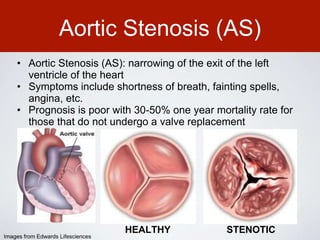
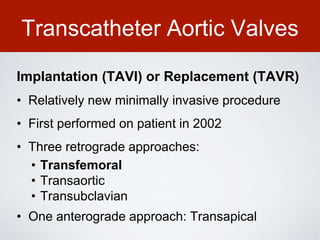
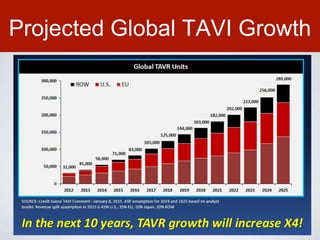
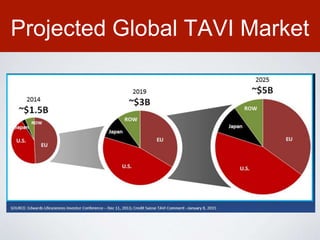
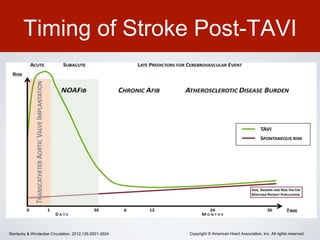
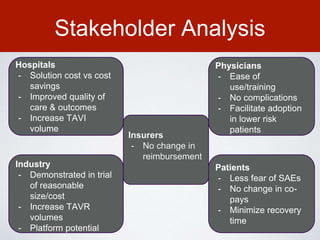
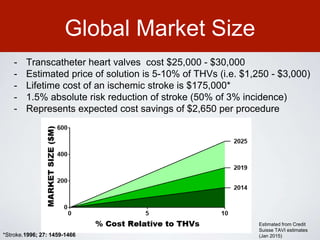
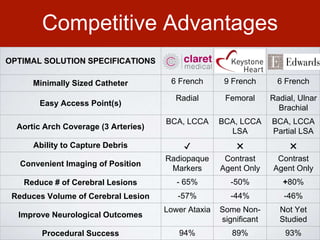
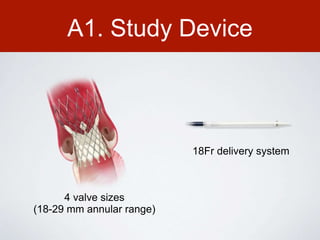
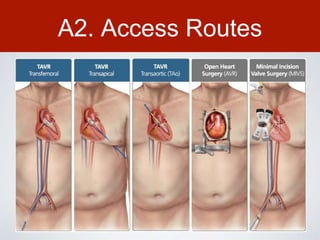
This document discusses transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) and the risk of cerebral embolization during the procedure. TAVI is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat aortic stenosis that is growing rapidly worldwide. However, TAVI is associated with a risk of stroke between 2-4% within 30 days after the procedure due to cerebral embolization of debris. The document proposes developing a solution to reduce the risk of cerebral embolization and associated strokes during TAVI by at least 50%. It outlines criteria for an effective solution, competitive advantages over existing devices, hurdles to overcome, as well as the large market potential given the growth of TAVI procedures globally.