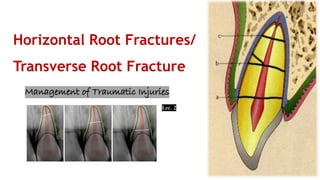
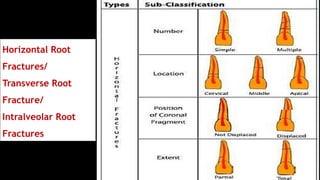
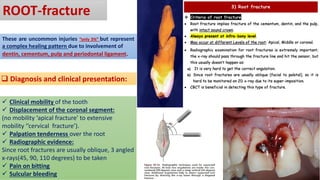
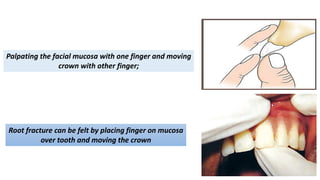
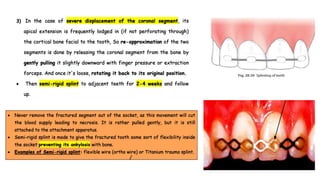
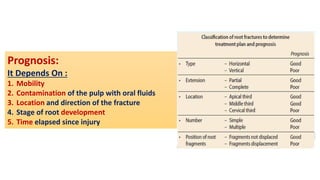
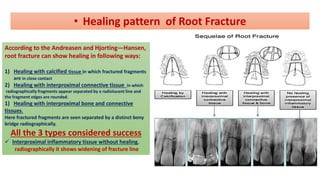
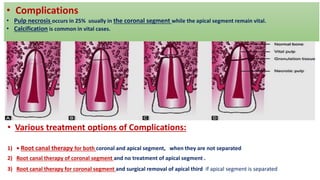
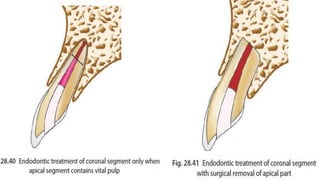
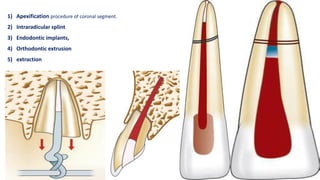
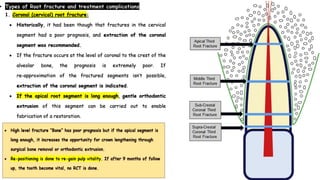
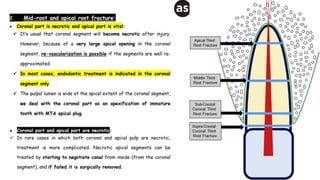
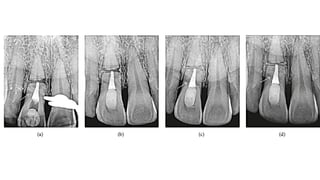
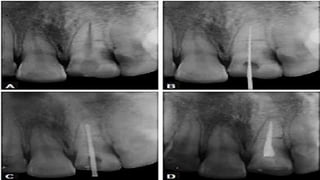
Horizontal root fractures represent 3% of dental traumatic injuries but have a complex healing process. Diagnosis involves clinical mobility, displacement of the coronal segment, palpation tenderness, and radiographic evidence from multiple angles. Treatment objectives are repositioning and splinting the root segments for 2-4 weeks. Prognosis depends on mobility, pulp contamination, fracture location and direction, root development stage, and time since injury. Healing can occur with calcified tissue, interproximal connective tissue, or interproximal bone and connective tissue. Complications include pulp necrosis in the coronal segment and various treatment options depend on whether segments are separated.