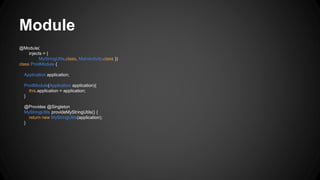
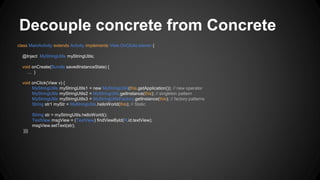
The document discusses dependency injection in Android using Dagger, emphasizing its benefits such as decoupling of components, improved testability, and reduced dependency management. It illustrates various examples of dependency injection patterns with code snippets, showcasing how to implement these ideas in Android applications. Additionally, it highlights the use of Dagger for testing and includes references to resources for further exploration.
















![Build the Graph
class CoffeeApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ObjectGraph objectGraph = ObjectGraph.create(new
DripCoffeeModule());
CoffeeMaker coffeeMaker = objectGraph.get(CoffeeMaker.class);
coffeeMaker.brew();
} }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l1prplthto6wsjowk72v-140529143552-phpapp01/85/Dependency-Injection-for-Android-Ciklum-speakers-corner-Kiev-29-May-2014-19-320.jpg)