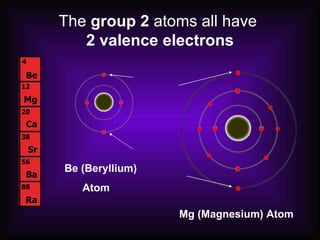
The document summarizes the classification and properties of elements on the periodic table. It describes how elements are arranged by period and group based on their atomic number and valence electrons. Metals are generally located on the left side of the periodic table, are solids, shiny, good conductors, malleable and ductile. Non-metals are usually located on the right side, can exist as solids, liquids or gases, are poor conductors and have many valence electrons. Metalloids border the zigzag line and have properties of both metals and non-metals.