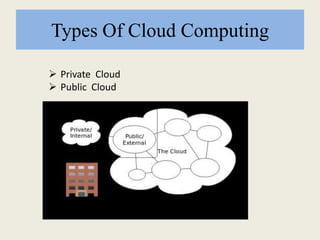
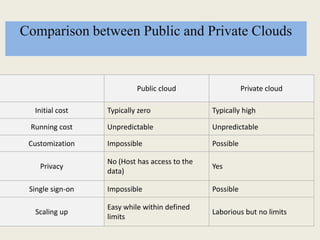
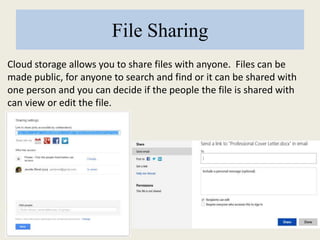
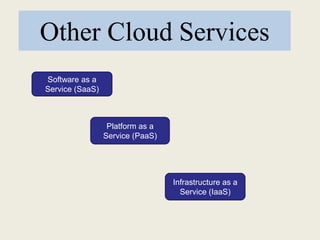
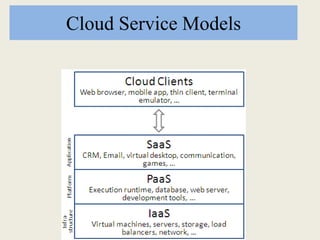
This document discusses cloud computing, including definitions, types, and models. It defines cloud computing as internet-based computing using shared resources provided on-demand. The types of cloud include public and private clouds. The cloud service models are Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS). The document also covers advantages like lower costs, unlimited storage, and universal access, as well as disadvantages like internet dependence and potential security issues.