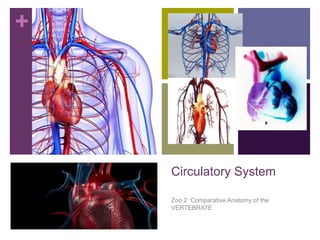
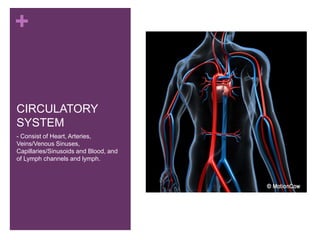
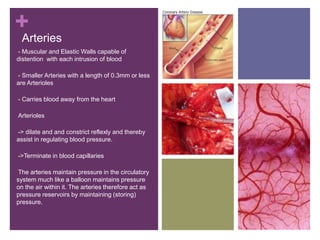
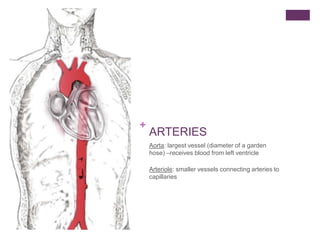
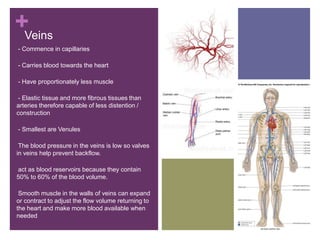
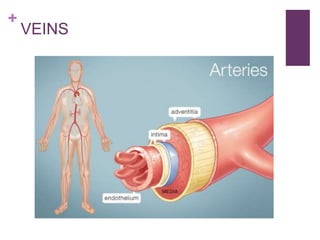
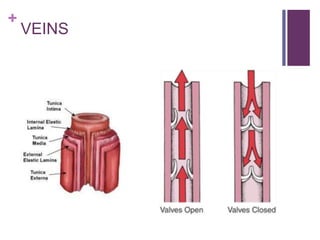
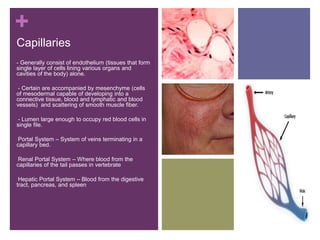
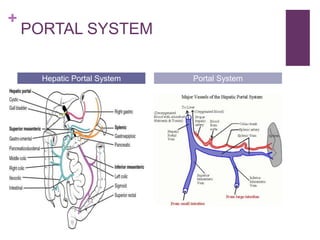
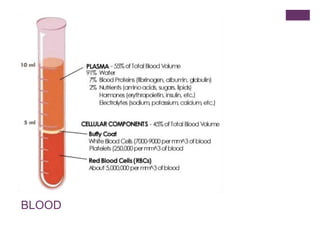
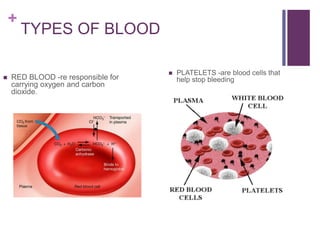
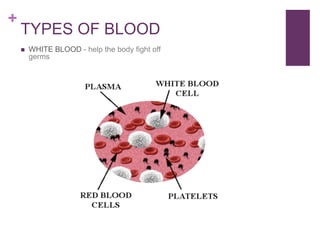
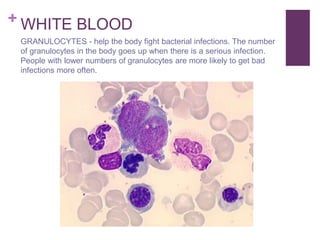
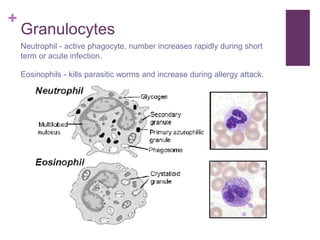
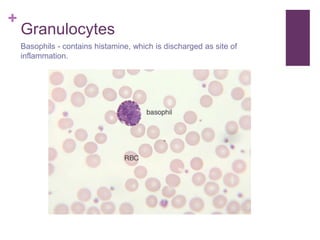
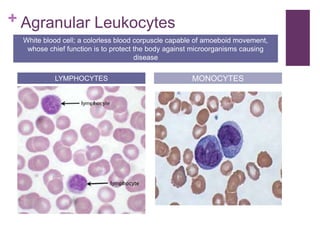
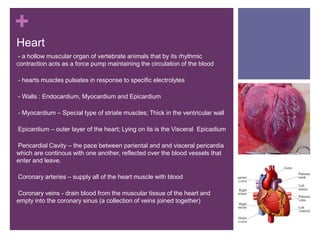
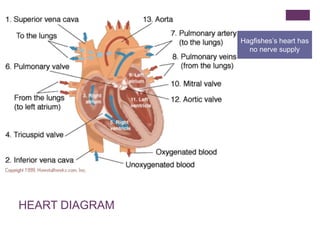
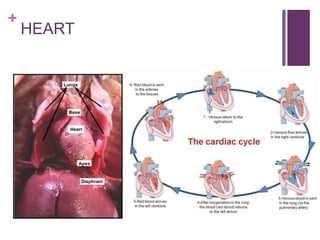
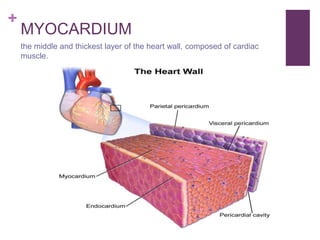
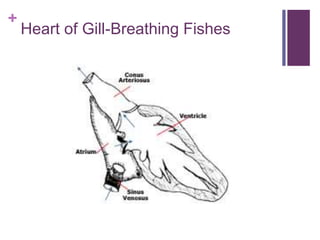
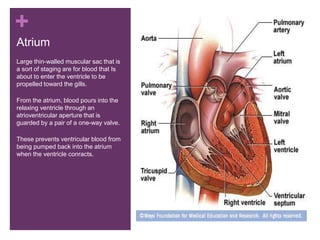
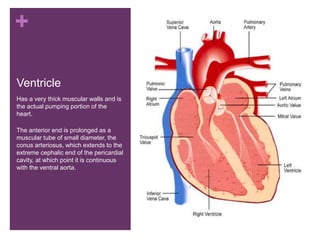
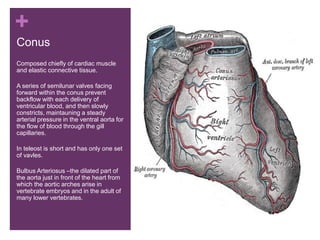
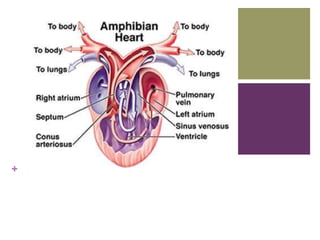
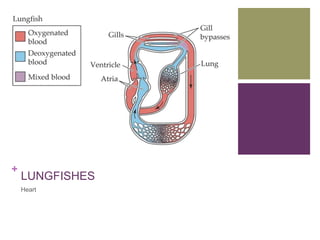
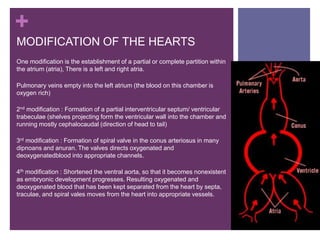
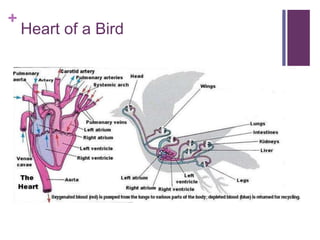
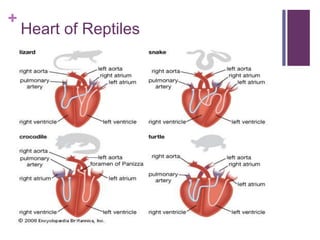
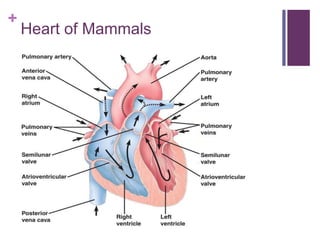
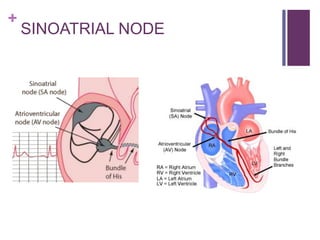
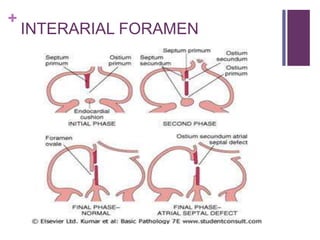
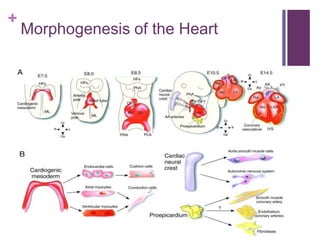
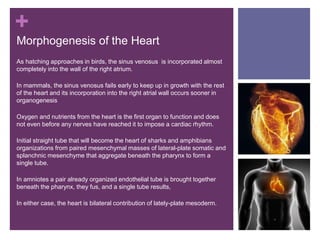
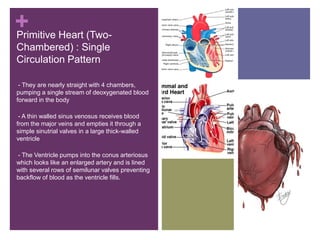
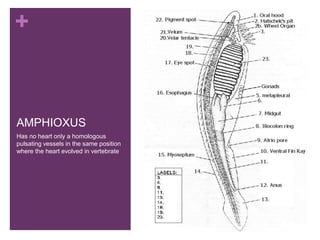
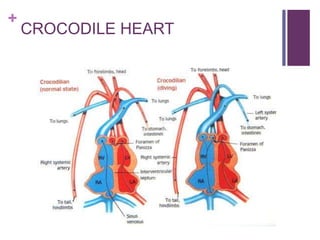
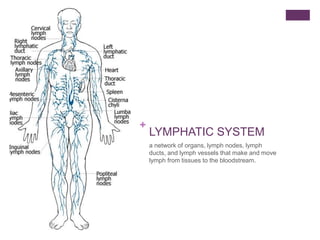
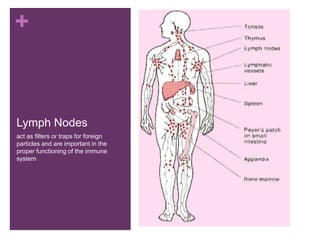
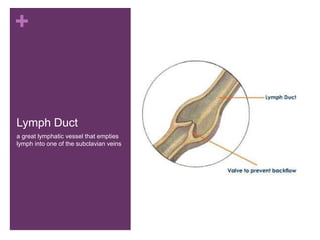
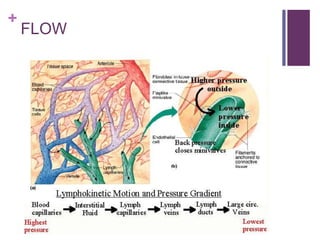
The circulatory system transports blood, nutrients, oxygen, hormones, and other materials throughout the body while removing wastes. It consists of the heart, arteries, veins, capillaries, lymph vessels, and blood. In most vertebrates, the heart has four chambers - two atria that collect blood and two ventricles that pump blood. The heart circulates blood through two circuits - the pulmonary circuit, which transports blood to the lungs to receive oxygen, and the systemic circuit, which transports oxygenated blood to the rest of the body. Over time, the vertebrate heart evolved divisions and modifications to more efficiently support gas exchange via lungs or other organs.