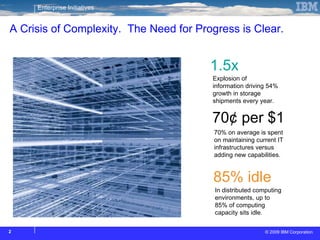
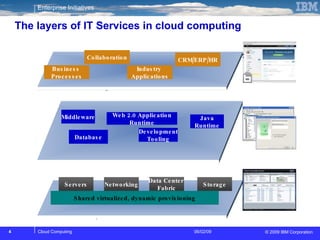
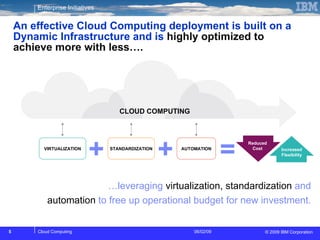
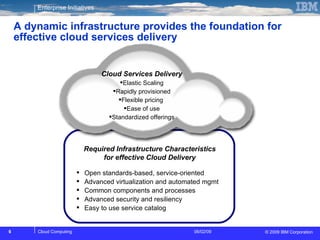
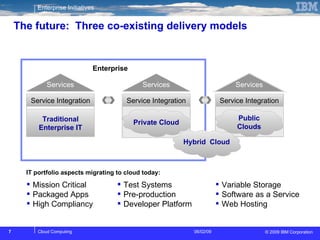
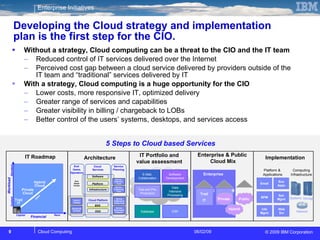
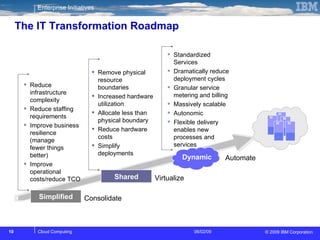
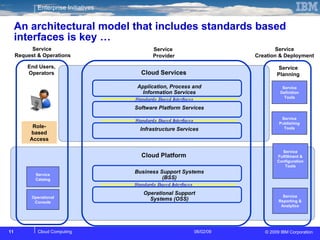
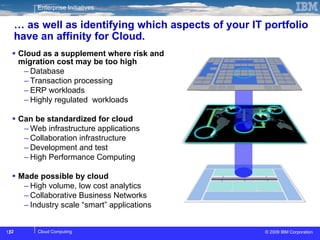
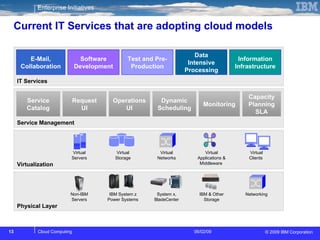
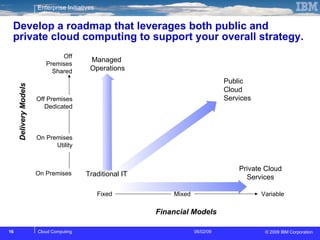
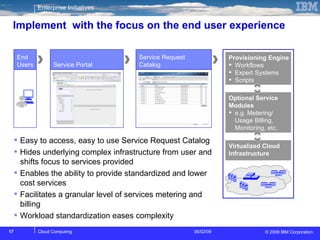
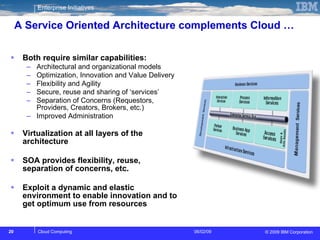
The document discusses cloud computing and its benefits, including increased flexibility and reduced costs. It notes that cloud computing provides standardized offerings that can rapidly scale resources in a flexible and easy-to-access manner. The document outlines a strategy for developing a cloud architecture and implementation plan to help organizations manage IT challenges and realize the opportunities of cloud computing.
![Cloud Computing Expanding IT flexibility and agility Virgílio Vargas IBM [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudcomputingforisep-v3-090602171902-phpapp01/75/Virgilio-Vargas-Presentations-CloudViews-Org-Cloud-Computing-Conference-2009-1-2048.jpg)









![Thank you! For more information, please visit: ibm.com/cloud Or contact me at: [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudcomputingforisep-v3-090602171902-phpapp01/85/Virgilio-Vargas-Presentations-CloudViews-Org-Cloud-Computing-Conference-2009-24-320.jpg)