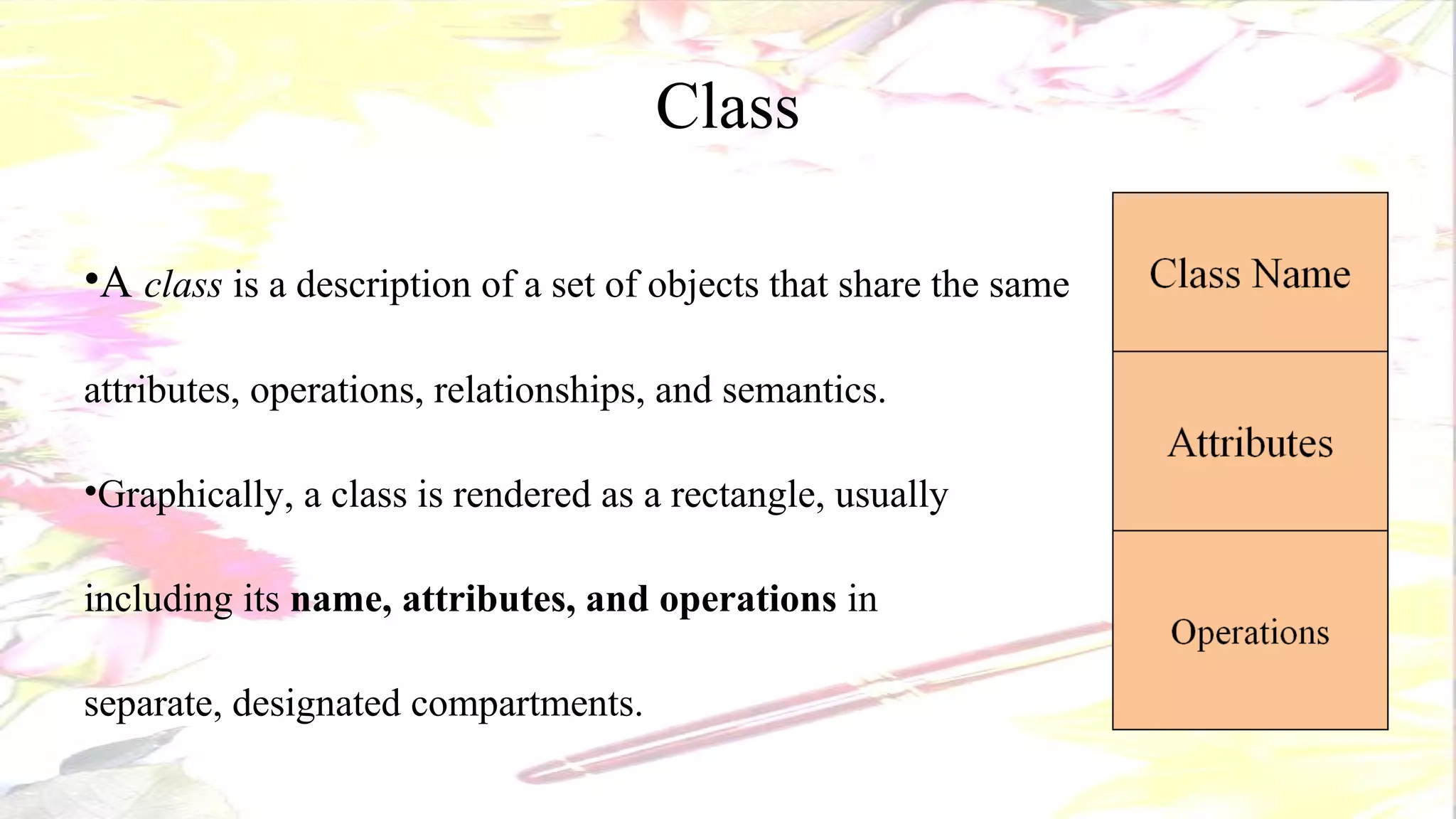
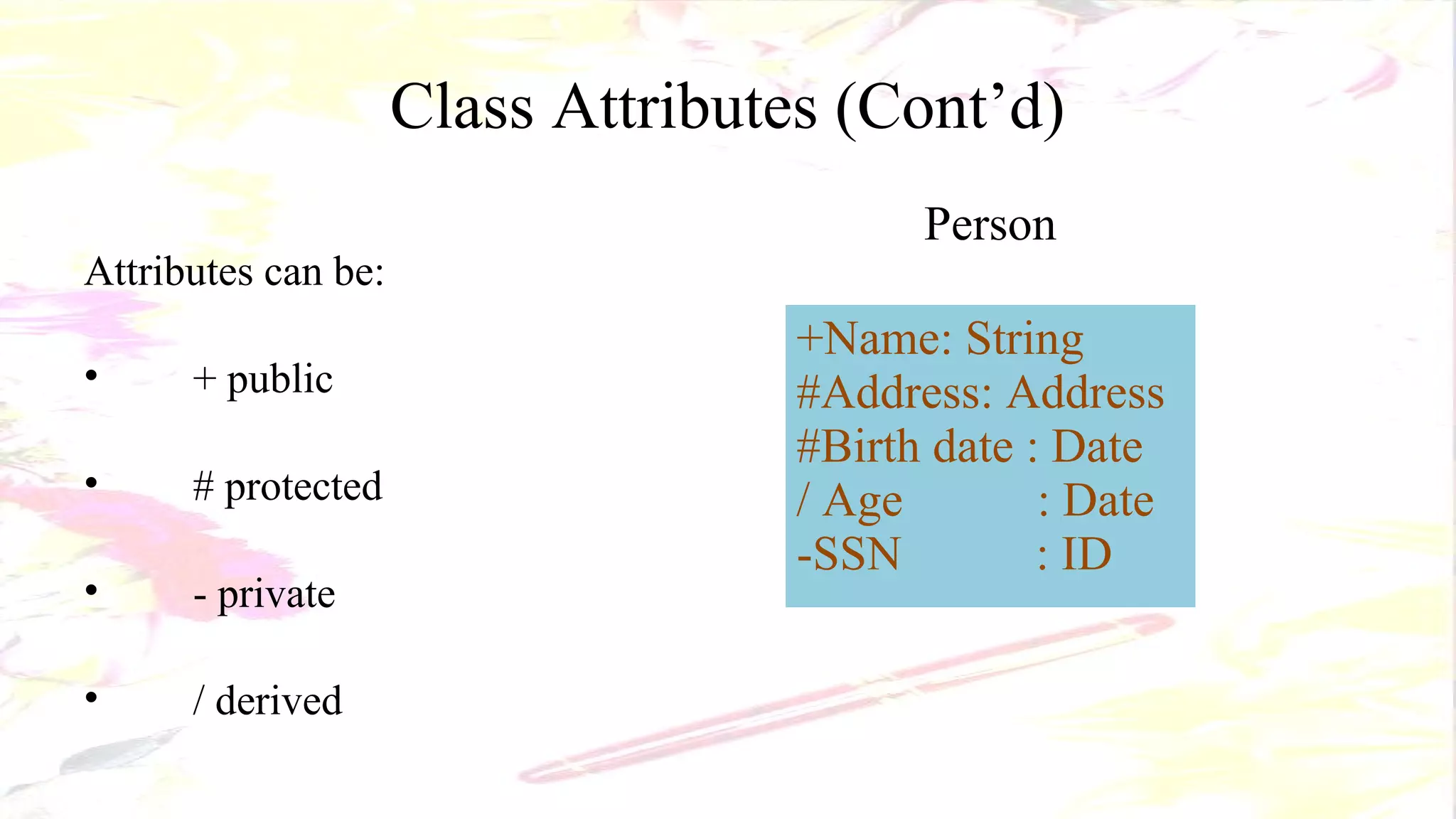
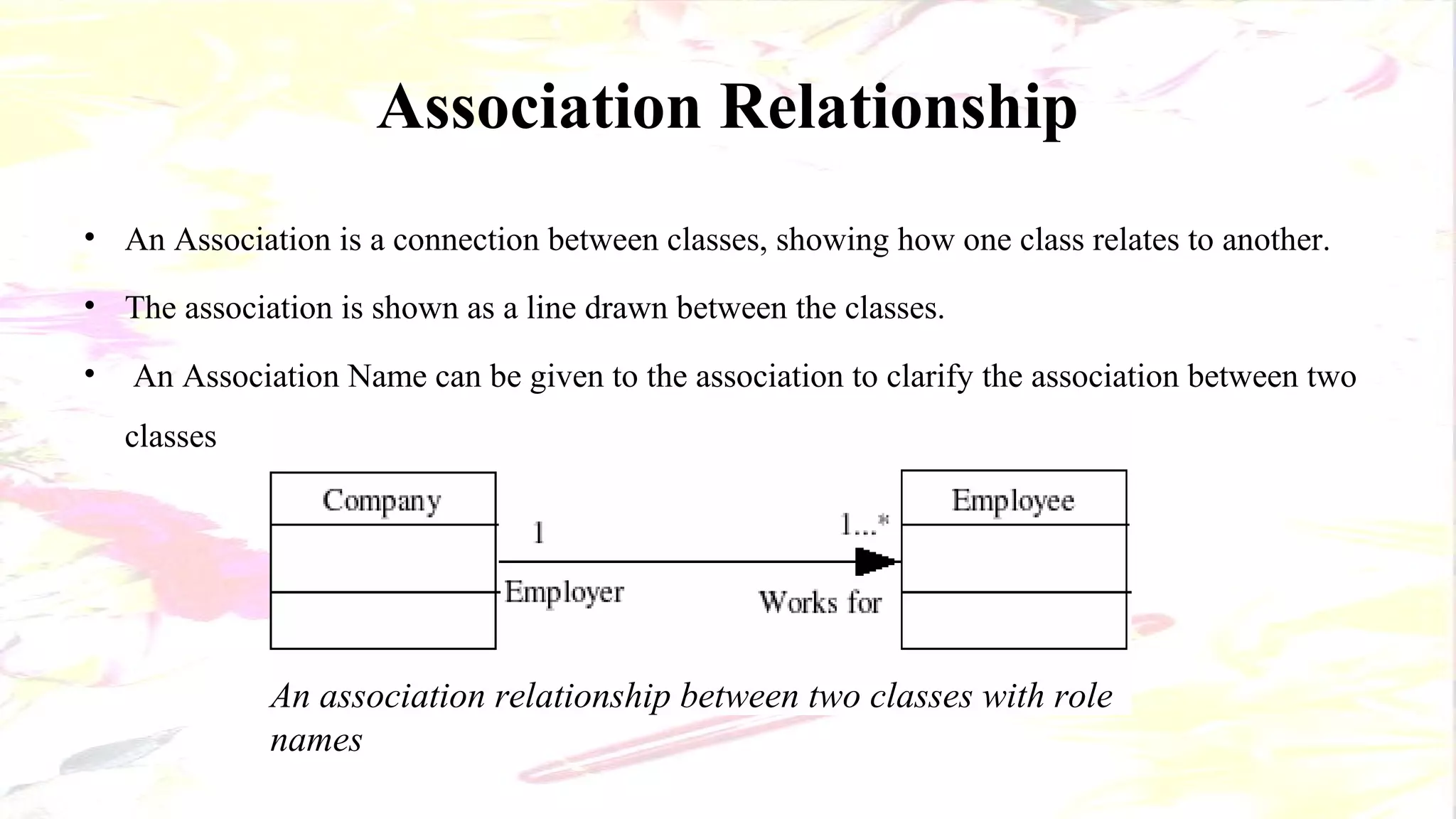
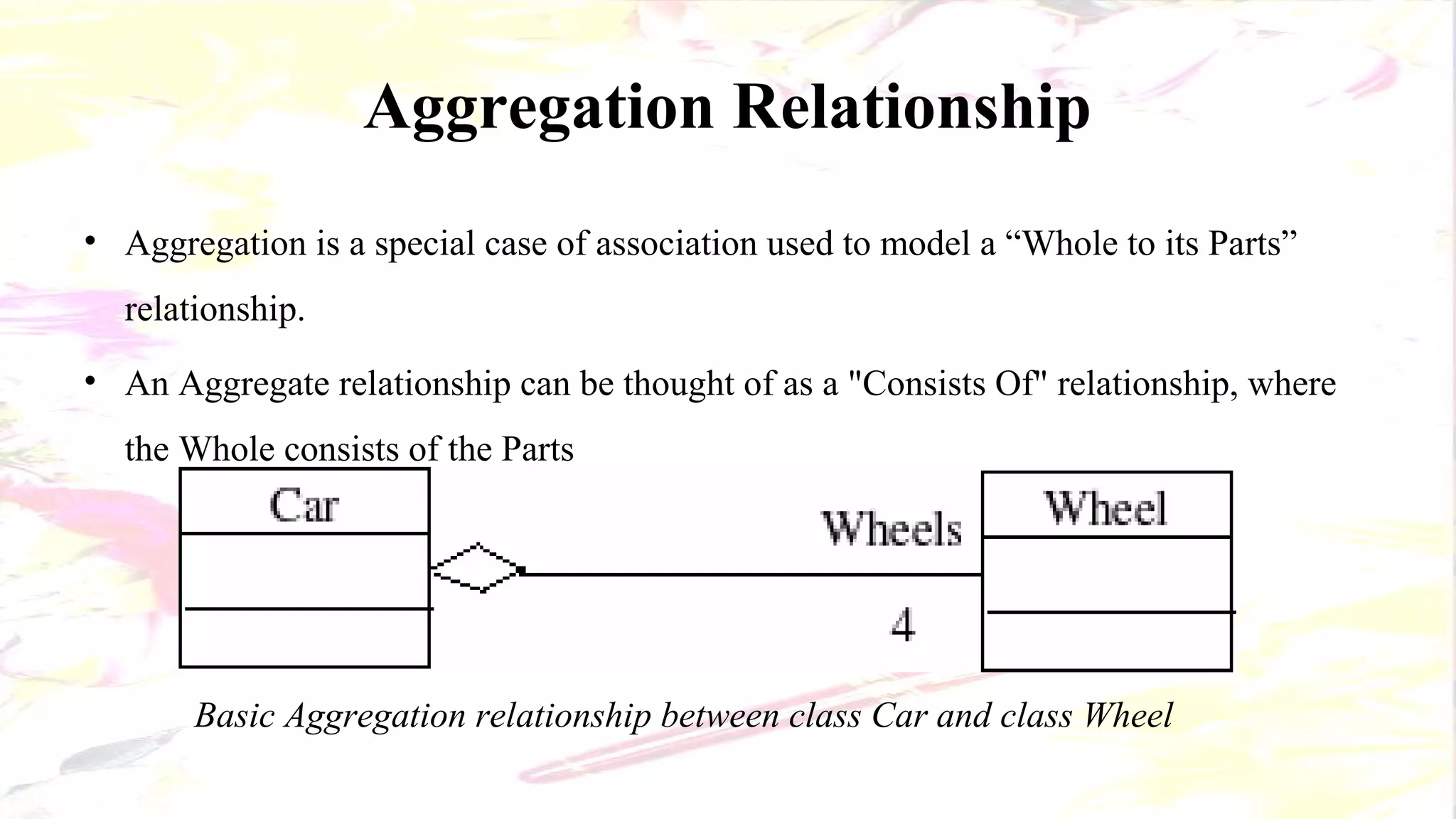
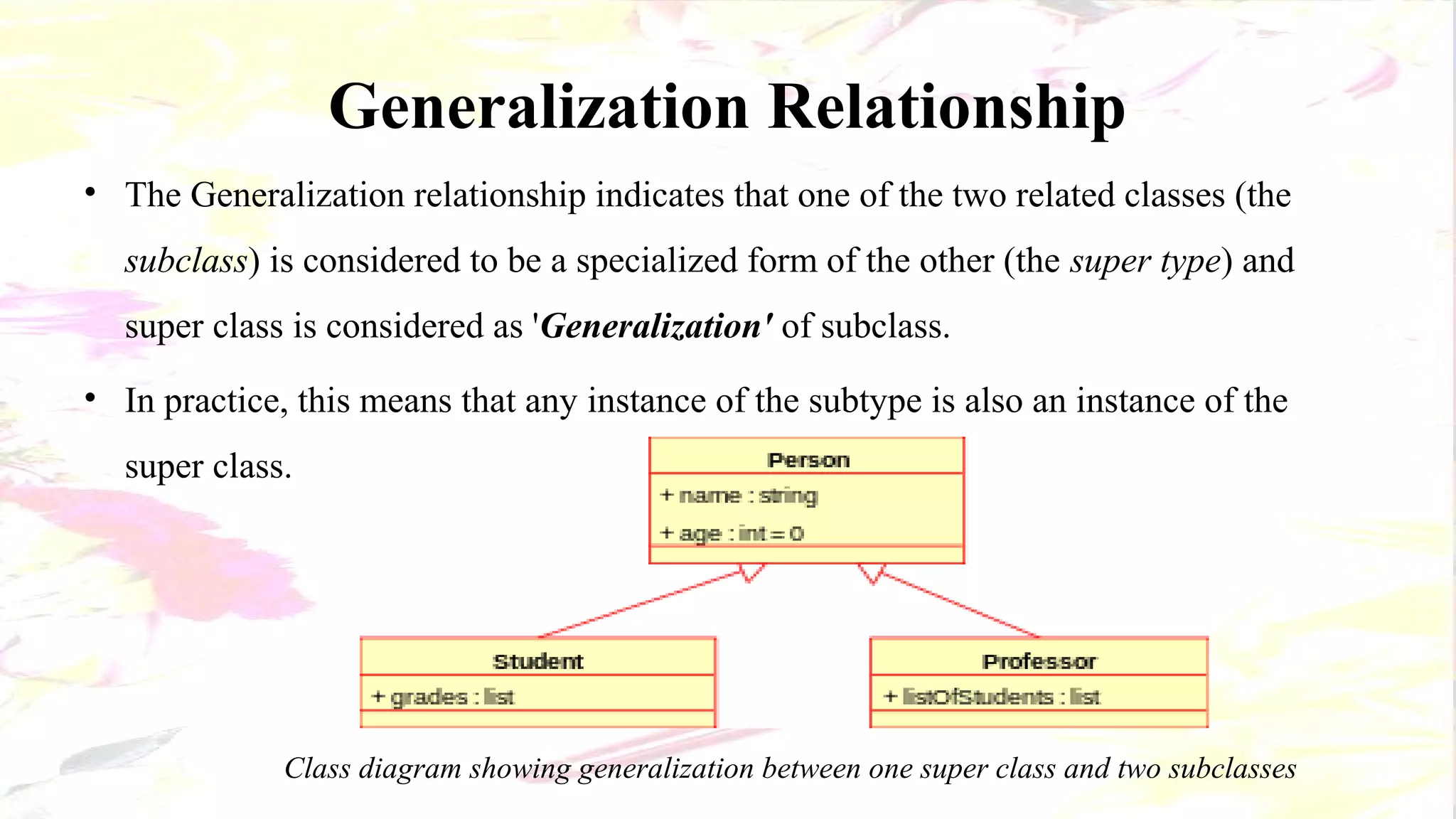
The document describes the key elements of a class diagram in UML including classes, attributes, operations, and relationships. A class represents a set of objects with shared characteristics like attributes and behaviors. Common relationships shown are association, aggregation, and generalization. An example class diagram for a Bank Account class is provided to illustrate these concepts.