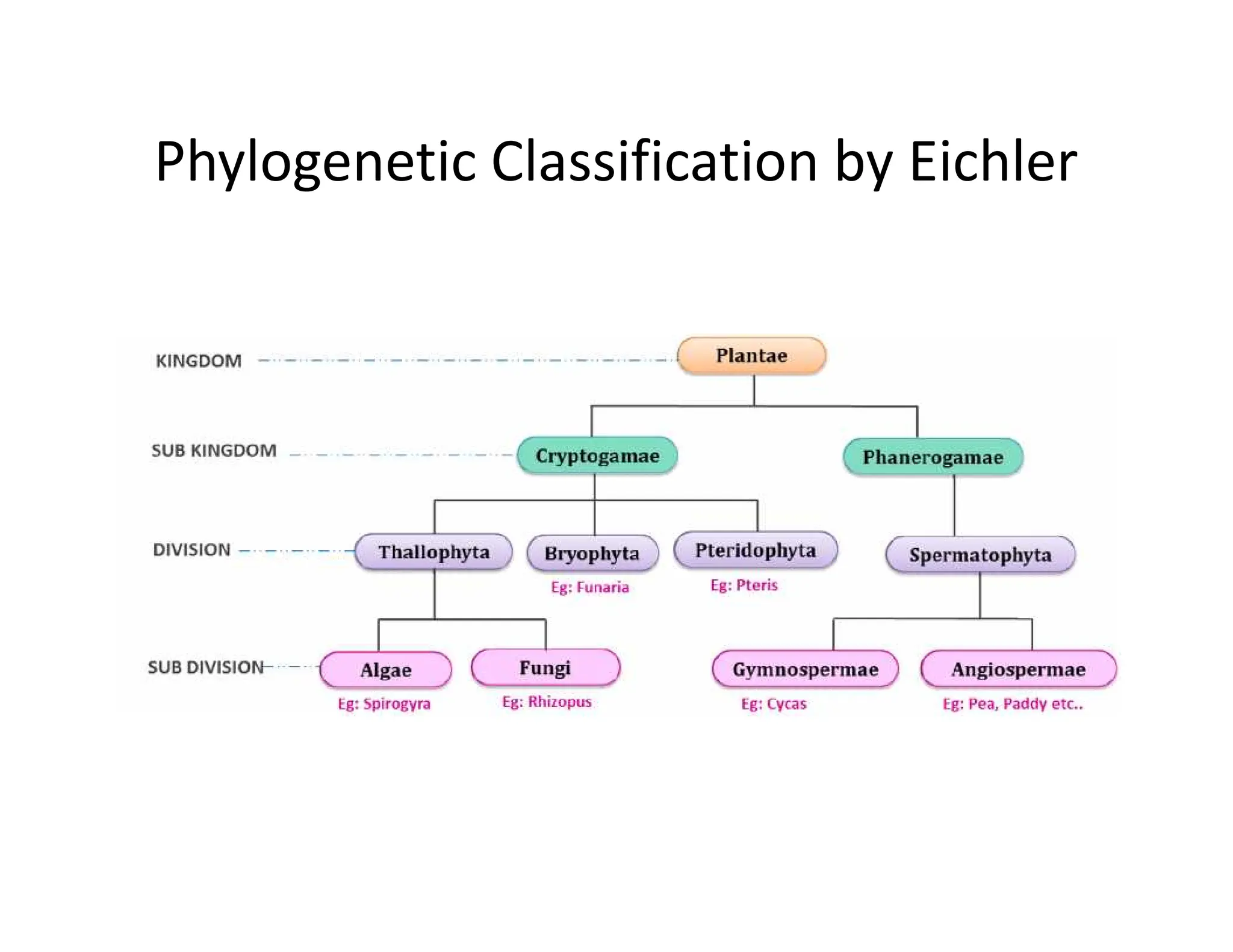
Carl Linnaeus proposed a two kingdom system of classification in 1758 that divided organisms into the animal and plant kingdoms. He named the kingdoms Regnum Animale and Regnum Vegetable. However, this system had limitations as it did not account for the diversity of organisms. In the late 1800s, August Wilhelm Eichler developed a new phylogenetic classification system for plants that divided them into two subkingdoms - Cryptogamae for non-flowering plants like algae, fungi, mosses and ferns, and Phanerogamae for flowering seed plants. This system better reflected evolutionary relationships among organisms.