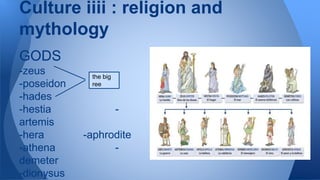
The document examines Classical Greece, highlighting major historical events such as the Peloponnesian and Greco-Persian Wars, and notable figures like Alexander the Great and philosophers Plato and Aristotle. It discusses the democratic institutions of Athens, contrasting them with the oligarchic and military-focused lifestyle of Sparta. The culture, economy, and religious beliefs of the time are also explored, showcasing advancements in art, architecture, and philosophy.