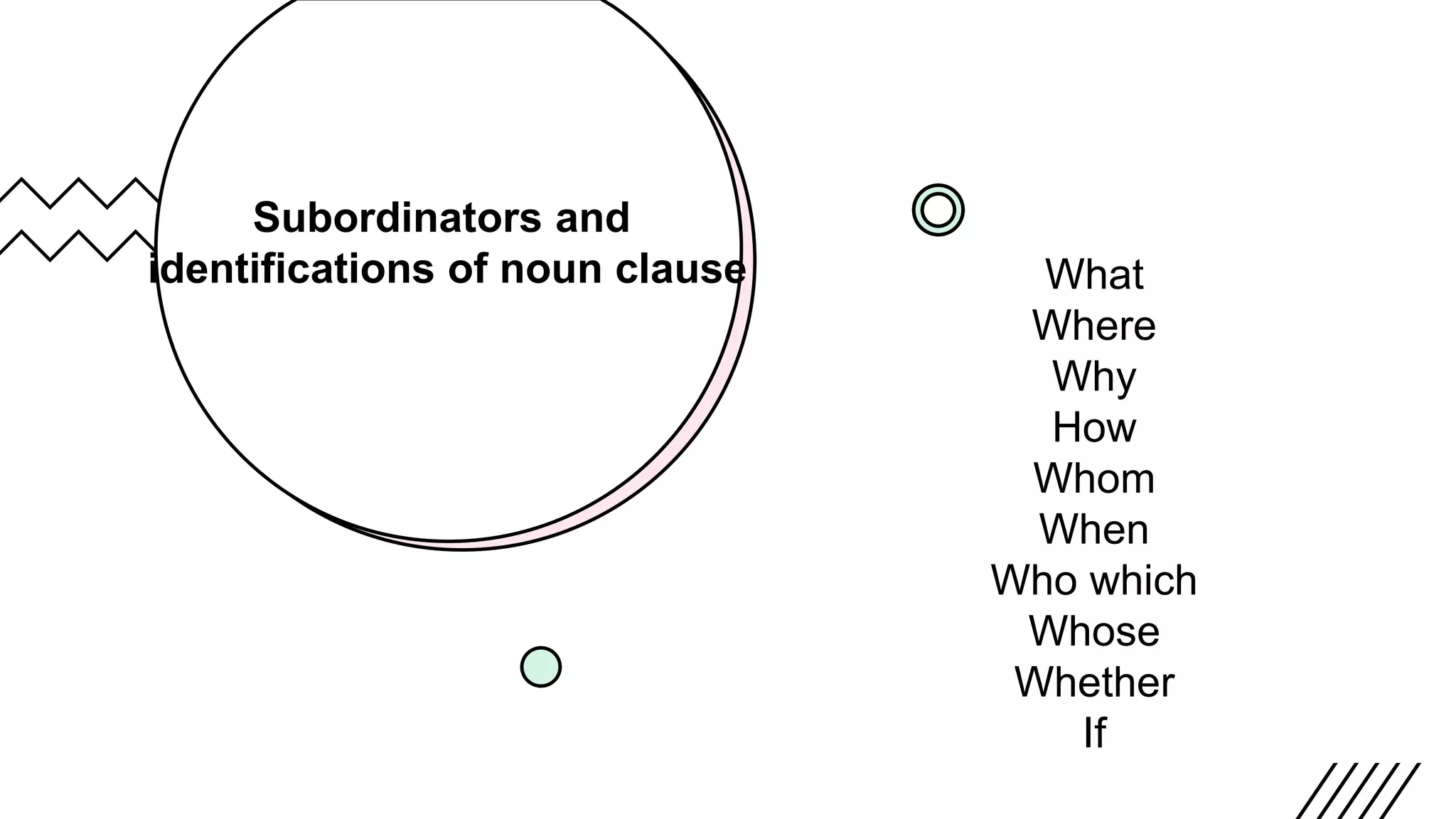
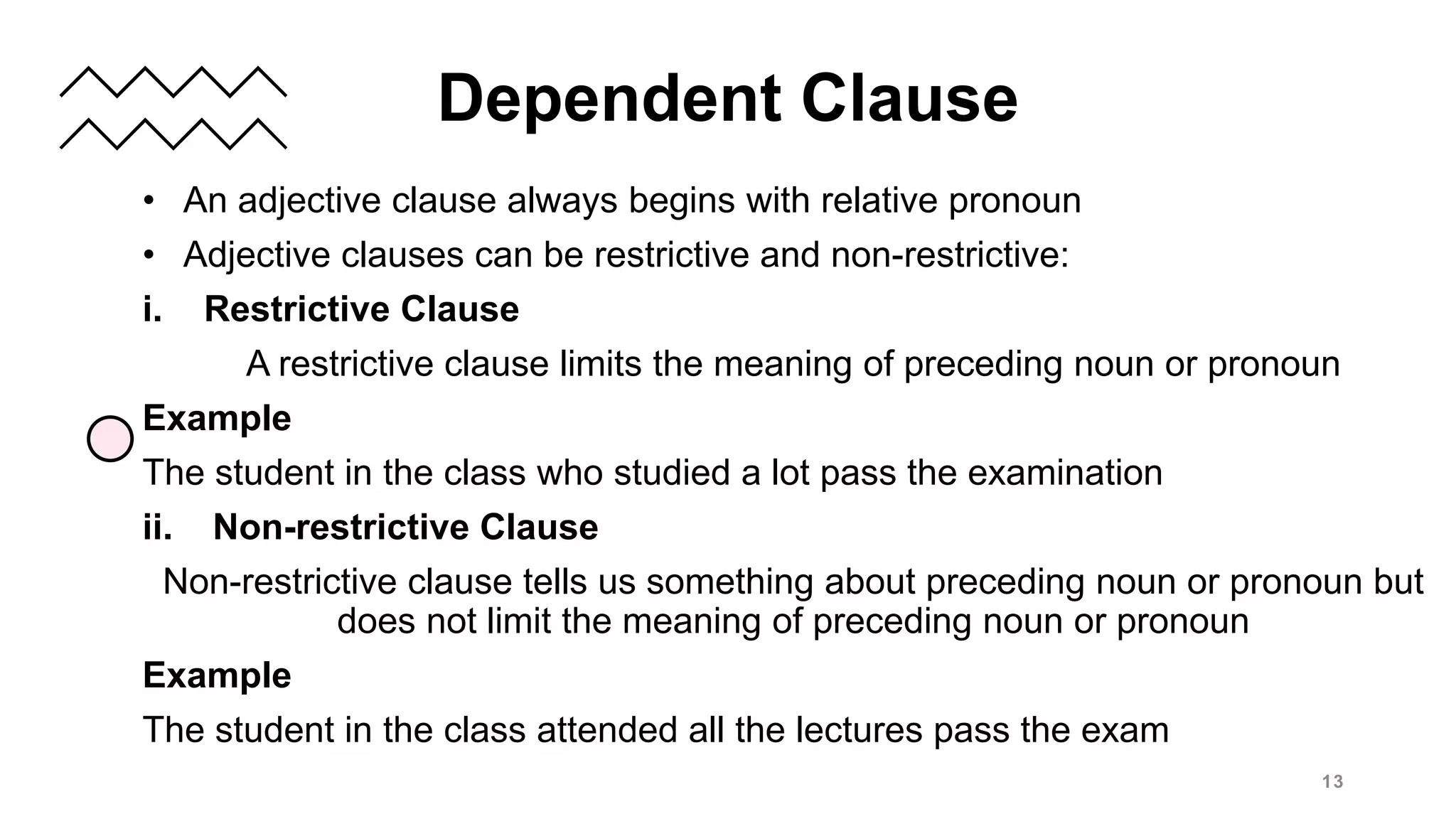
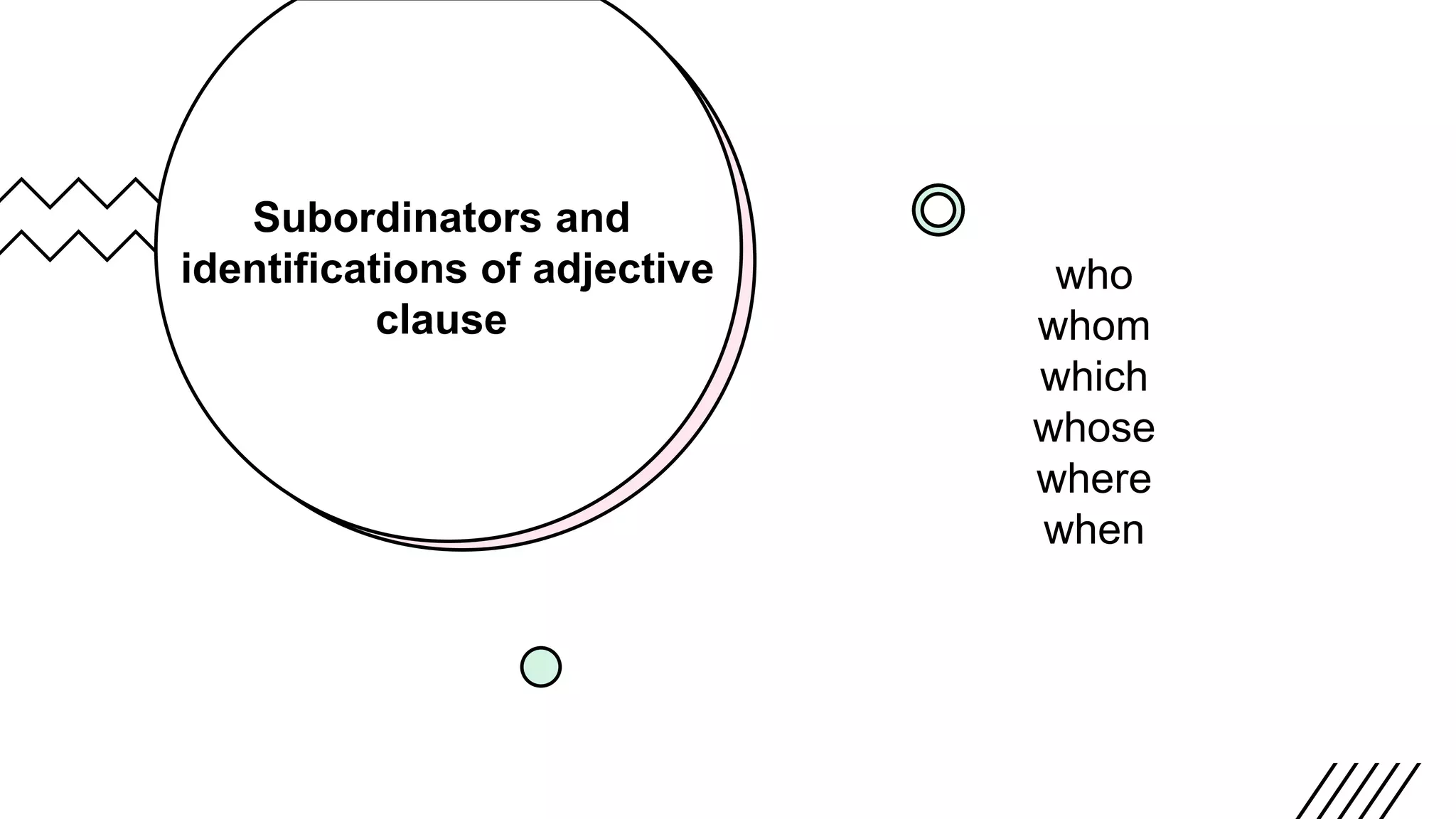
This document defines and provides examples of different types of clauses, including main/independent clauses and dependent clauses. It discusses that a clause contains a subject and a verb and can form a complete sentence or part of a sentence. There are three main types of dependent clauses: noun clauses, which function as nouns; adjective clauses, which function as adjectives; and adverb clauses, which function as adverbs to describe verbs or other clauses. The document provides examples and introduces common subordinators that can introduce each type of dependent clause.