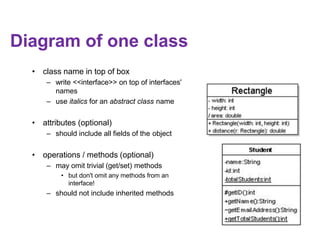
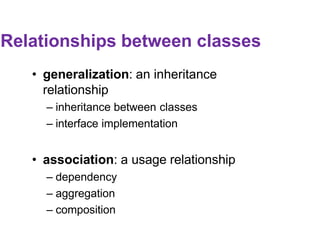
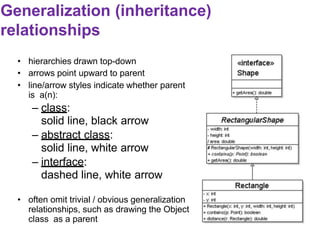
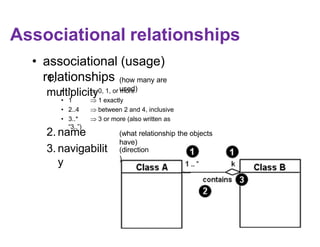
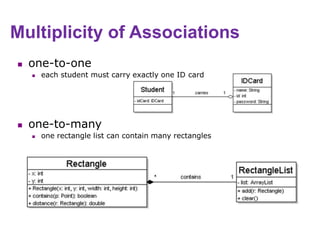
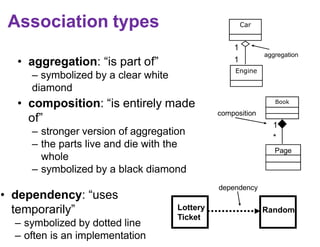
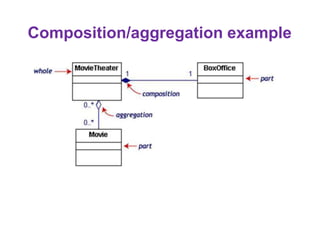
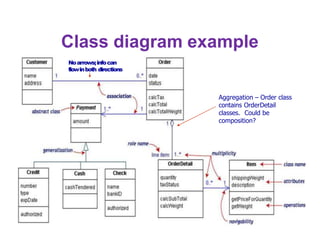
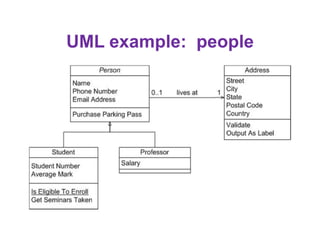
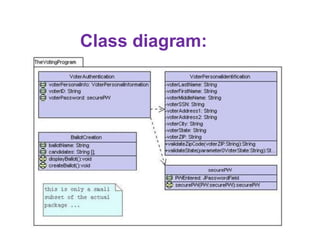
This document provides an introduction to the Unified Modeling Language (UML). UML is a standard modeling language that includes various diagram types like use case diagrams, class diagrams, sequence diagrams, and state machine diagrams. Class diagrams specifically show classes, fields, methods, and relationships between classes like inheritance, association, aggregation, and composition. Examples of class diagrams are provided to demonstrate how classes, attributes, methods, and relationships are depicted. Tools for creating UML diagrams are also listed.


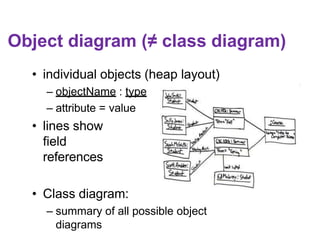
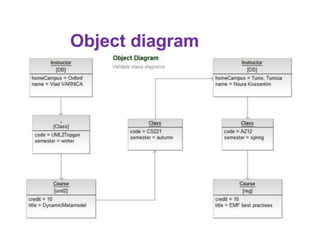
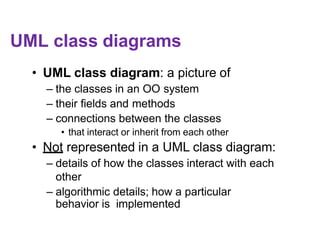
![Class attributes / fields
• attributes (fields, instance variables)
– visibility name : type [count] =
default_value
– visibility: + public
# protected
- private
~ package
(default)
/ derived
– underline static attributes
– derived attribute: not stored, but can
be computed from other attribute
values
• “specification fields “ from CSE 331
– attribute example:
- balance : double = 0.00](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/umlppt-200403063047/85/Uml-ppt-7-320.jpg)

![Class diagram example:
student
StudentBody
+ main (args : String[])
1 100
Student
- firstName : String
- lastName : String
- homeAddress : Address
- schoolAddress : Address
+ toString() : String
Address
- streetAddress : String
- city : String
- state : String
- zipCode : long
+ toString() : String](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/umlppt-200403063047/85/Uml-ppt-18-320.jpg)