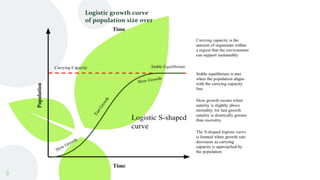
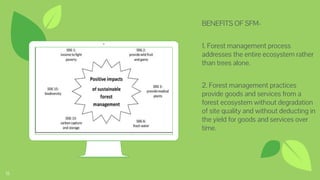
The document discusses sustainability as a socio-ecological process and contrasts it with sustainable development, which focuses on meeting present needs without compromising future generations. It emphasizes the interconnected domains of sustainability, including environmental, economic, and social aspects while addressing the importance of maintaining ecological limits and social justice. The document also outlines sustainable forest management principles, highlighting the need for a balanced approach that benefits ecosystems, local livelihoods, and adherence to human rights.