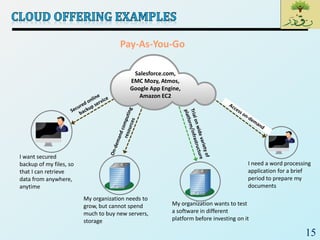
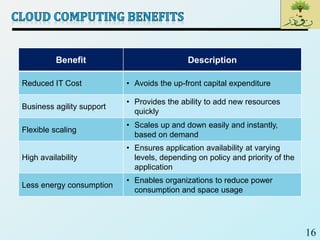
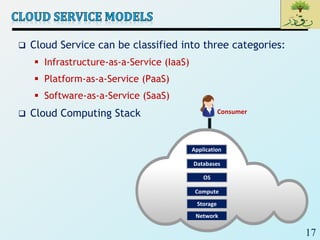
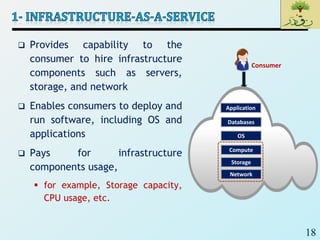
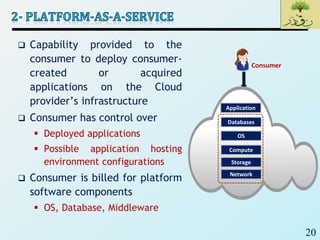
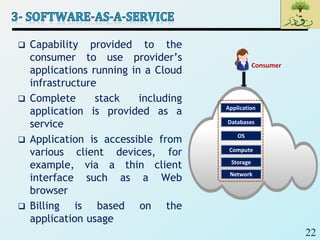
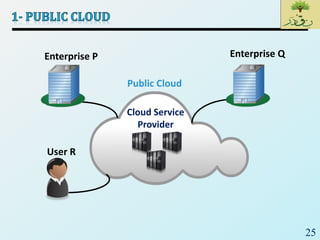
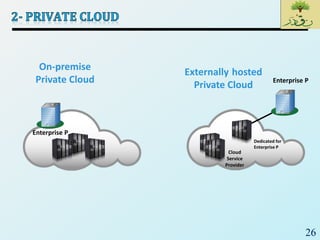
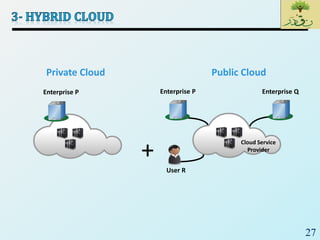
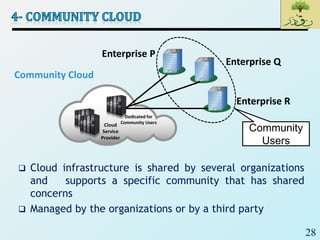
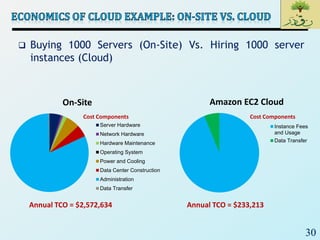
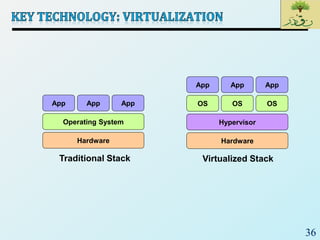
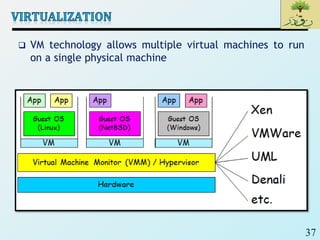
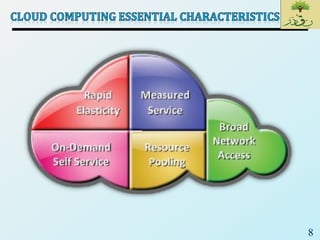
Cloud computing provides on-demand access to shared computing resources like networks, servers, storage, applications and services that can be rapidly provisioned with minimal management effort. Key characteristics of cloud computing include rapid elasticity, broad network access, resource pooling, measured service and self-service provisioning. Cloud computing offers benefits like reduced costs, increased scalability and flexibility. There are different types of cloud services and deployment models that organizations can leverage for different needs. While cloud computing provides many opportunities, there are also challenges to consider from both the consumer and provider perspectives related to security, performance and standardization.


![4
What if …
You could have hundreds of millions of storefronts
worldwide?
• Without real estate
• Without fixtures
• Without maintenance
• Without shrinkage
• With [relatively] zero cost to entry
The Web changed everything](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/se2lec23introductiontocloudcomputing-170421074333/85/SE2_Lec-23_Introduction-to-Cloud-Computing-4-320.jpg)







![14
If you use Flickr or Facebook or LinkedIn or Twitter or
Backpack or [insert hundreds of other sites here], you’re
using the cloud
Cloud is a metaphor for the internet](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/se2lec23introductiontocloudcomputing-170421074333/85/SE2_Lec-23_Introduction-to-Cloud-Computing-14-320.jpg)