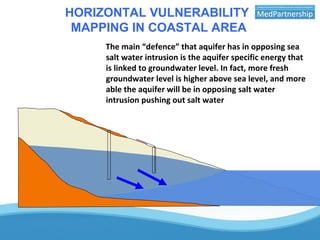
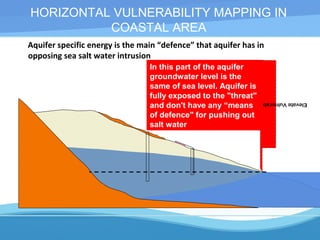
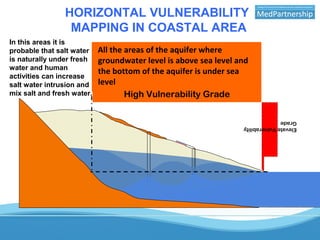
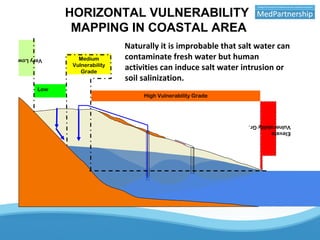
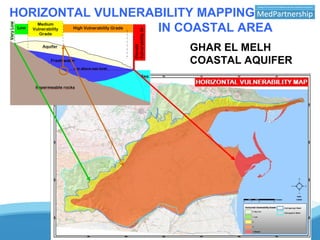
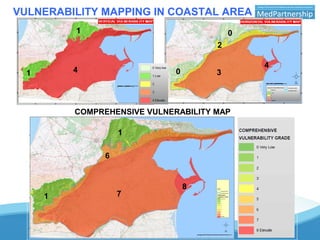
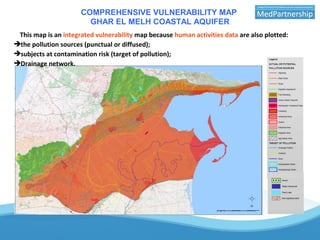
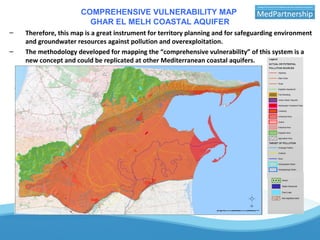
The UNESCO-IHP project demonstrated a methodology for mapping the vulnerability of coastal aquifers to both vertical pollution from the surface and horizontal saltwater intrusion. The project mapped the comprehensive vulnerability of the Ghar El Melh coastal aquifer in Tunisia in a single parameter. It considered the aquifer's intrinsic properties that provide defense against these threats, such as groundwater levels and the aquifer's specific energy to resist saltwater intrusion. The resulting comprehensive vulnerability map integrated these factors with human activities data to provide a planning tool for safeguarding groundwater resources. The demonstrated methodology can be applied to other Mediterranean coastal aquifers.