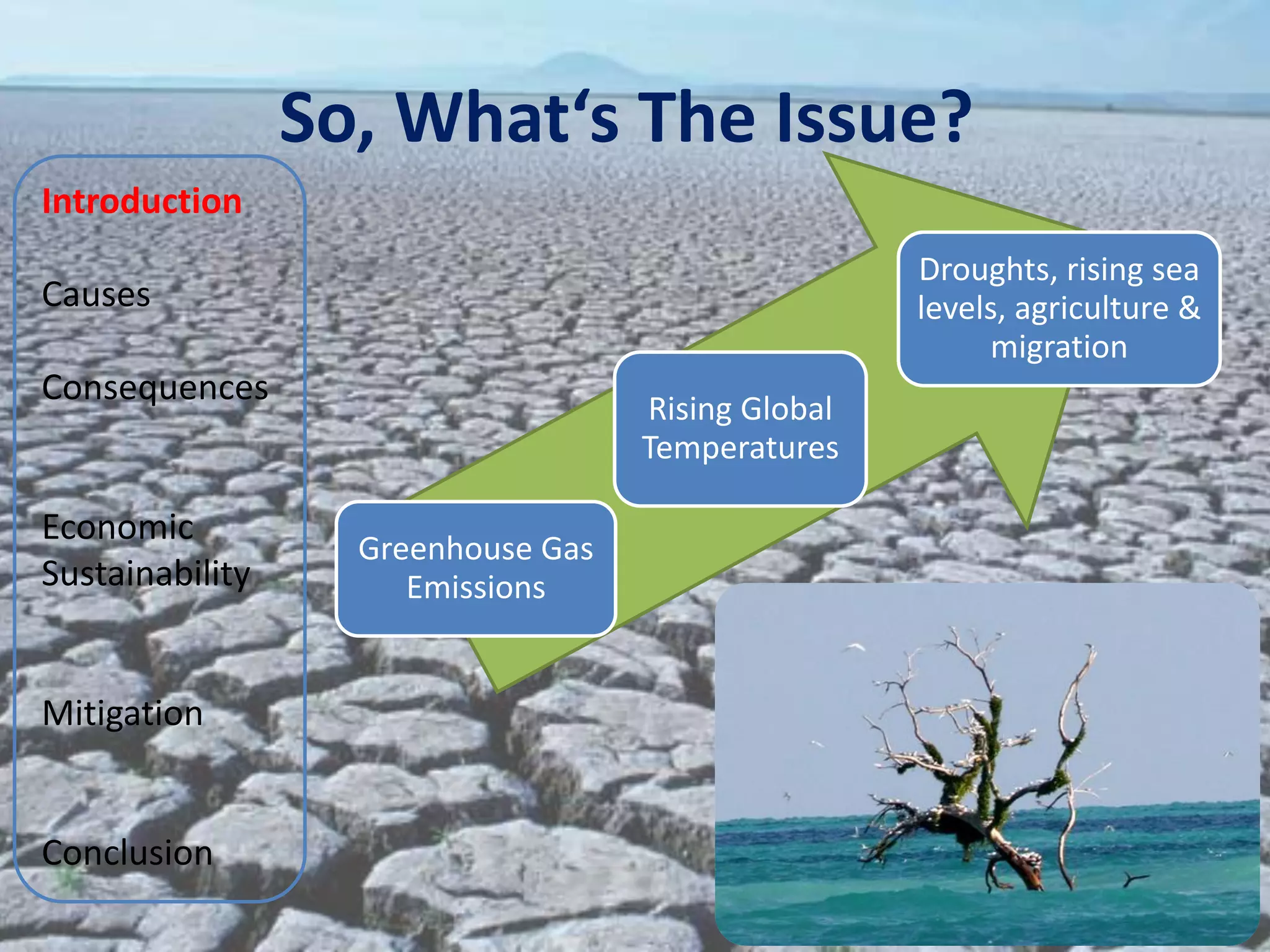
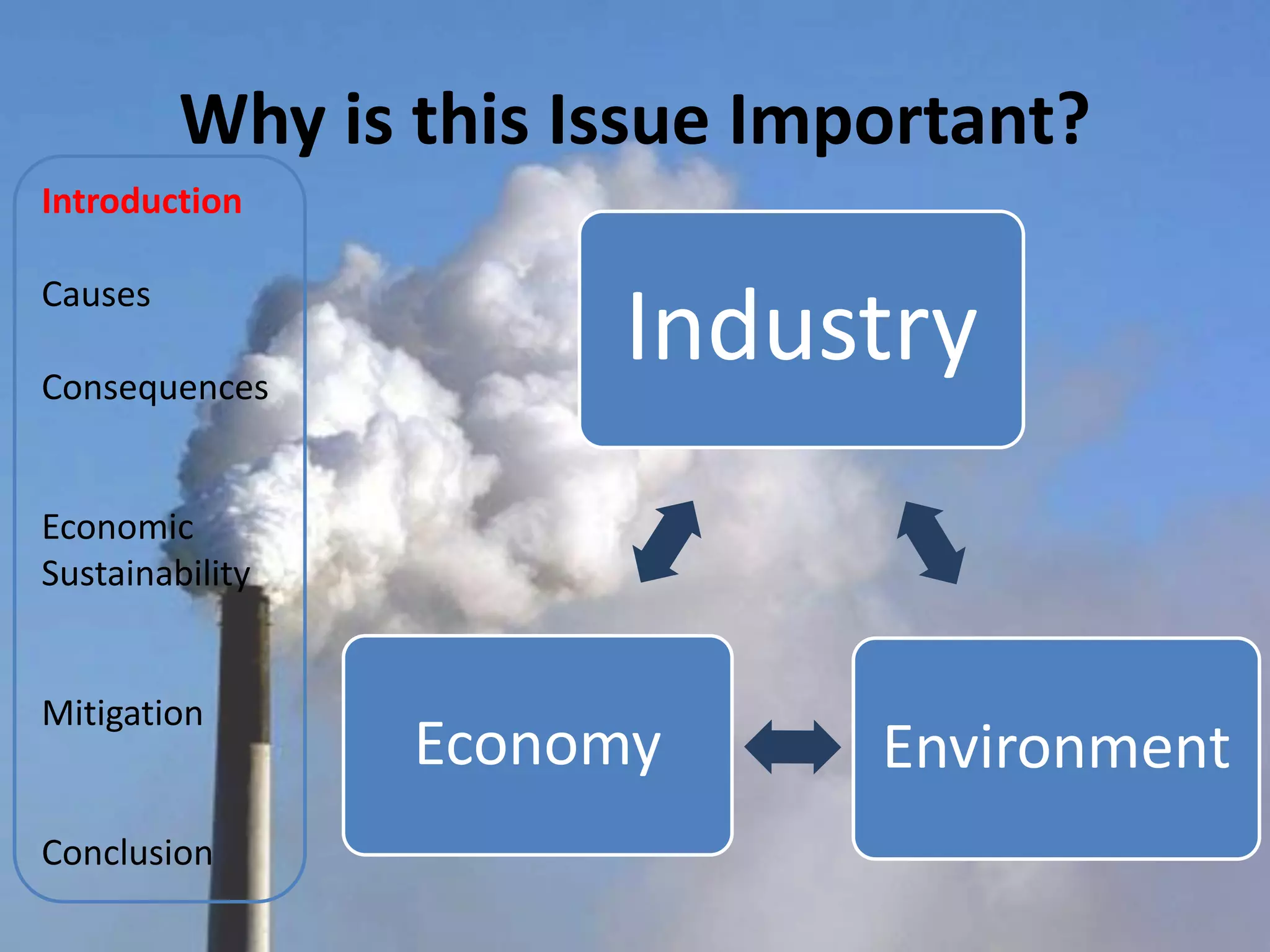
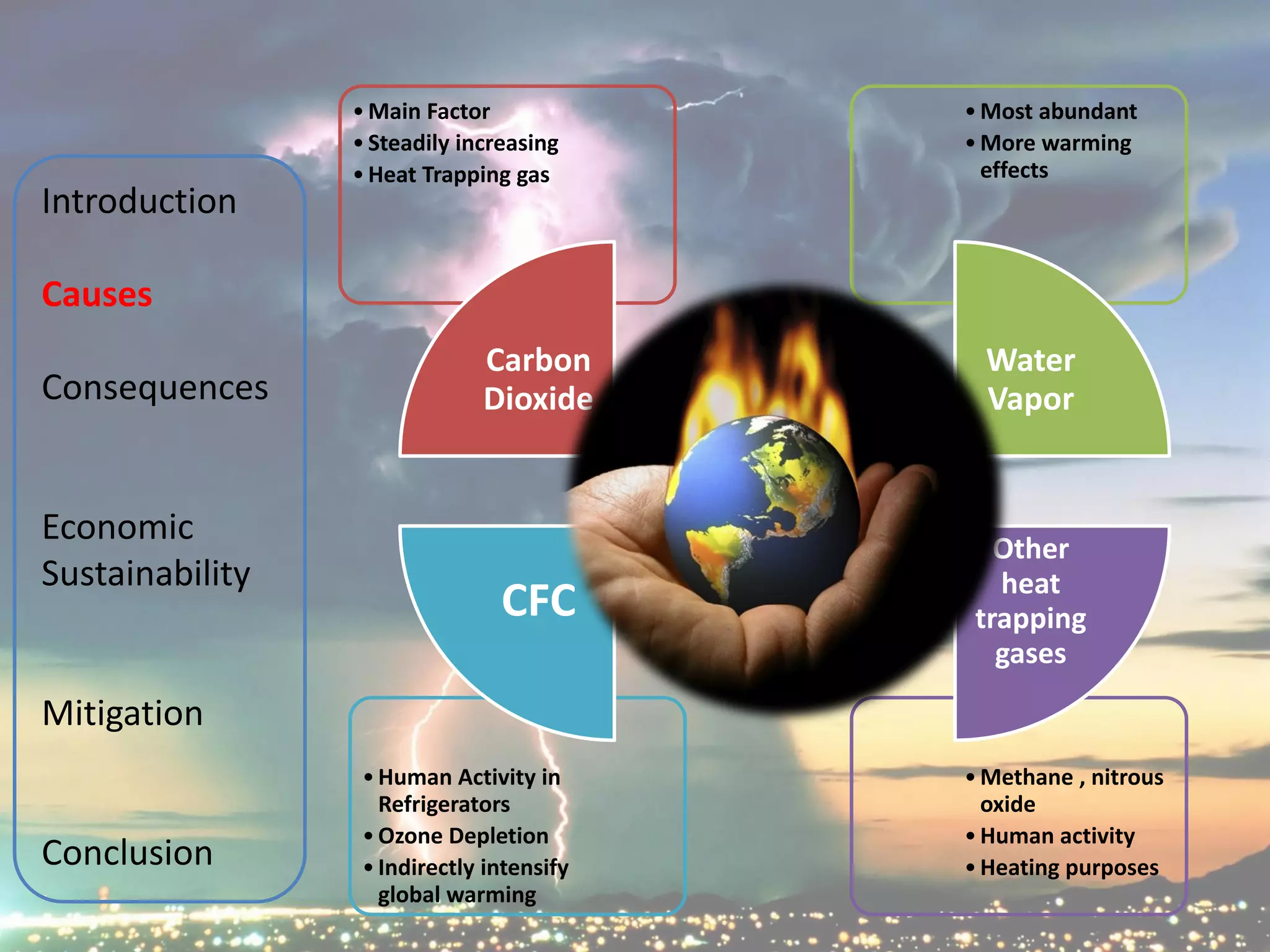
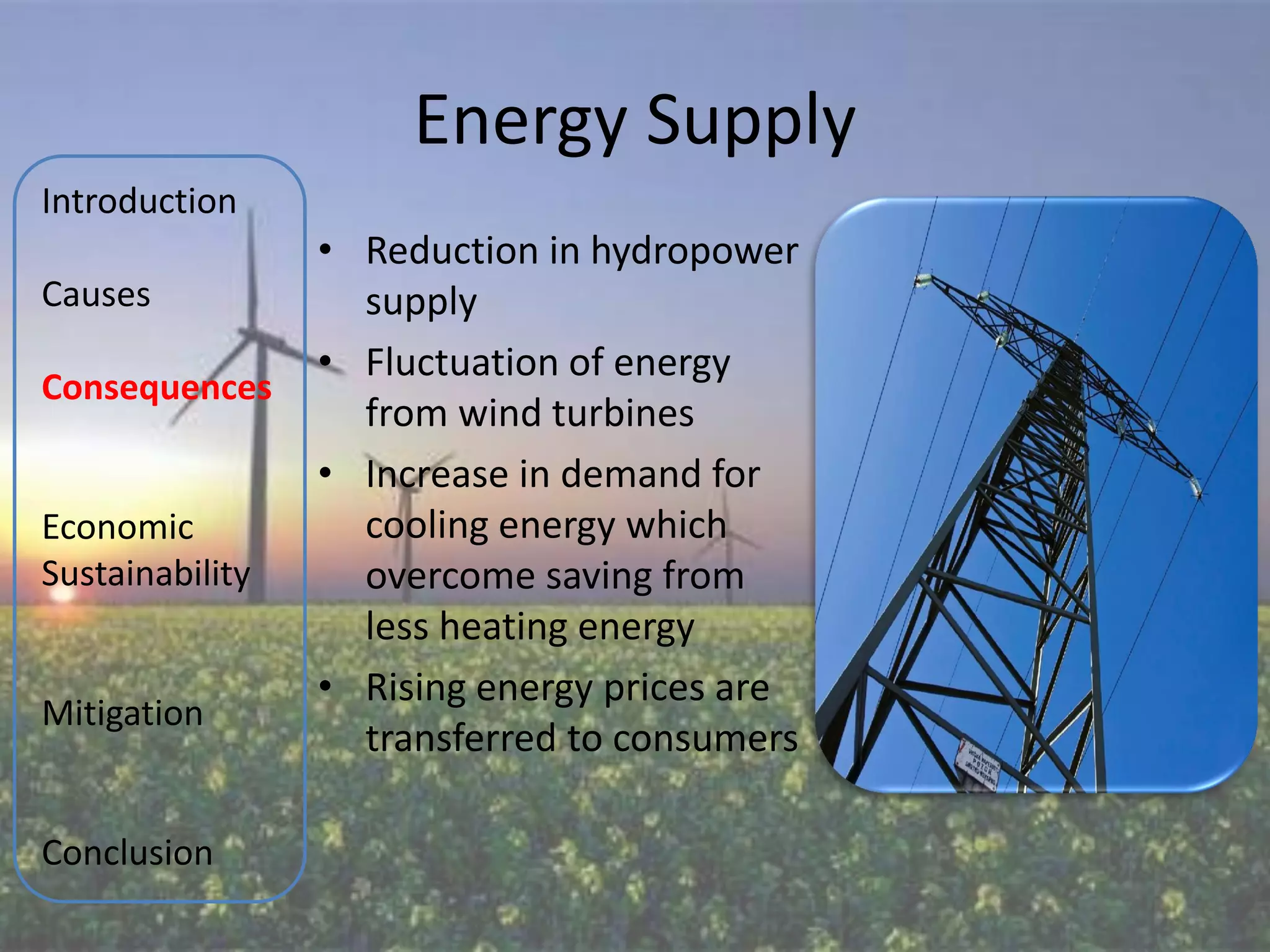
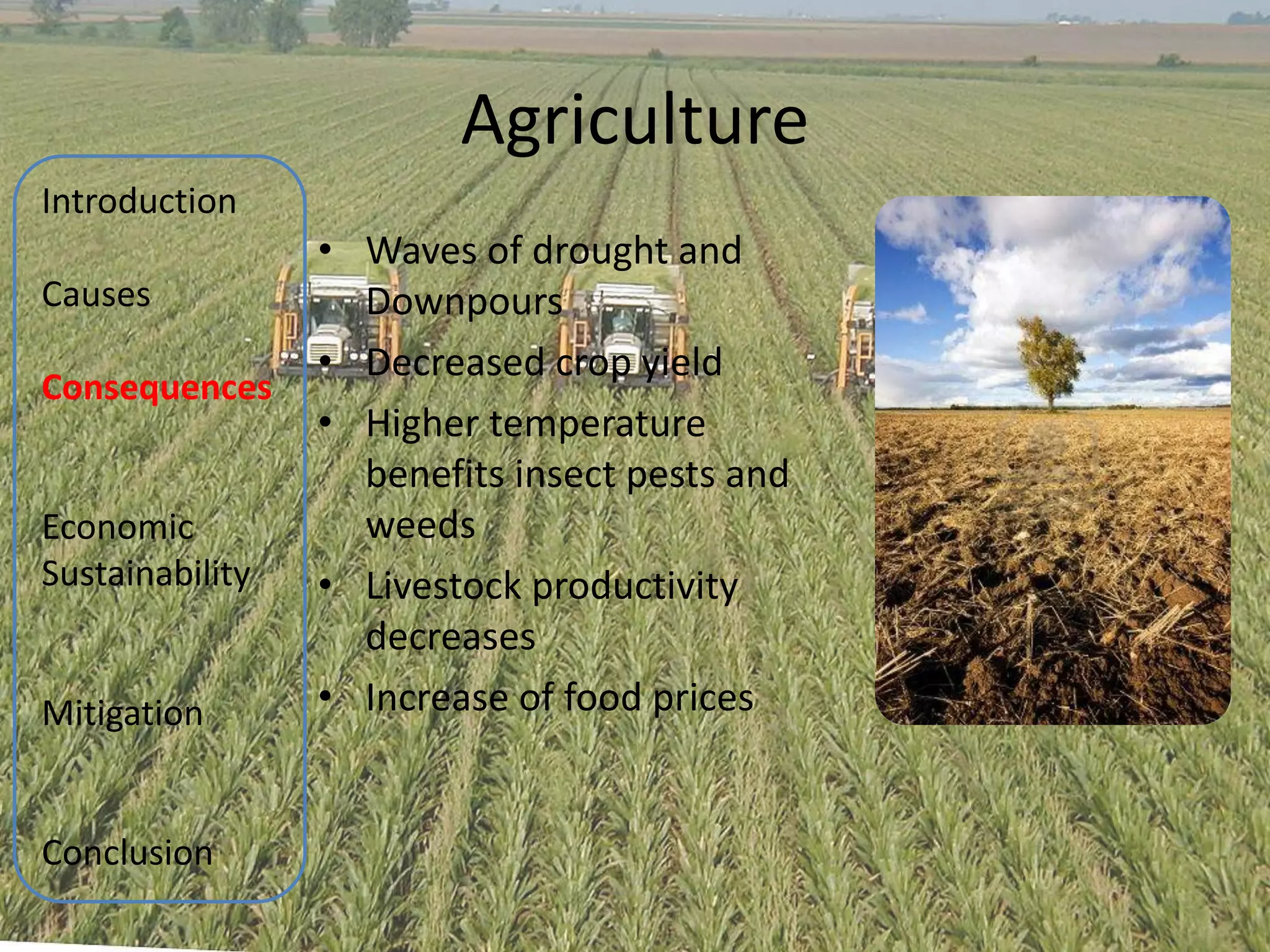
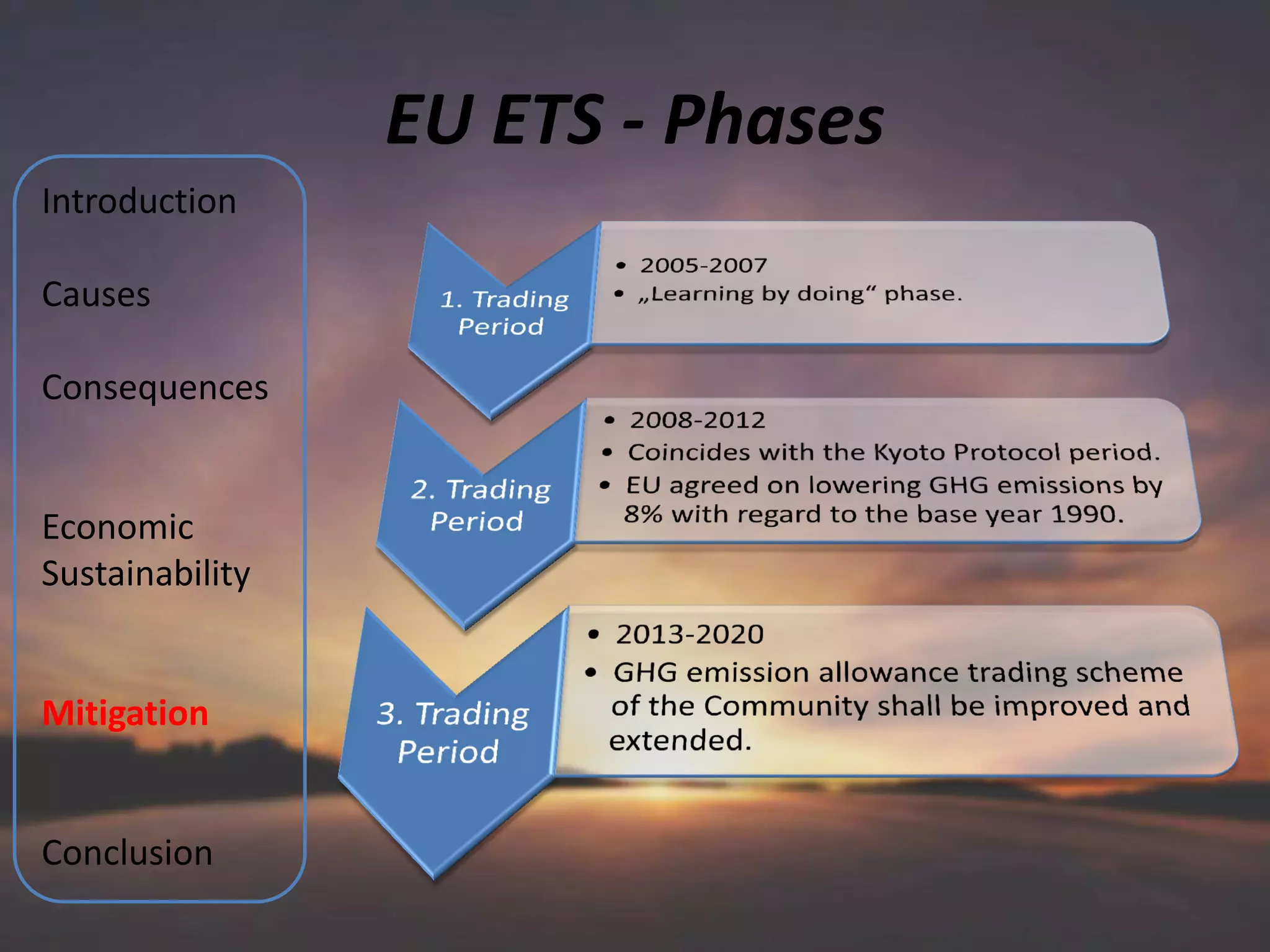
The document discusses various aspects of climate change including causes, consequences, economic impacts, and mitigation strategies. It covers topics such as the key greenhouse gases that cause global warming, effects on water resources, energy supply, agriculture, and economic sustainability. International agreements aimed at mitigating climate change are also summarized, such as the UNFCCC, Kyoto Protocol, and EU Emissions Trading Scheme. The document provides an overview of the issue of climate change from various perspectives in a comprehensive manner.