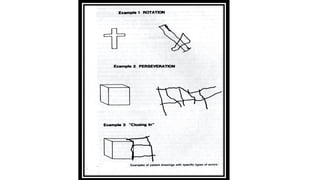
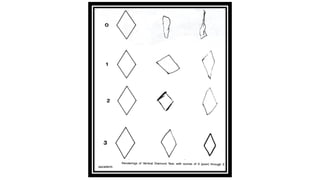
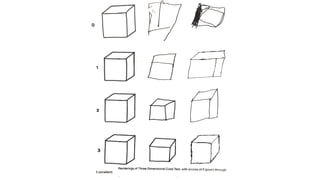
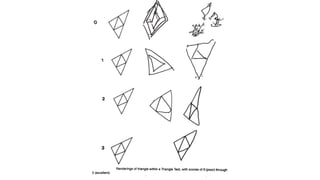
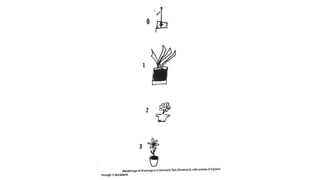
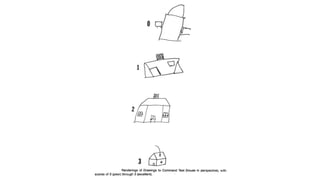
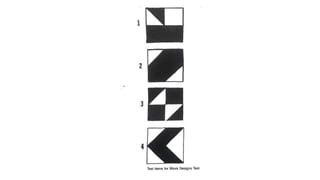
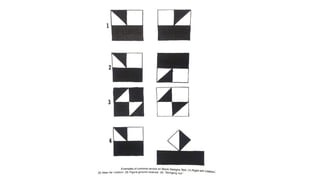
1. Constructional ability refers to the capacity to draw or construct 2D and 3D figures and involves the integration of visual, sensory, and motor functions across different brain regions.
2. Tests of constructional ability can help detect subtle brain damage as even small early lesions frequently disrupt performance on tasks like copying simple line drawings.
3. Despite their clinical usefulness, constructional tasks are often omitted from mental status exams but can yield valuable information, especially in detecting dementia.