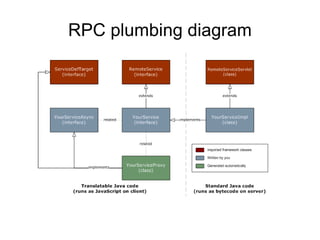
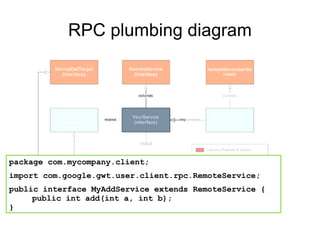
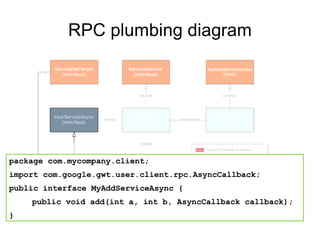
The document discusses Google Web Toolkit (GWT) Remote Procedure Calls (RPC) and how to implement RPC between a GWT client and server. It describes the key classes and interfaces used for RPC, how to define the service interface and implementation classes, deploying the service, and making an asynchronous call from the client to retrieve the response.