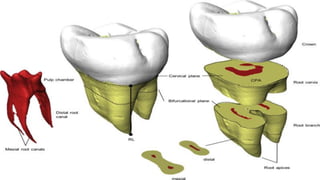
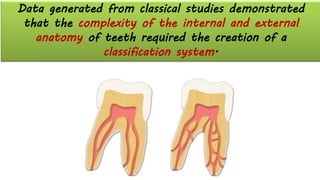
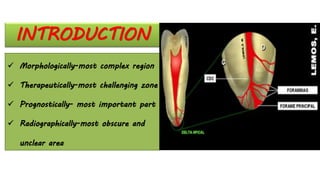
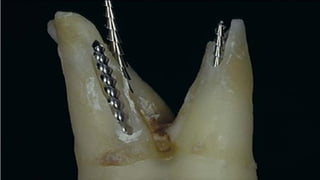
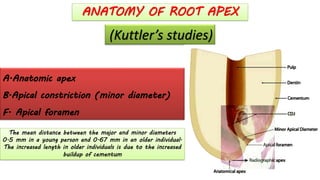
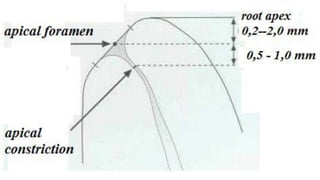
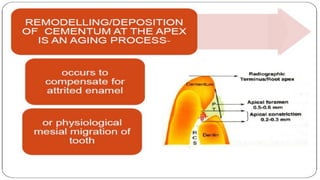
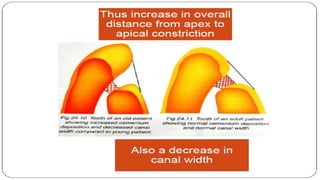
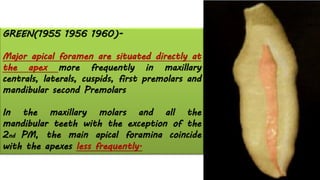
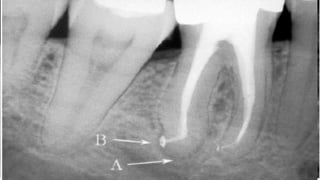
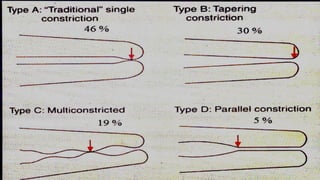
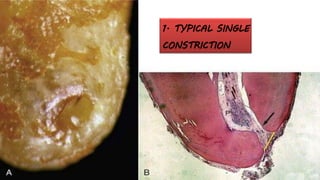
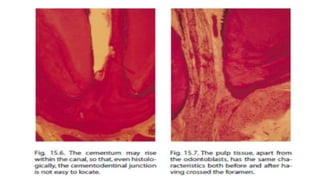
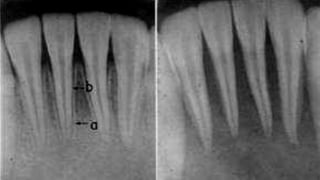
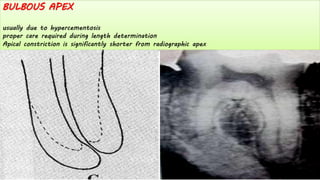
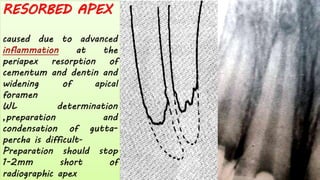
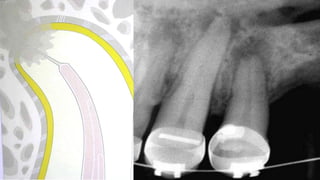
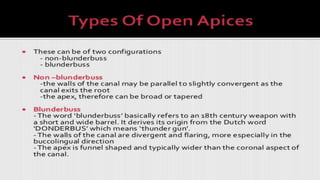
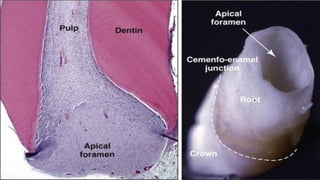
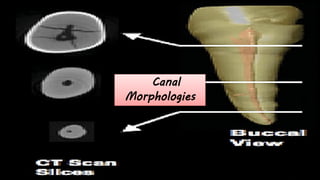
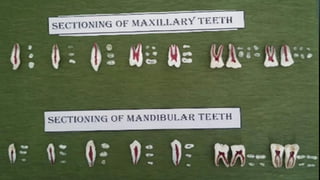
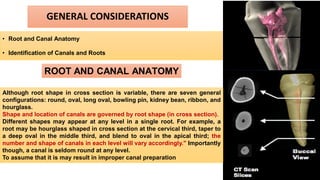
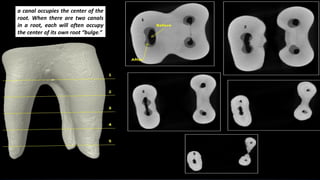
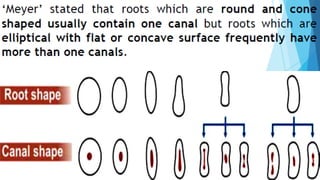
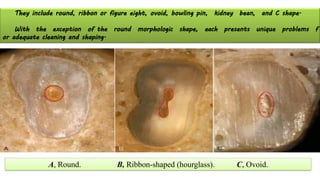
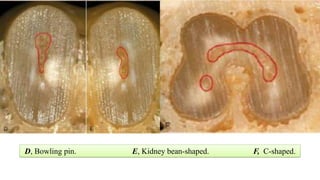
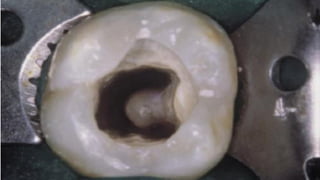
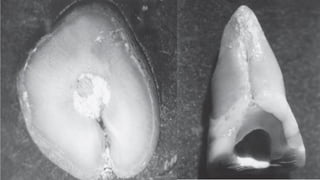
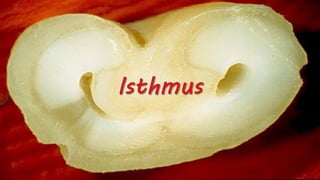
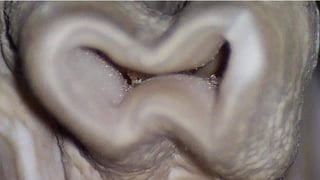
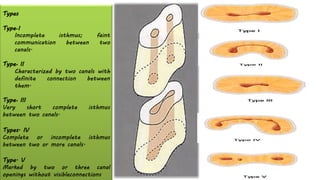
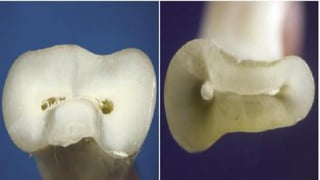
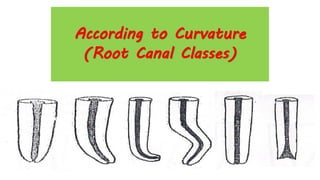
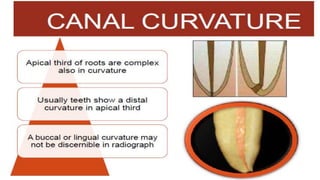
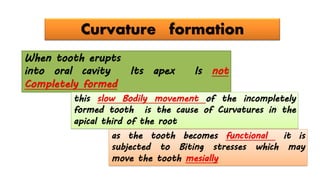
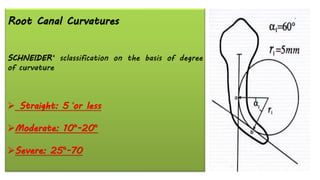
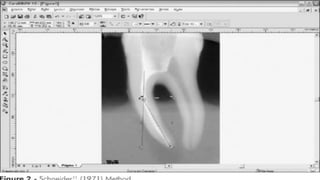
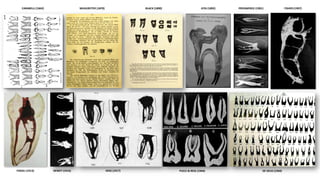
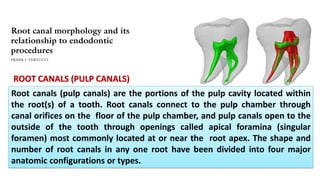
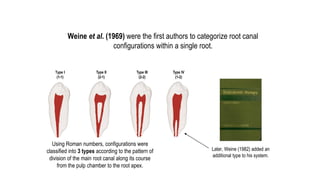
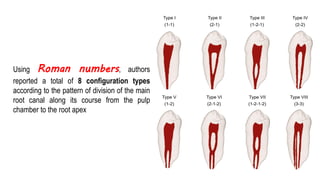
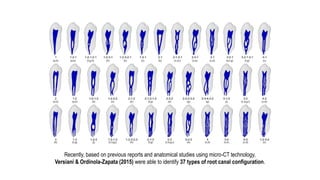
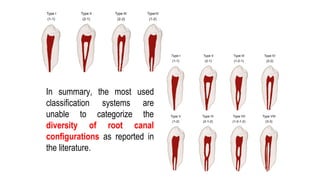
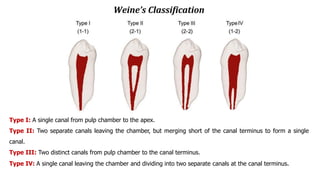
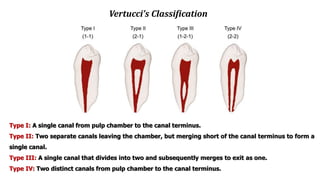
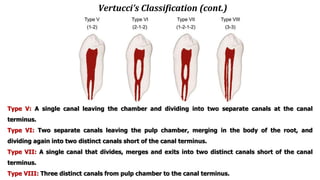
The document discusses the anatomy of root canals and classifications of root canal morphologies. It introduces several past classification systems from Weine, Vertucci, and others. However, it notes that these systems are unable to categorize all the diversity seen in root canal configurations based on more recent anatomical studies using micro-CT technology. A new simplified classification system is needed that can be adopted universally to better describe the complex variations in root and root canal anatomy.