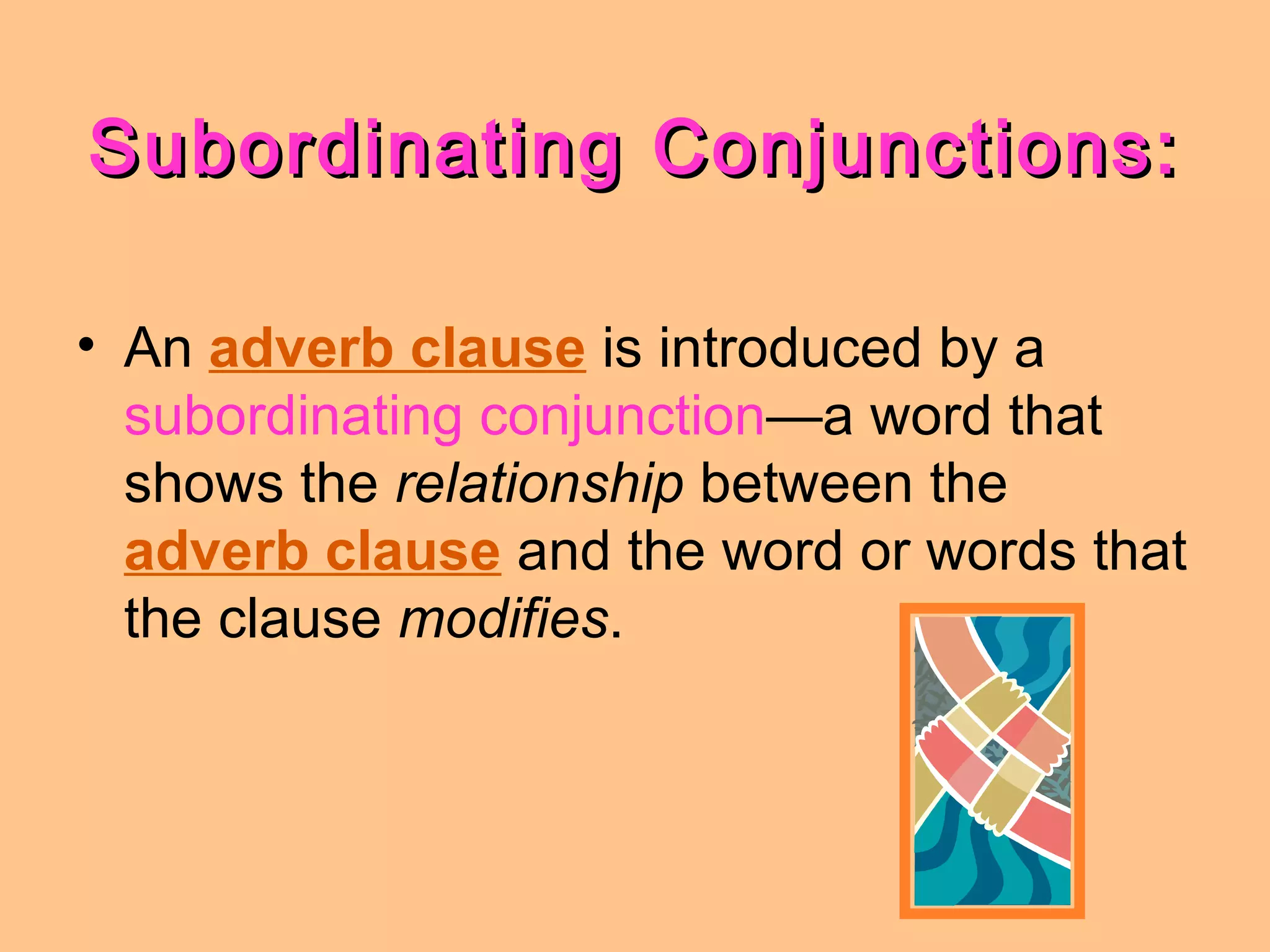
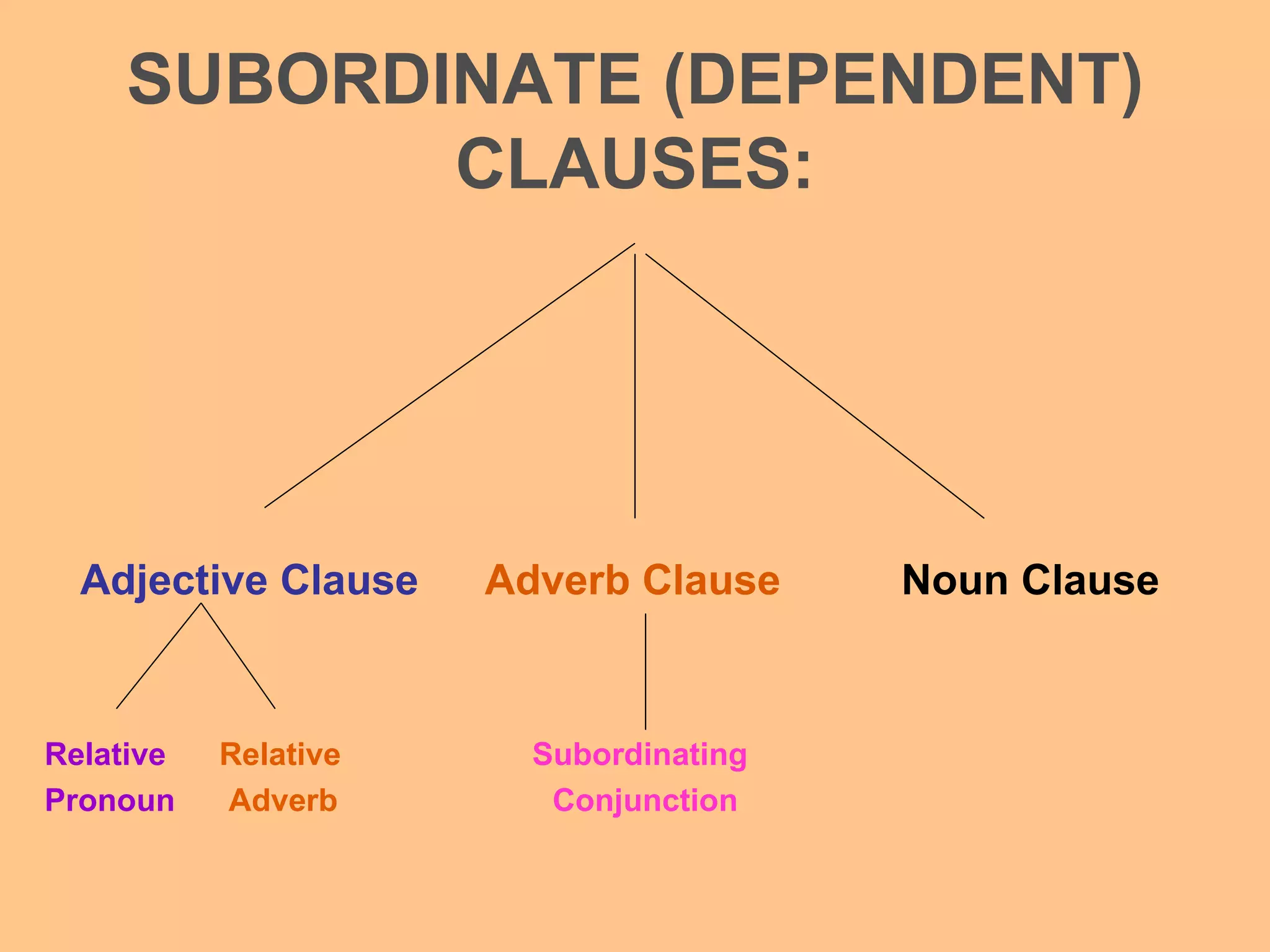
This document discusses adverb clauses. It defines an adverb clause as a subordinate clause that modifies a verb, adjective, or other adverb by providing information about when, where, how, why, to what extent, or under what condition. Adverb clauses can be found anywhere in a sentence and are introduced by subordinating conjunctions like after, as, before, since, until. Examples of adverb clauses and their functions are provided.