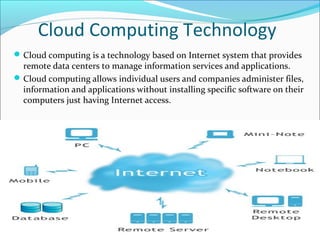
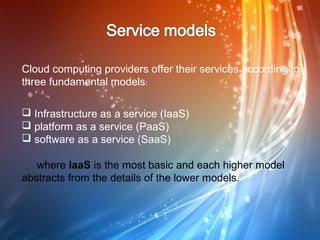
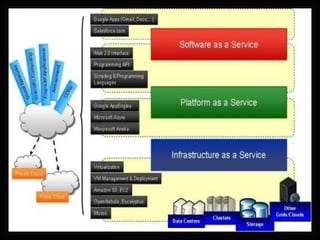
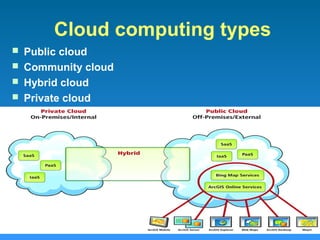
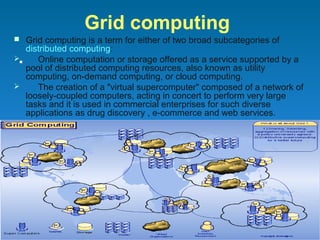
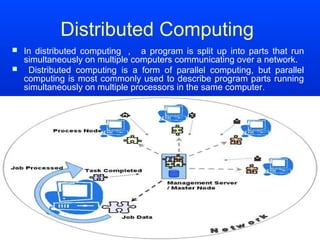
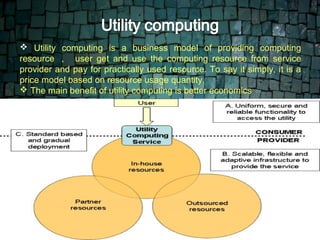
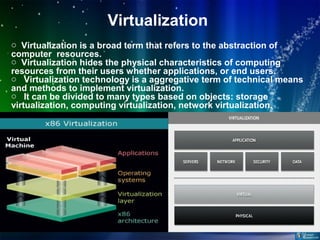
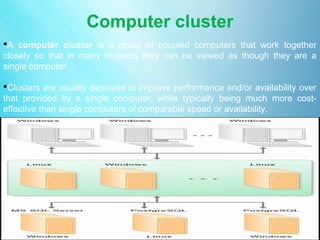
This document defines cloud computing and discusses its key technologies. It begins by defining cloud computing as the delivery of computing resources over a network. It then explains the three main cloud computing models: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). The document also discusses cloud computing types, related technologies like virtualization, and the pros and cons of cloud computing.