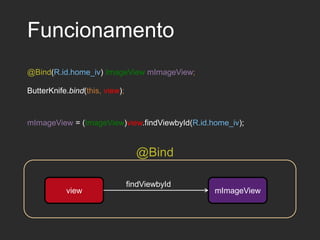
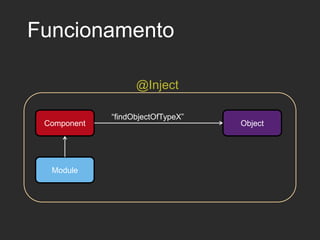
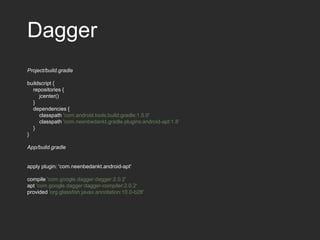
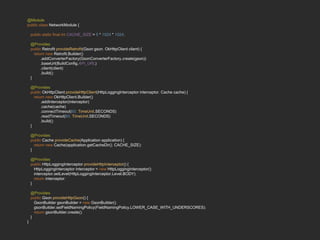
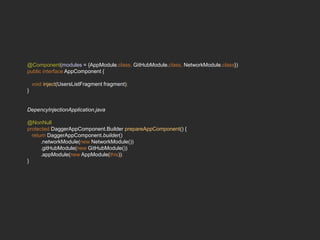
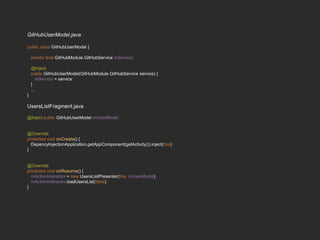
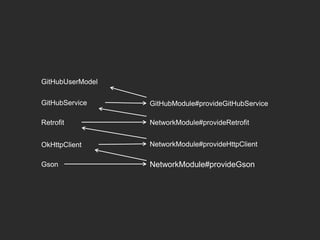
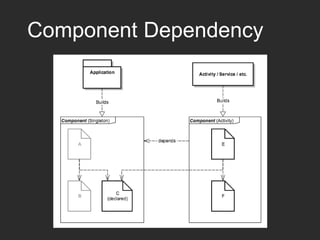
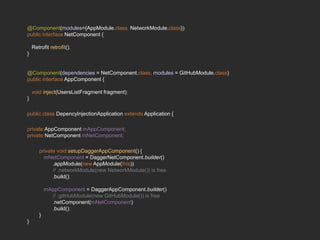
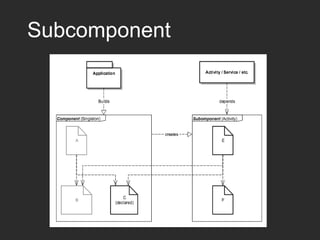
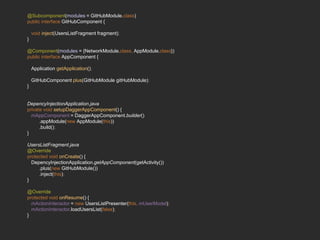
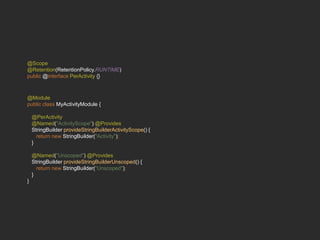
Dagger 2 is a dependency injection framework that allows for decoupling of classes through injection of dependencies. It uses modules to provide dependencies, with @Inject used to request dependencies and @Component linking modules and injections. Classes request dependencies through constructor injection or field injection with @Inject. Dagger manages the lifecycle and scoping of dependencies through its component and subcomponent functionality.