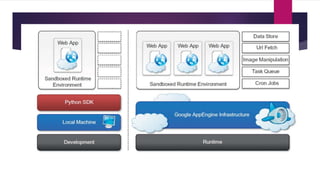
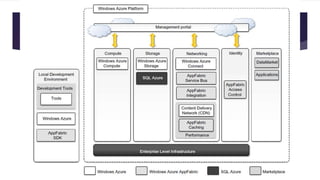
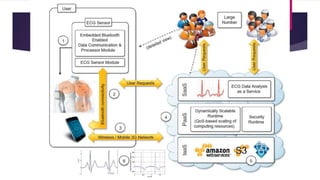
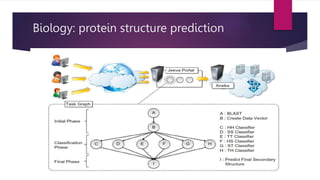
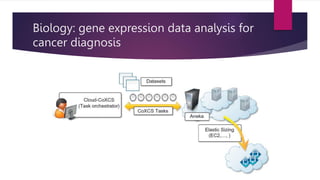
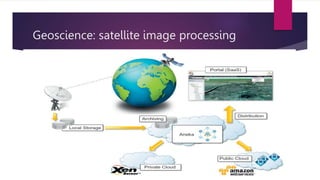
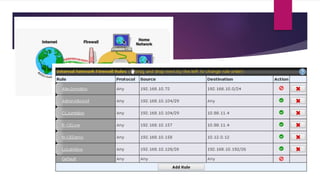
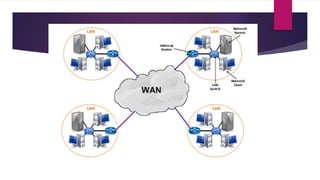
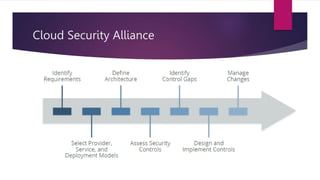
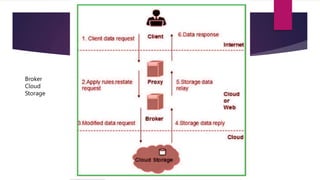
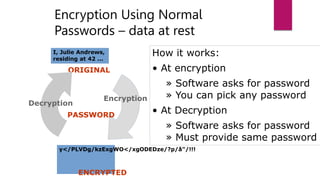
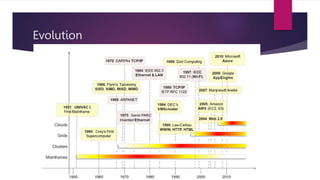
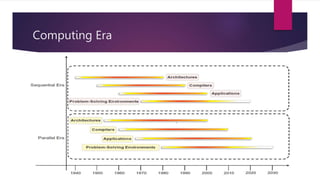
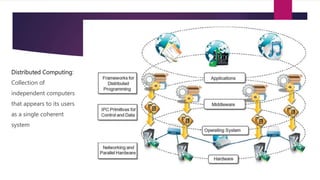
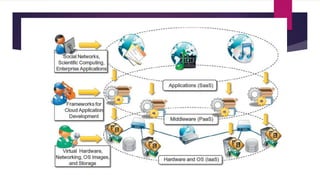
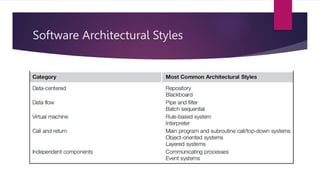
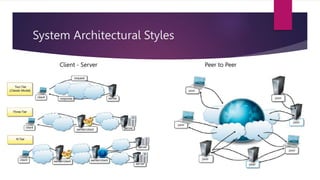
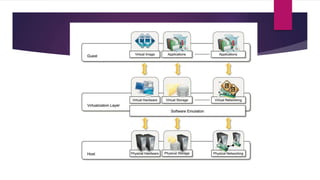
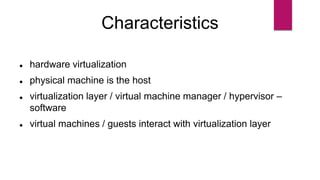
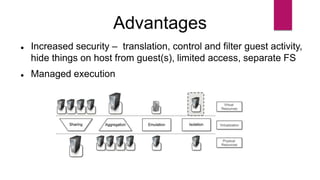
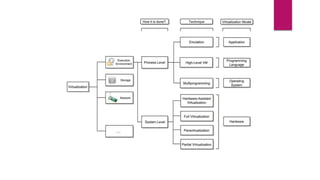
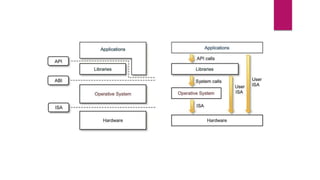
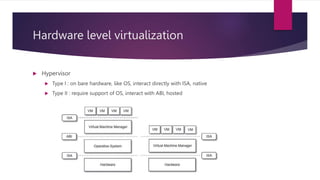
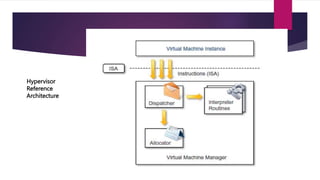
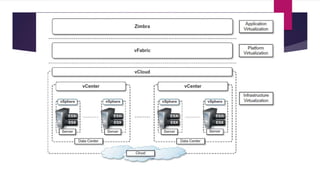
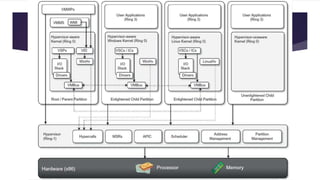
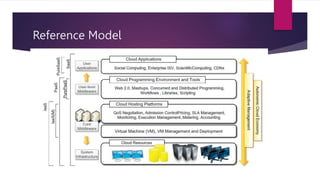
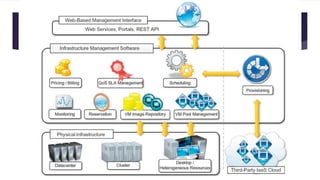
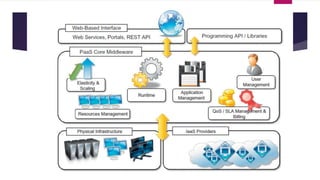
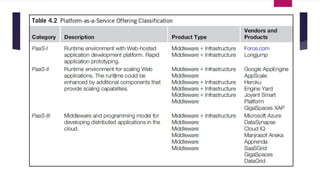
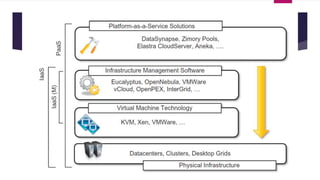
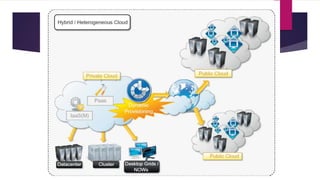
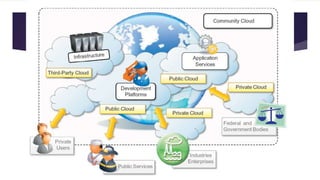
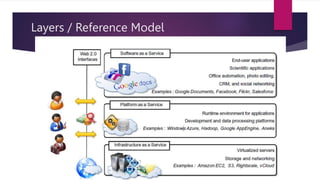
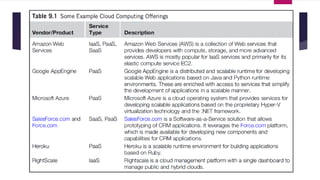
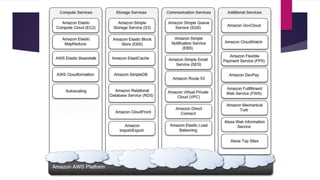
The document discusses the evolution of cloud computing from mainframes to modern cloud architectures, defining cloud computing as applications and services delivered over the internet using scalable resources. It outlines the different types of cloud computing including infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and software as a service (SaaS). The architecture of cloud computing is described as distributed infrastructure composed of data centers, clusters, and virtualized resources delivered as on-demand utilities over the internet.
















































![S3 (contd)
three different URI ways of addressing
Canonical form: http://s3.amazonaws.com/bukect_name/[object_name]
Subdomain form: http://bucket-name/s3.amzonaws.com/[object_name]
Virtual hosting form: http://bucket-name.com/[object_name] needs DNS
S3 is flat data store so unique bucket names across all users
Object ACL: http://s3.amazonaws.com/bukect_name/object_name?acl
Bucket server logging: http://s3.amzonaws.com/bucket_name?logging
Metadata are manipulated as attributes of in the request
Bucket and all its objects belong to a specific region](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudcomputing-221230074123-18c8e31d/85/Cloud-Computing-88-320.jpg)