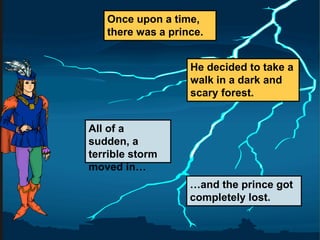
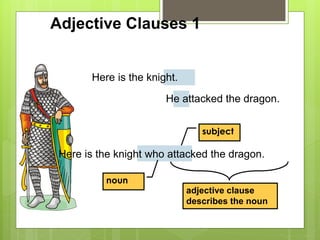
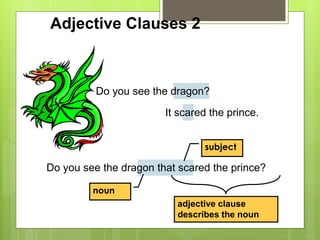
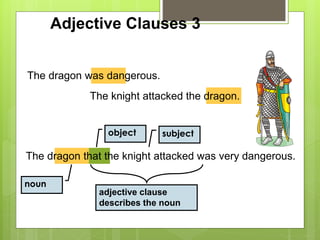
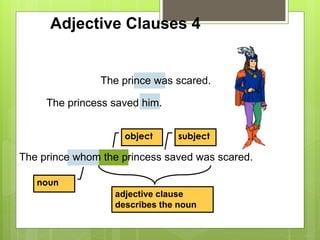
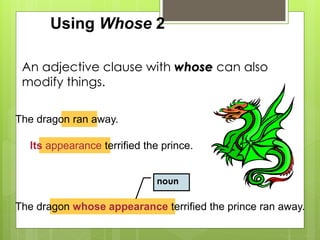
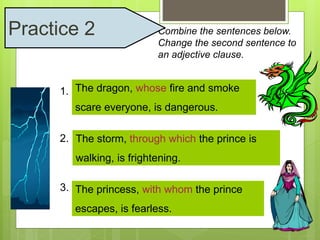
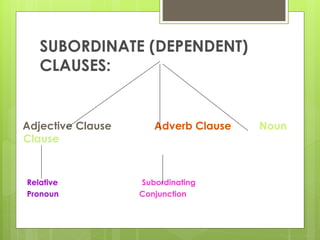
The document discusses different types of clauses in English grammar: independent clauses, dependent clauses, adjective clauses, adverb clauses, and noun clauses. It provides examples and definitions of each clause type, and how they can be used to modify verbs, nouns, adjectives, and other elements in sentences. Key points covered include the use of relative pronouns in adjective clauses and question words to introduce noun clauses.