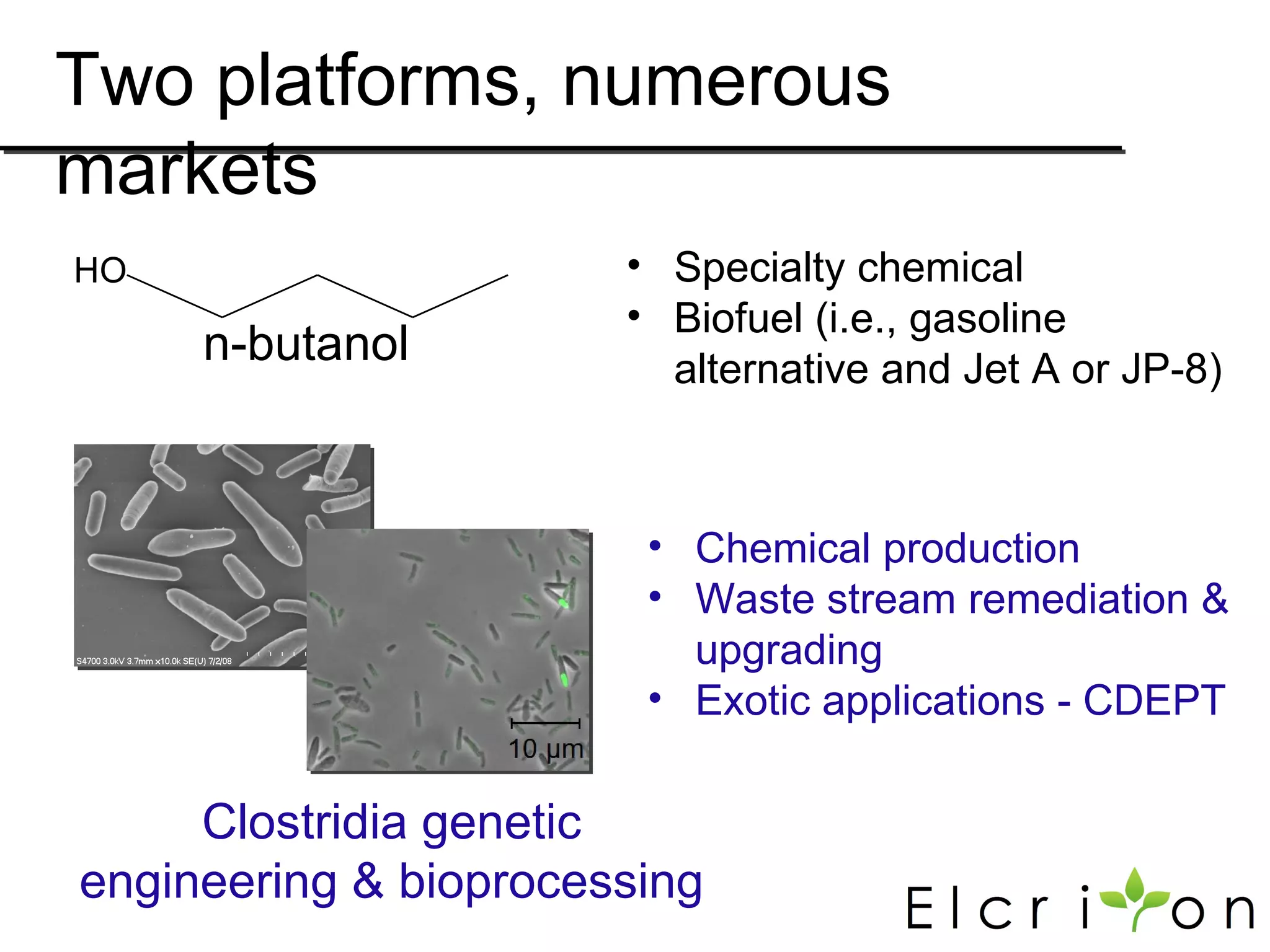
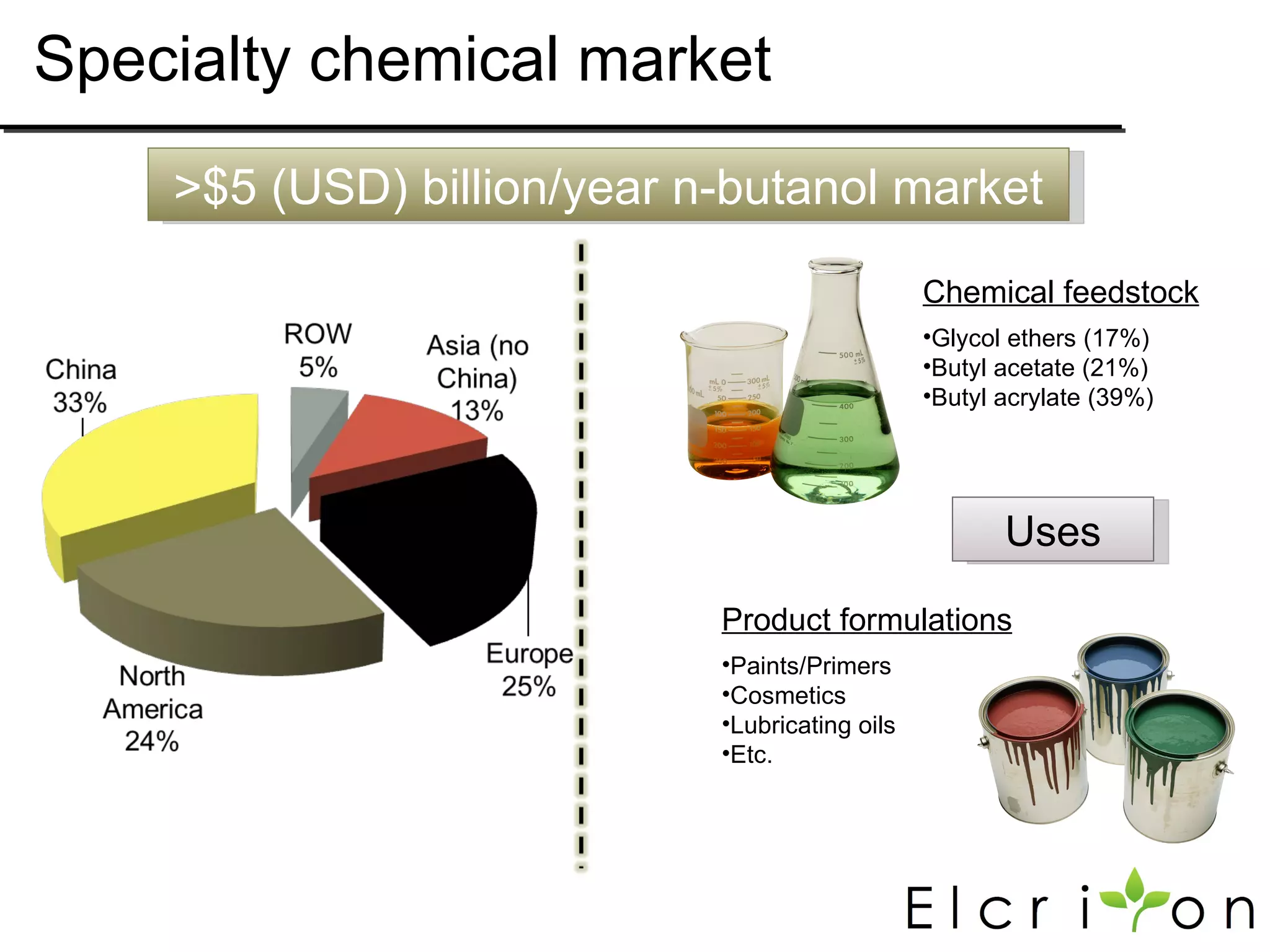
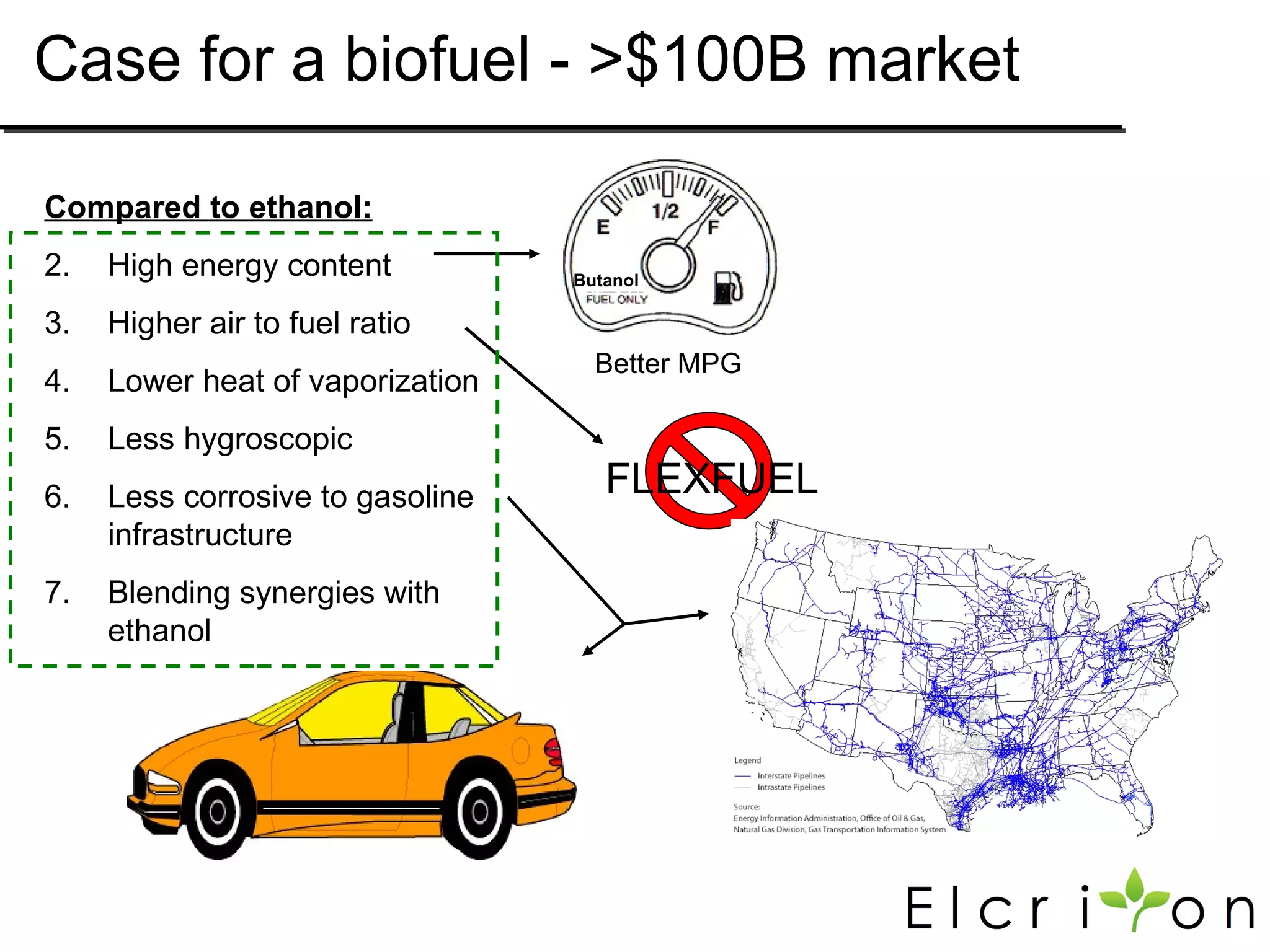
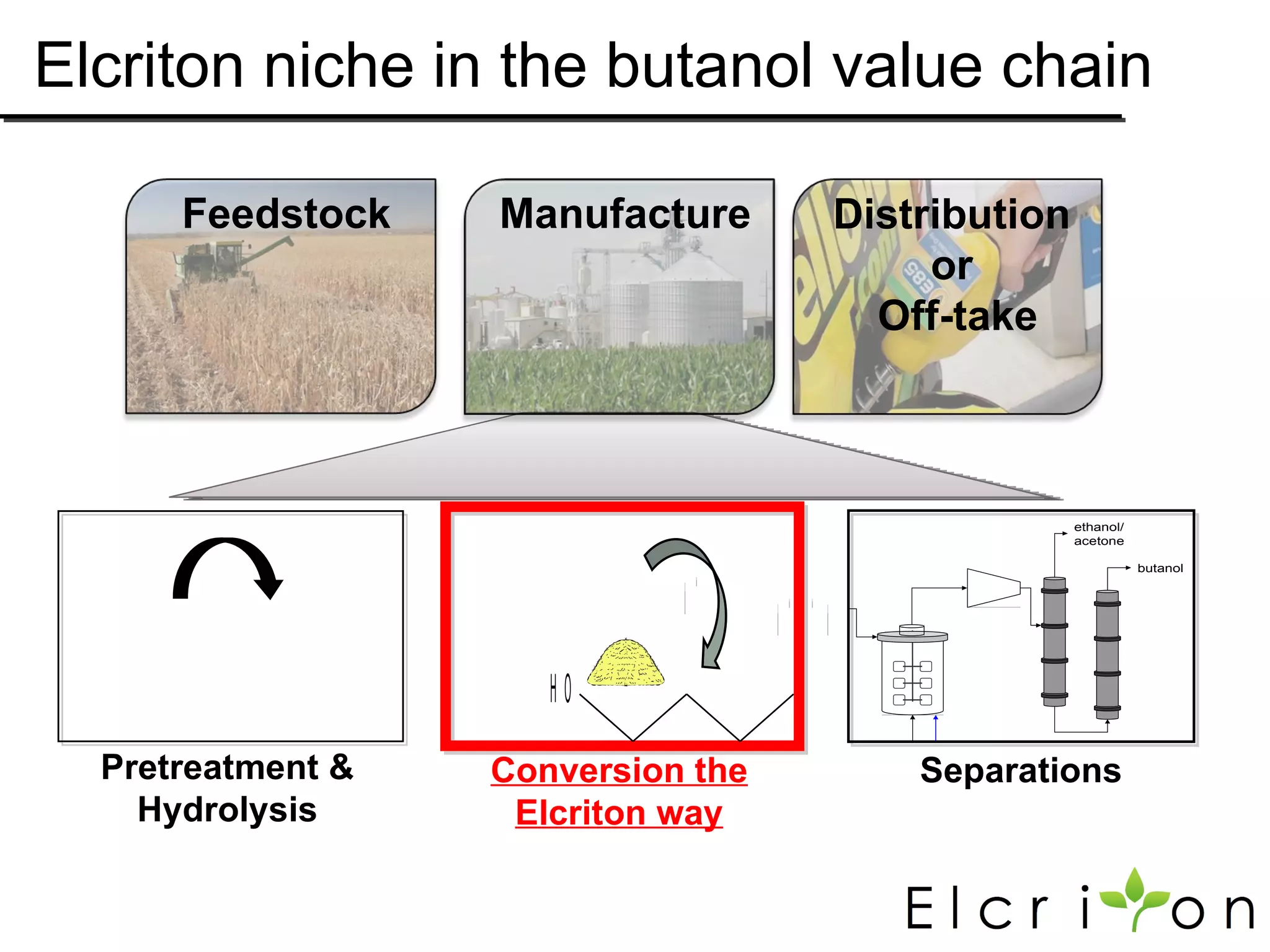
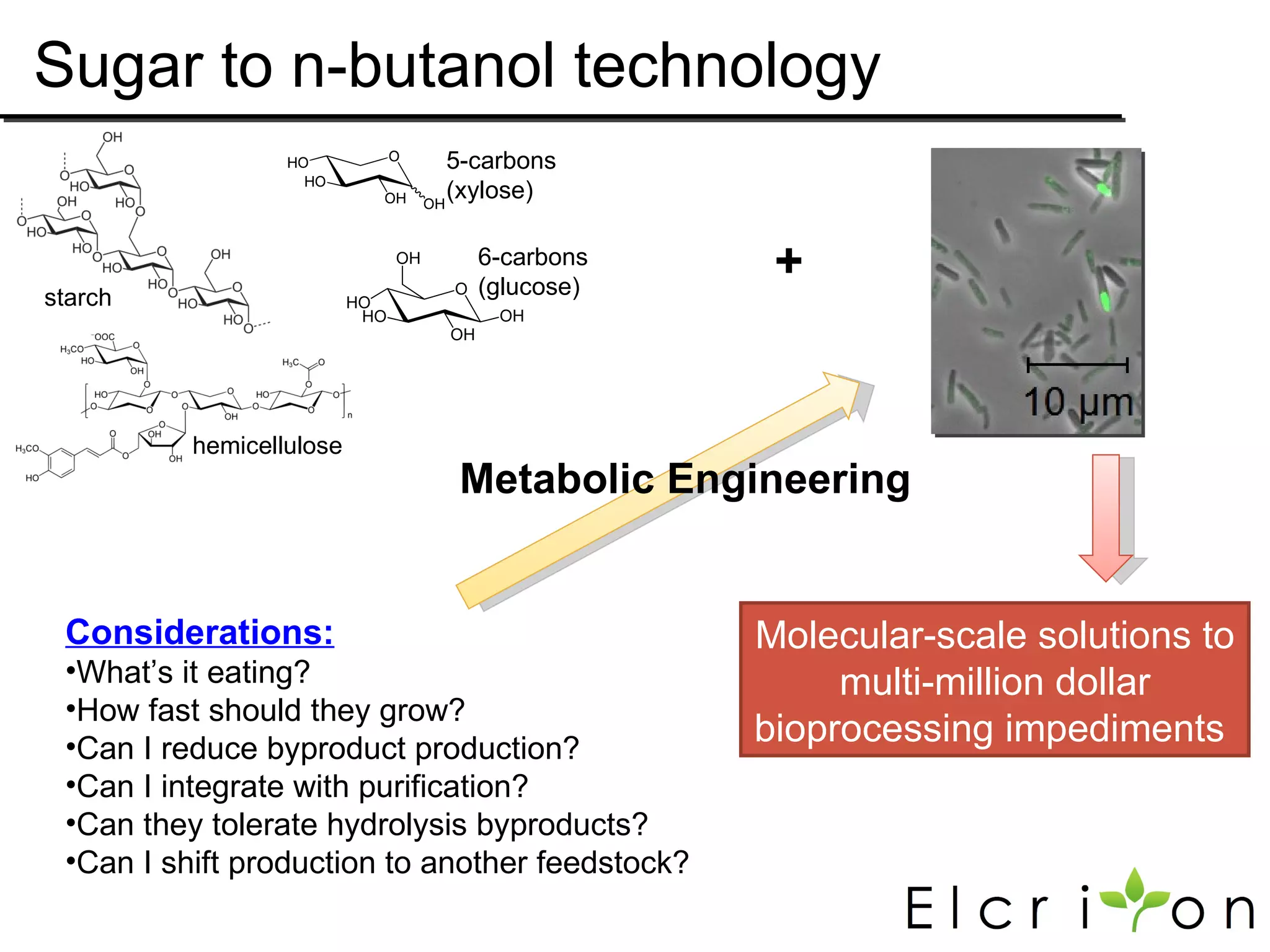
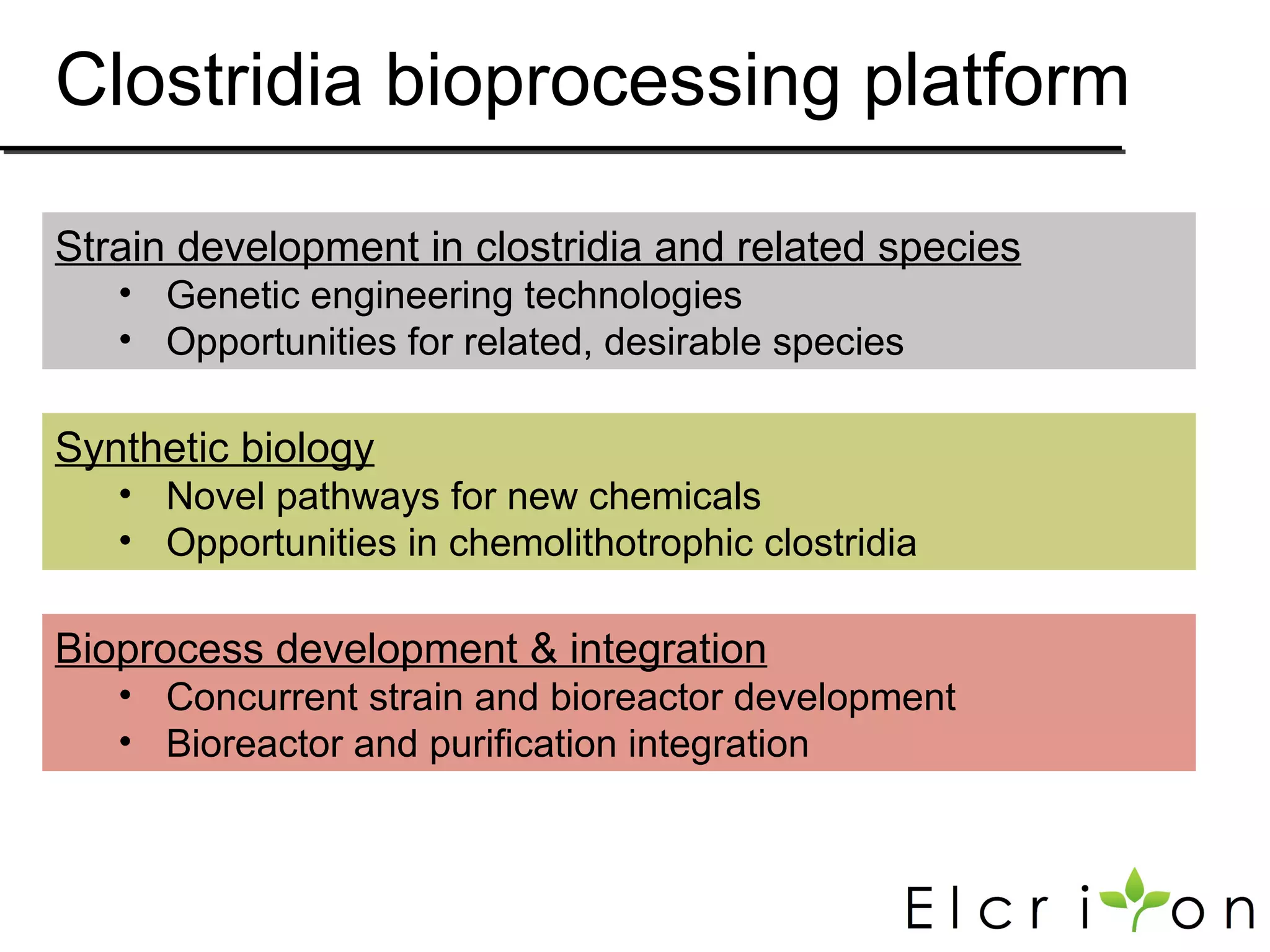
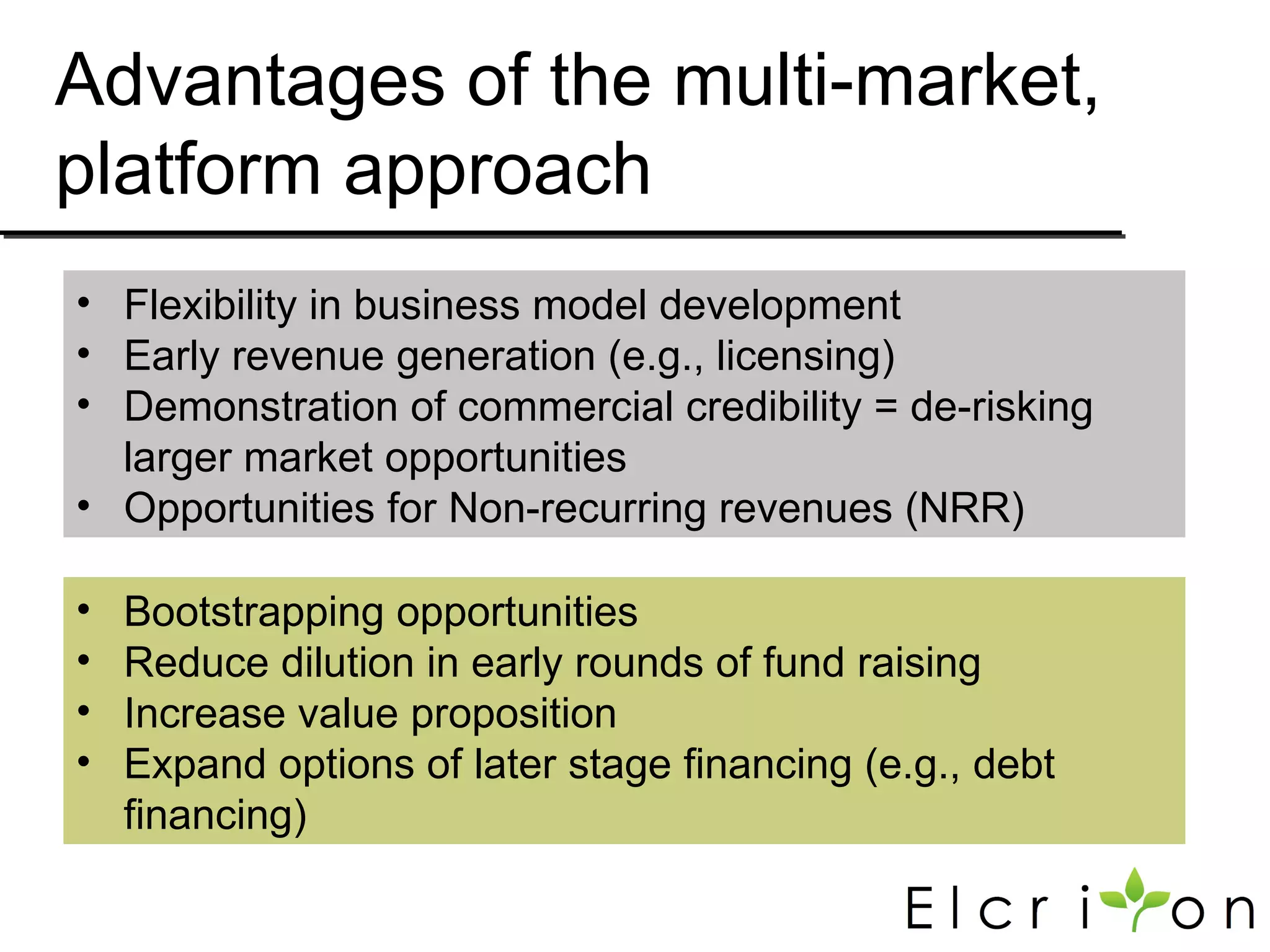
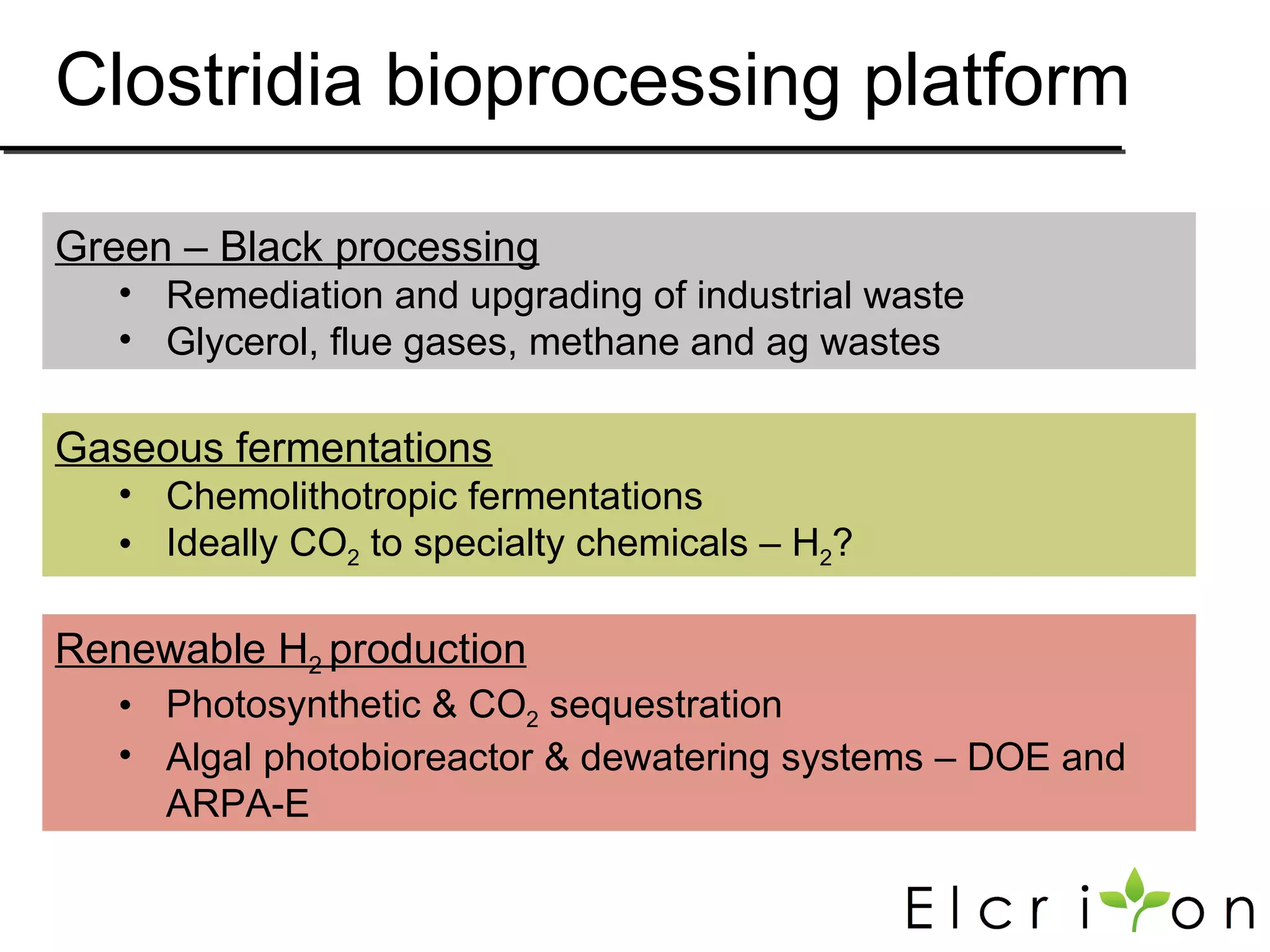
Elcriton is a company that was founded in 2009 to develop technologies to replace fossil fuel consumption and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. It aims to commercialize processes using Clostridia bacteria to produce specialty chemicals and biofuels like n-butanol from biomass. Elcriton licenses its technologies and forms strategic partnerships with large industry players. It has two technology platforms - one for producing n-butanol and another for genetic engineering of Clostridia bacteria. The company seeks to generate early revenue through licensing and partnerships to de-risk larger market opportunities in fuels and chemicals.