The key points are:
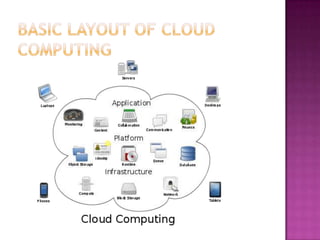
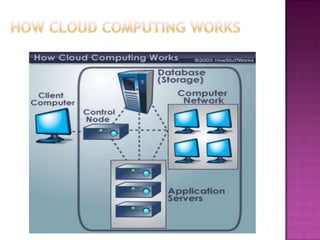
1. Cloud computing allows users to access computing resources like servers, databases, and applications over the internet without maintaining physical infrastructure.
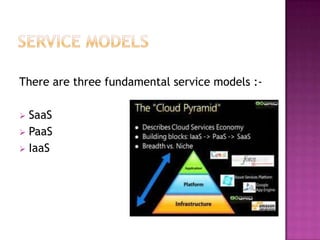
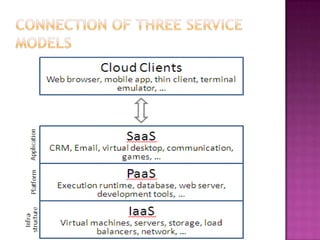
2. There are three main service models - SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS - that provide software, platforms, and infrastructure as a service.
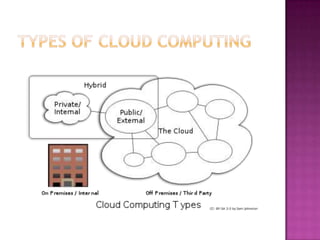
3. Deployment models include public, private, community, and hybrid clouds that vary based on who has access to the cloud resources.