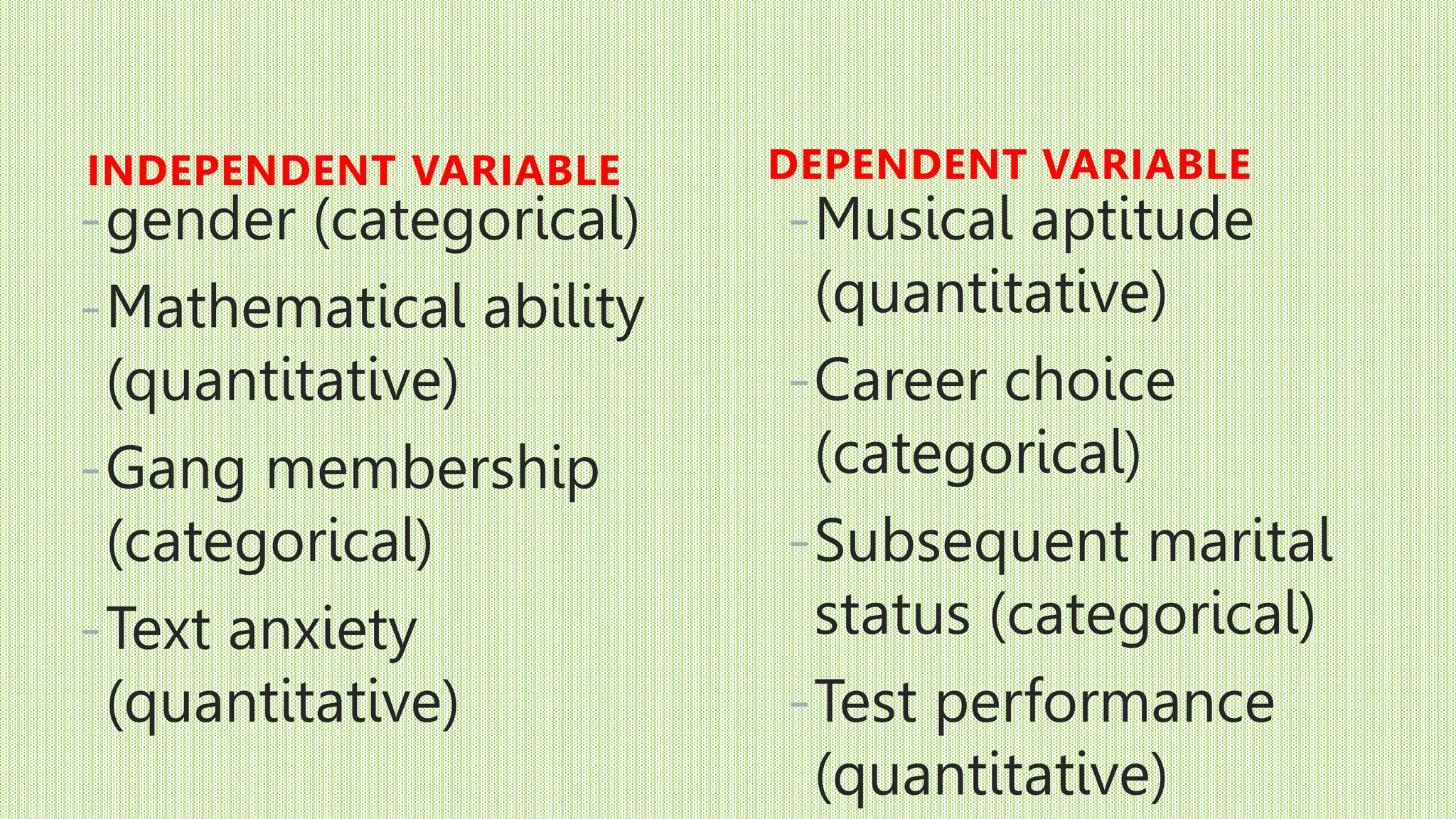
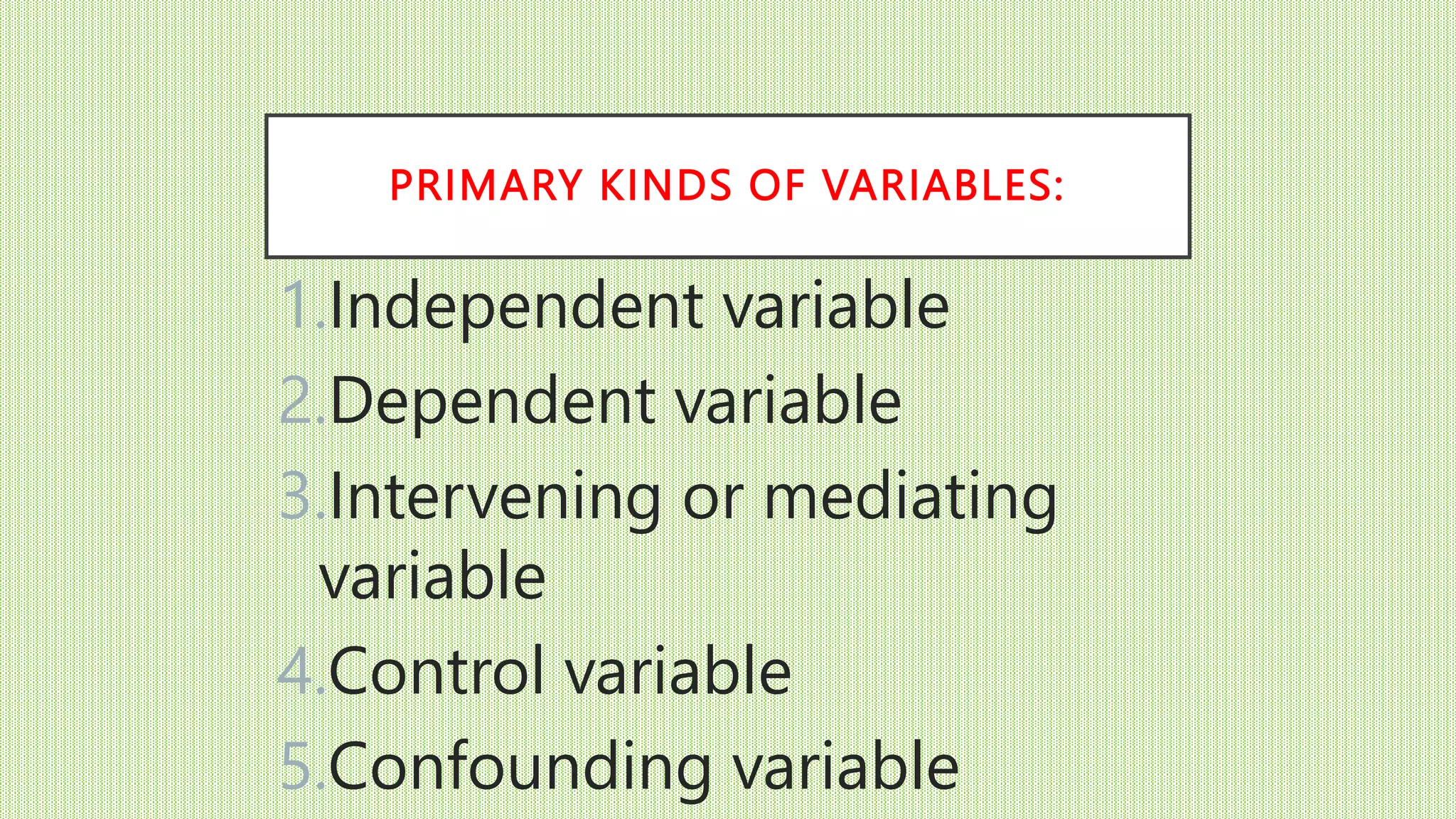
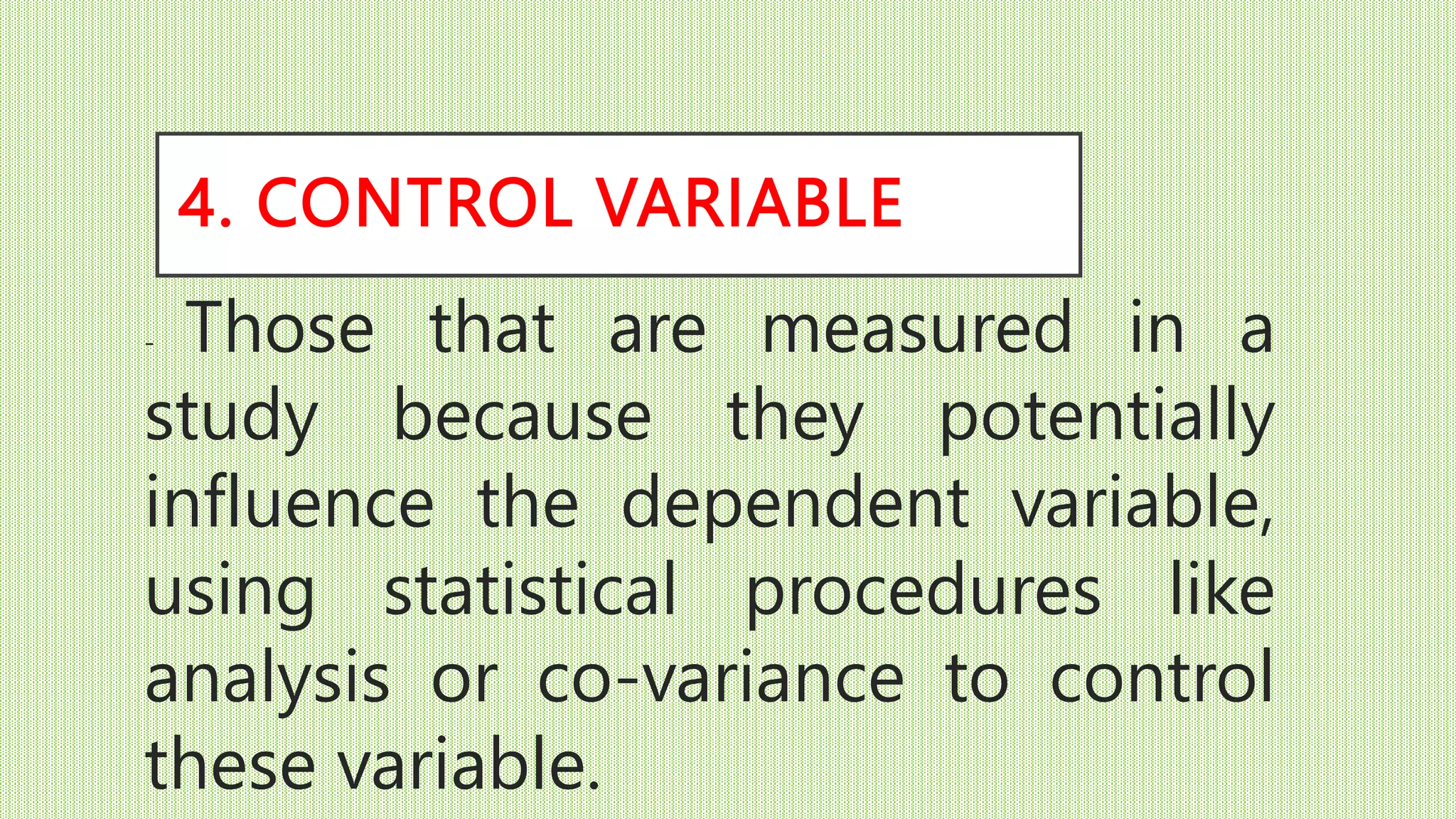
The document discusses different types of variables that can be studied in research, including independent, dependent, intervening, control, and confounding variables. It defines each variable type and provides examples. Quantitative variables contain numerical data that can be mathematically operated on, while categorical variables represent groupings. The independent variable is what a researcher manipulates to potentially cause an effect on the dependent variable, which measures the outcome. Control variables are measured to rule out their influence, while confounding variables may hide the true effect of another variable.