This document discusses different aspects of cloud computing including:
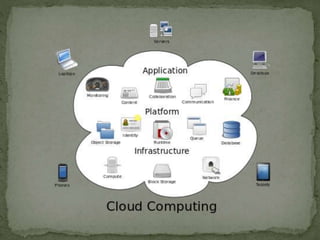
- Cloud computing involves storing and processing data on remote servers hosted on the internet rather than local servers.
- It provides on-demand access to shared computing resources like networks, servers, storage, applications and services.
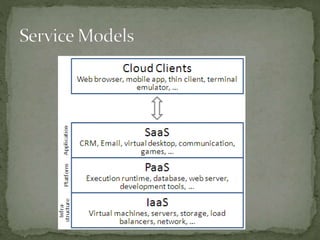
- There are different cloud service models including Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). IaaS provides virtual machines, storage, and other resources, PaaS provides platforms for developing applications, and SaaS provides access to application software.
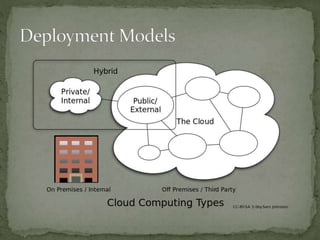
- There are also different deployment models for clouds including private clouds for a single organization, public clouds open for public