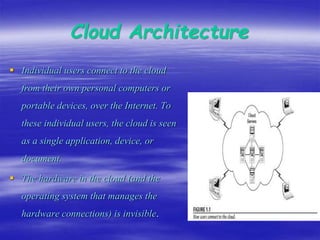
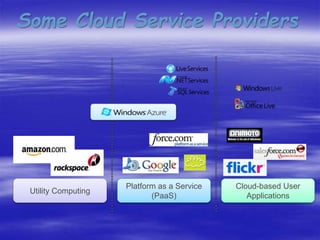
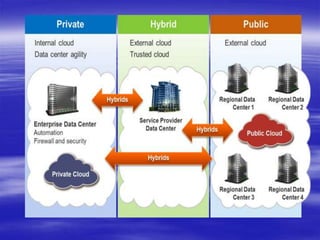
Cloud computing is a type of computing that relies on sharing computing resources over the Internet rather than local hardware. It provides software, platforms, and infrastructure as online services with advantages like lower costs, improved performance, universal access, and unlimited storage. However, it also has disadvantages like requiring a constant Internet connection and potential security and performance issues if the connection is slow.