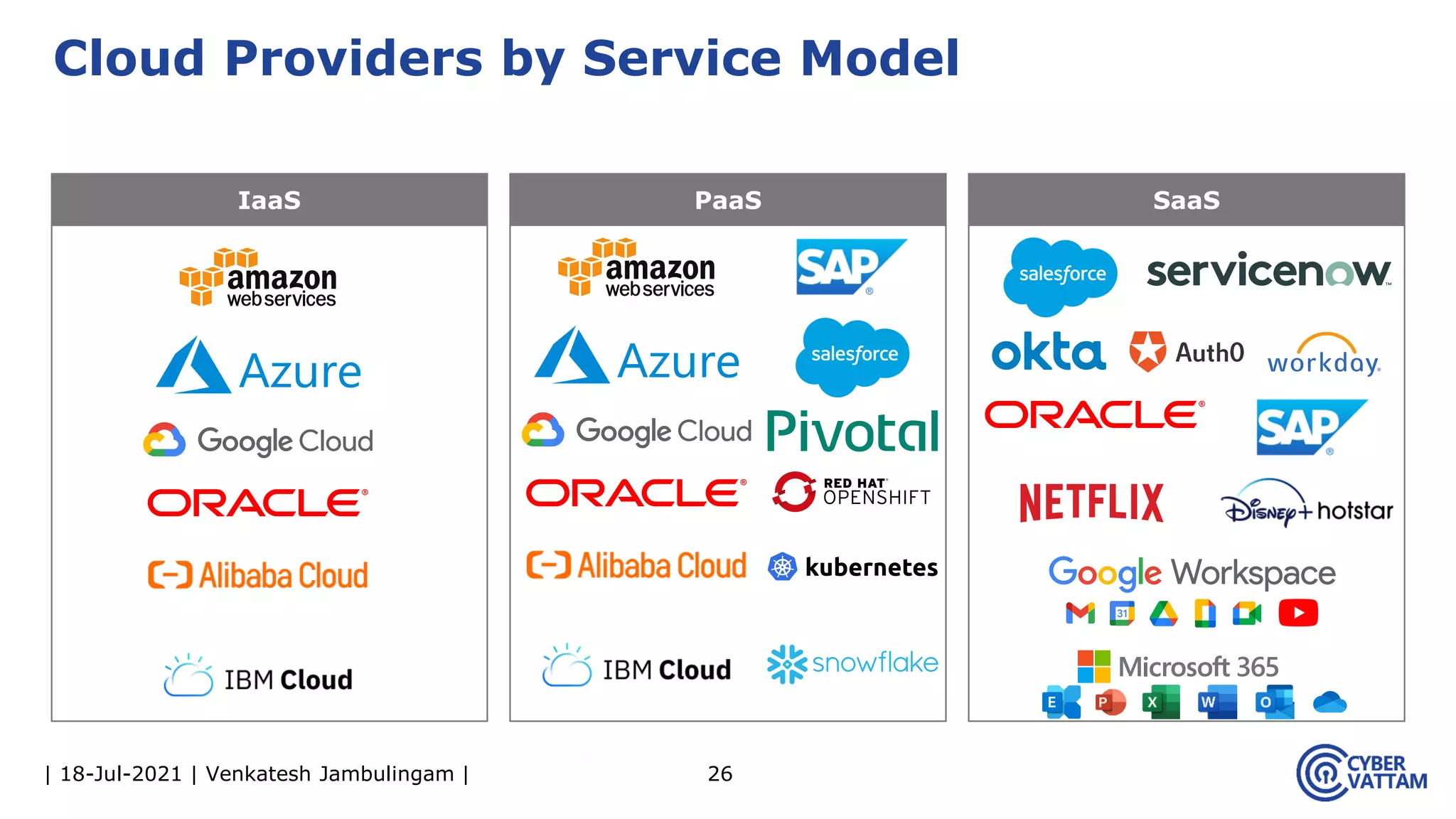
The document, presented by Venkatesh Jambulingam, covers the definition, characteristics, service, and deployment models of cloud computing, emphasizing its essential traits like rapid elasticity, on-demand self-service, and multi-tenancy. It discusses various service models including IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, along with benefits such as operational cost savings, security, scalability, and automatic updates. Furthermore, it outlines the roles of cloud providers, consumers, and brokers in the cloud ecosystem.