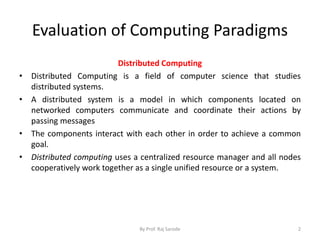
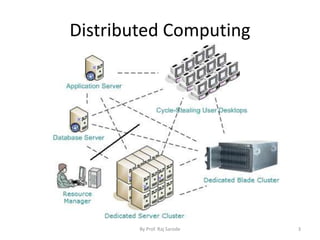
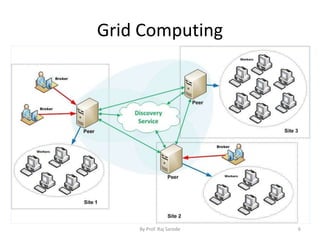
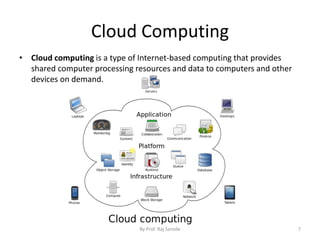
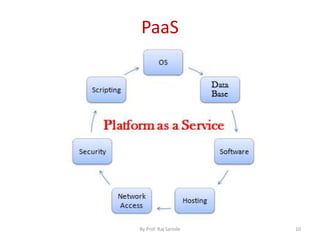
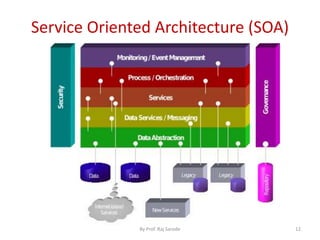
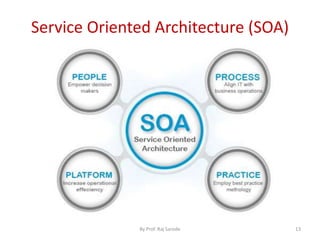
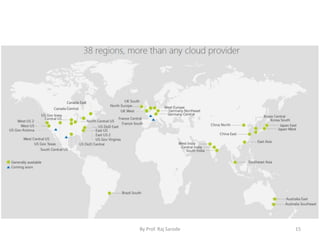
The document discusses various computing paradigms, including distributed computing, utility computing, grid computing, and cloud computing, particularly focusing on Platform as a Service (PaaS). PaaS offers a way for customers to develop, run, and manage applications without needing to manage the underlying infrastructure, allowing for flexibility, adaptability, and enhanced collaboration. Additionally, it introduces Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA) as a framework for creating agile and efficient business services.