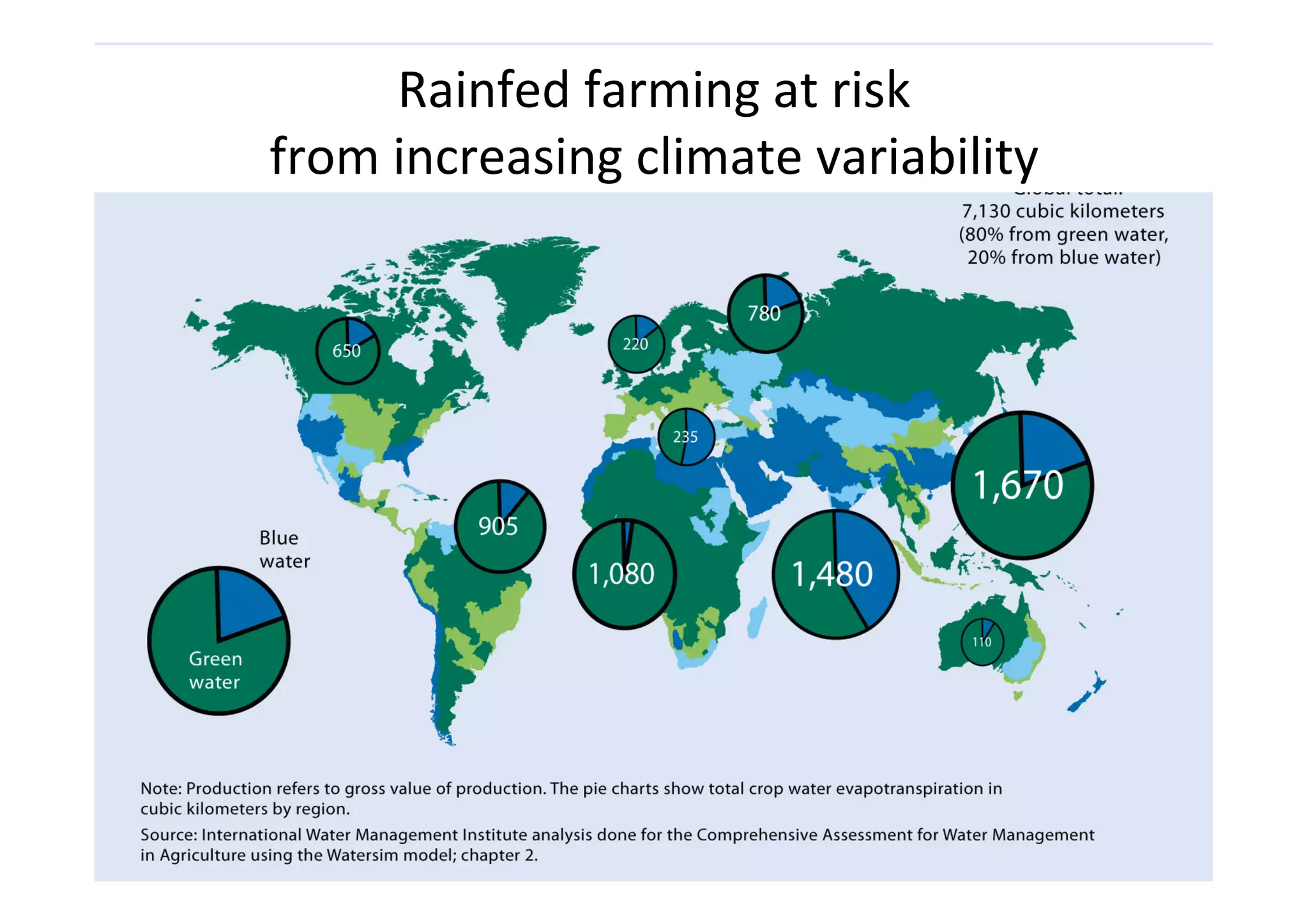
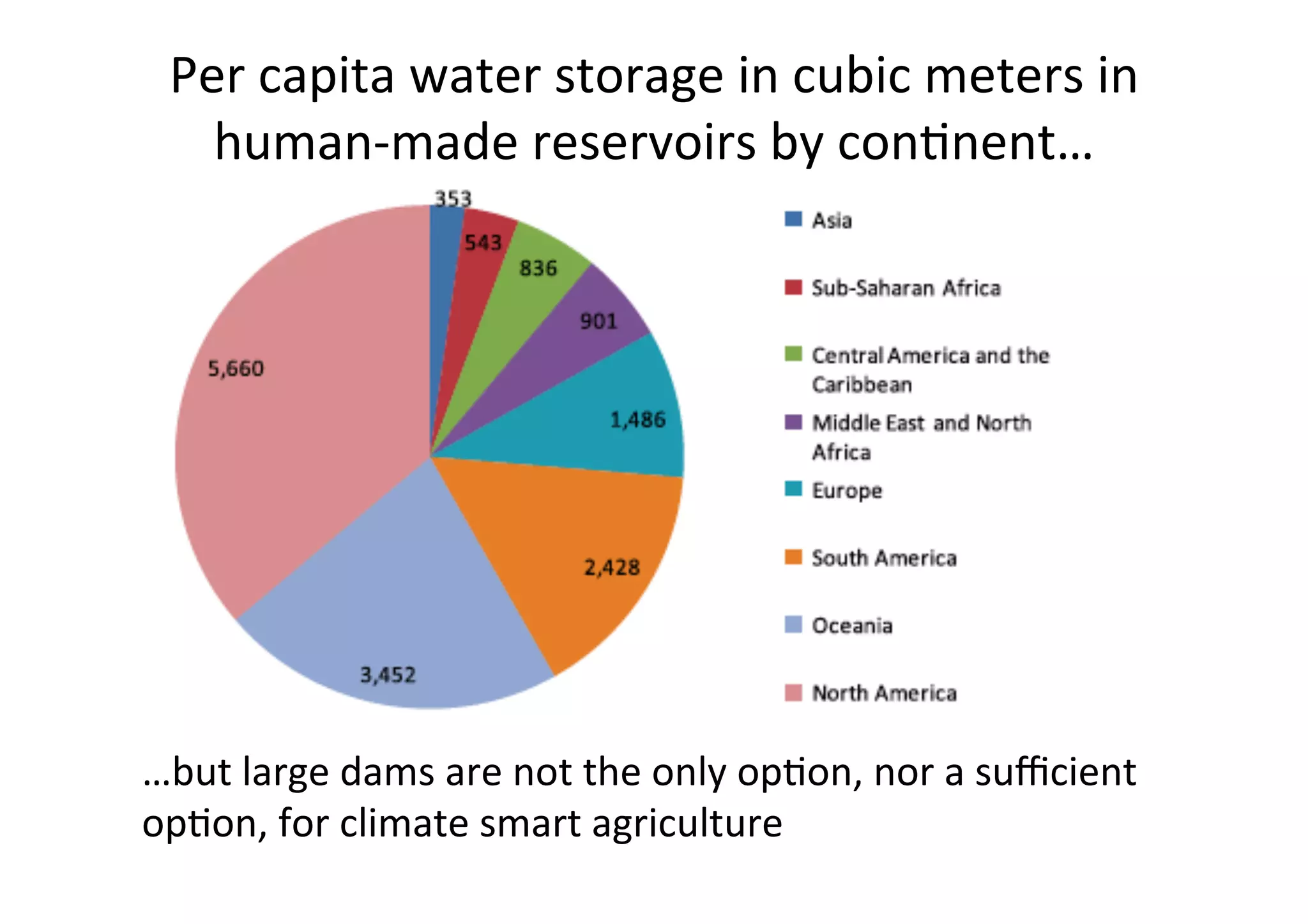
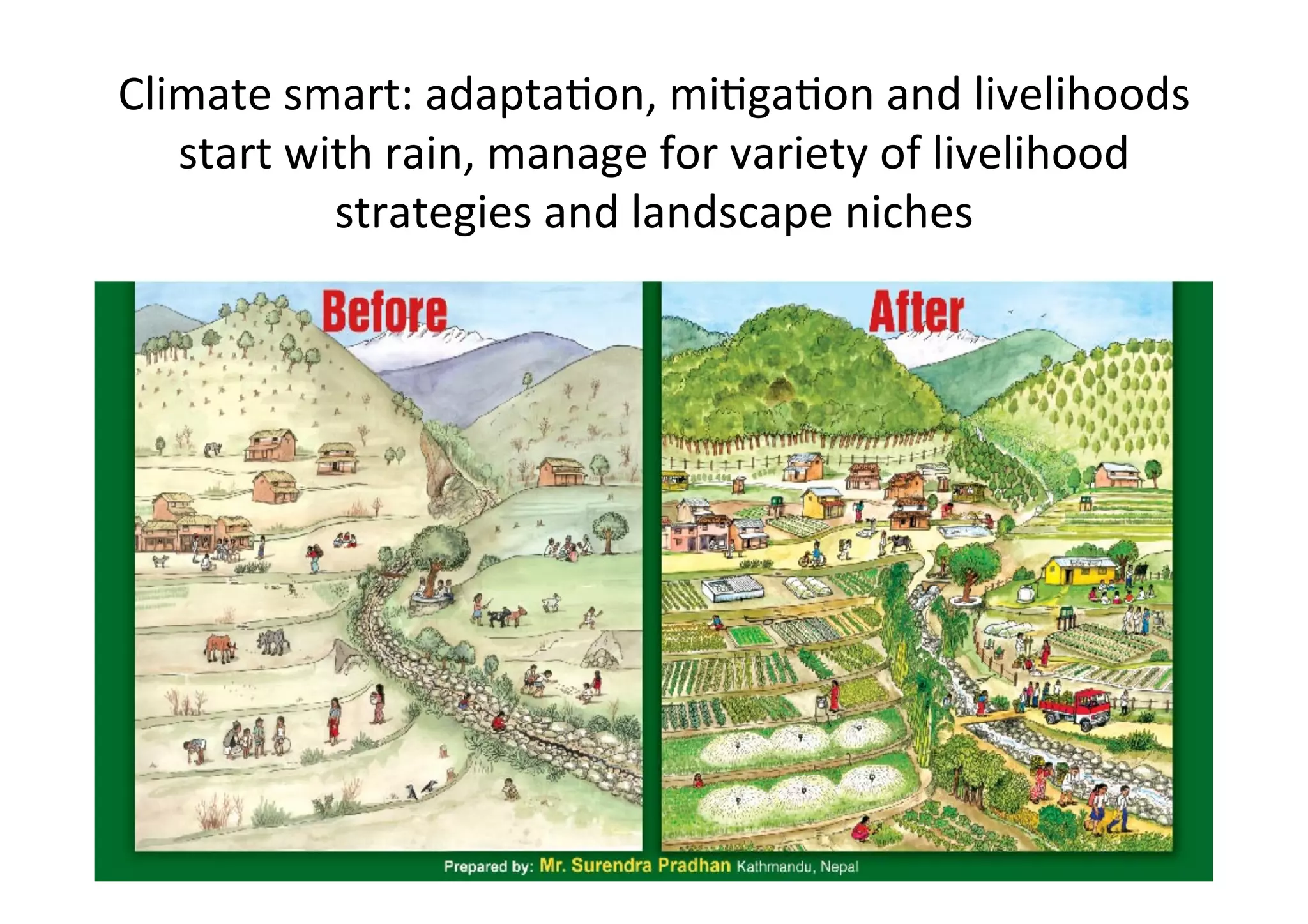
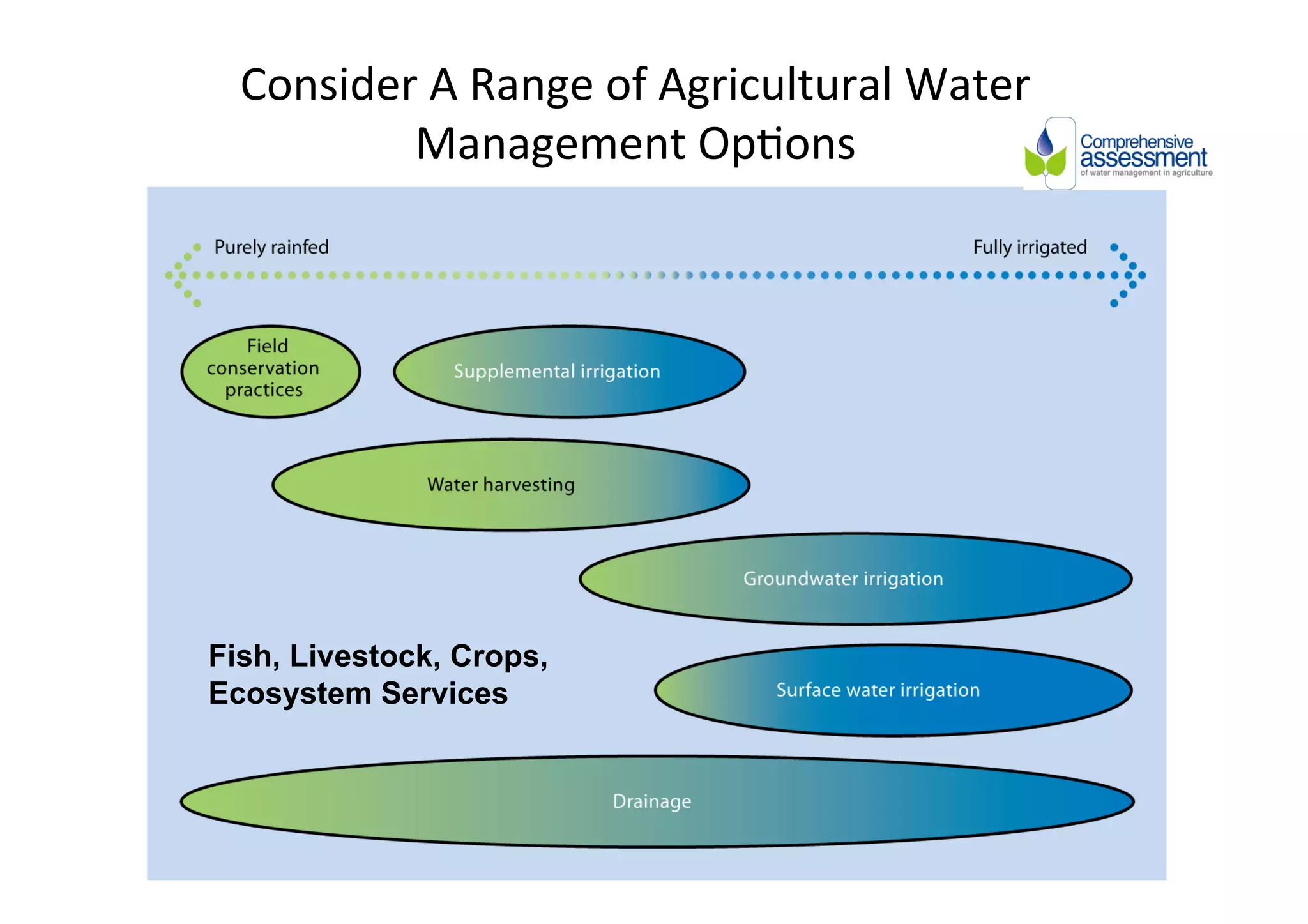
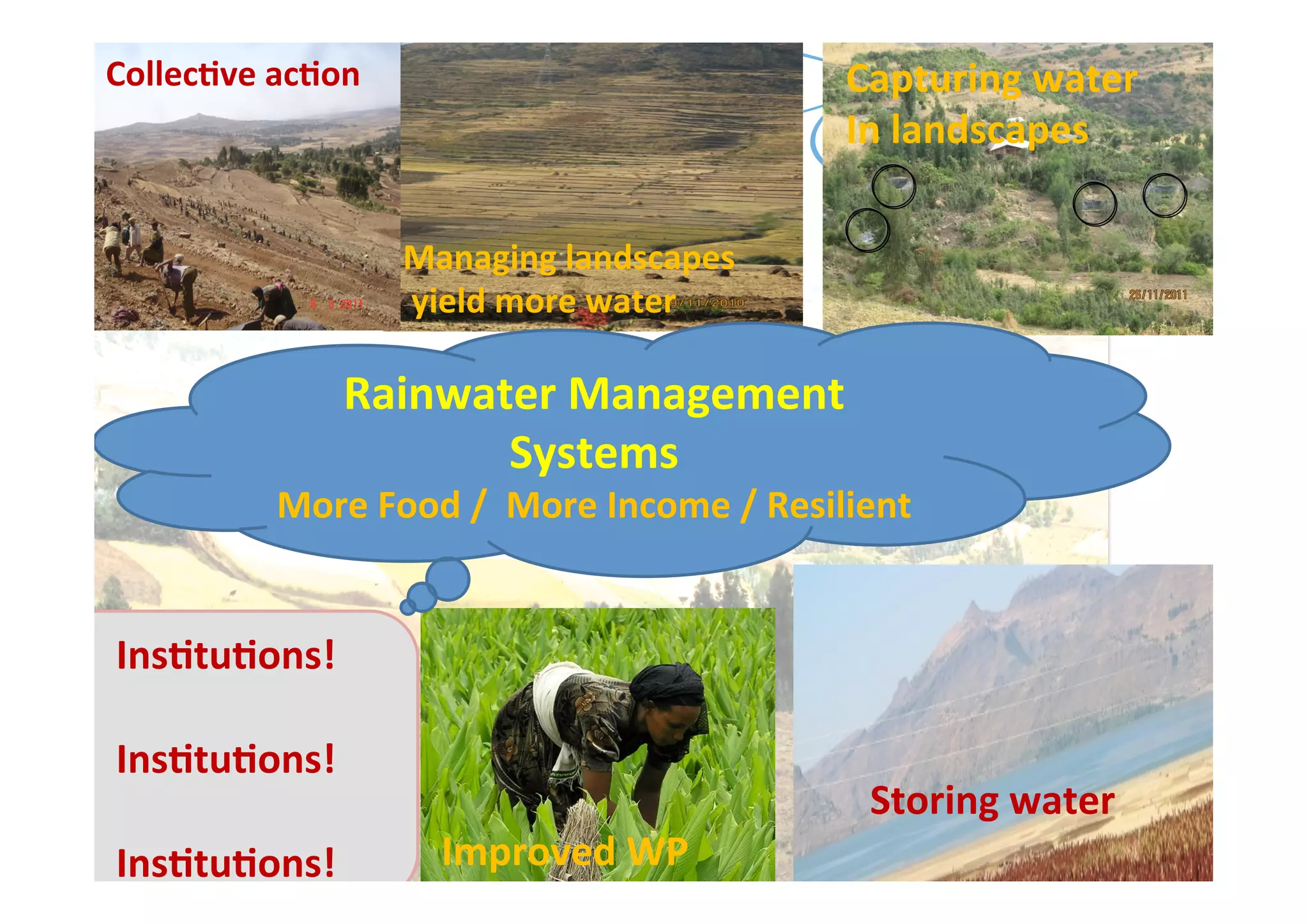
This document discusses how rainwater management can help smallholder farmers adapt to climate variability and change. It notes that rainfed farming is at risk from increasing climate variability. Several rainwater management options are presented, including capturing, storing, and managing water at the landscape level. Case studies of successful rainwater management innovations in Africa are provided, including Zai pits, groundwater utilization, and landscape water management. The document advocates for investing in rainwater management and strengthening local institutions to support smallholder farmers' resilience.