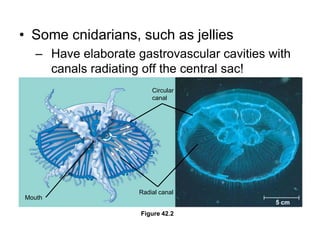
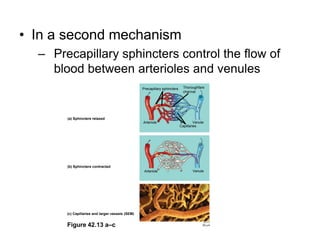
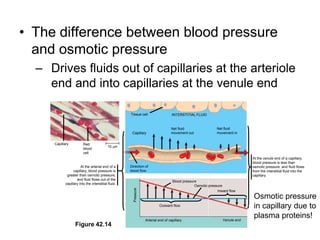
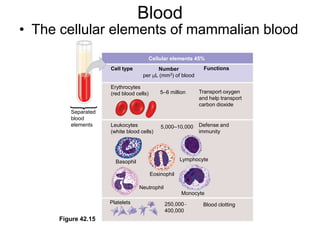
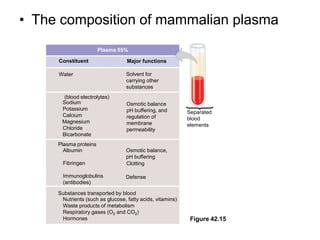
1. Circulation and gas exchange occur through specialized systems that have evolved in multicellular organisms. These systems allow for the exchange of oxygen, carbon dioxide, and nutrients between cells and the external environment.
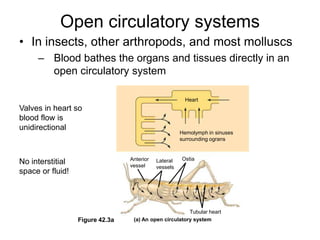
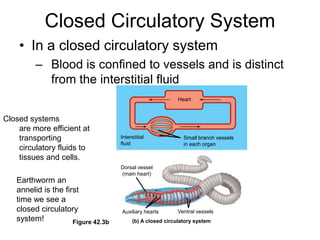
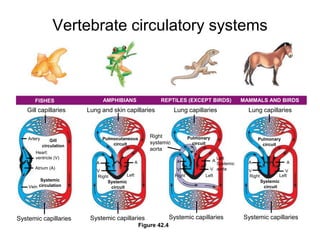
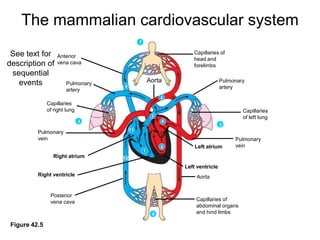
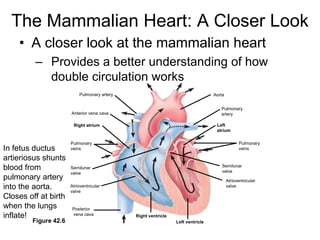
2. Gills, lungs, and internal transport systems have developed to facilitate gas and nutrient exchange across large diffusion distances in complex organisms. Vertebrates have closed circulatory systems with two-, three-, or four-chambered hearts that use arteries, capillaries and veins.
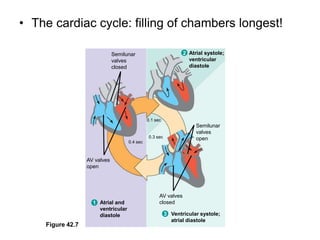
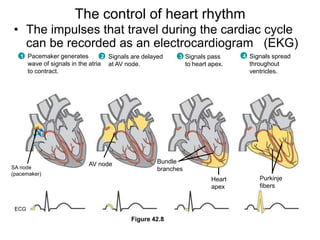
3. The heart pumps blood in a double circulation through the pulmonary and systemic circuits. Heart rate and cardiac output are regulated to meet the metabolic demands of the organism.