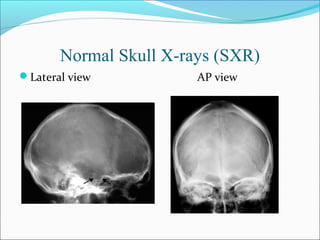
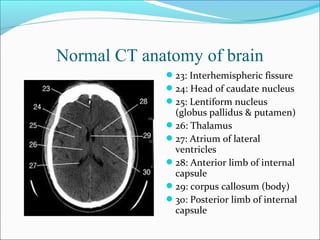
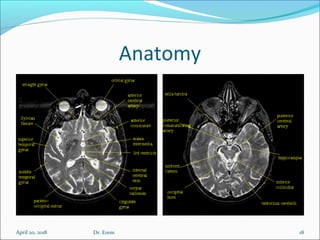
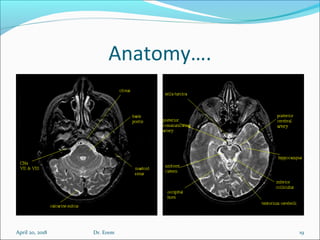
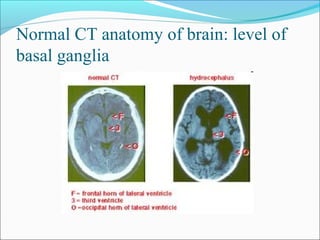
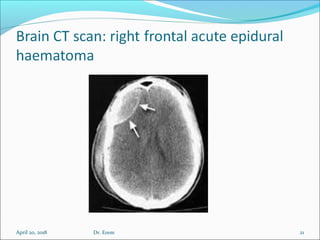
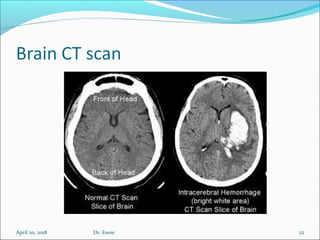
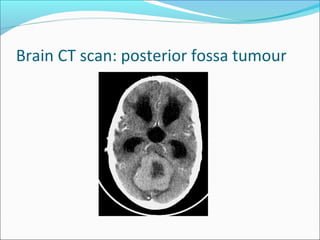
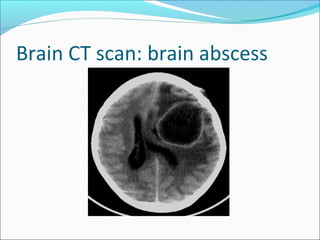
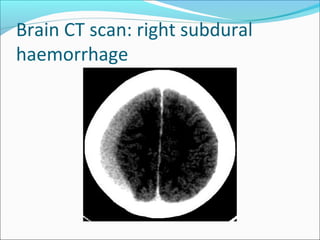
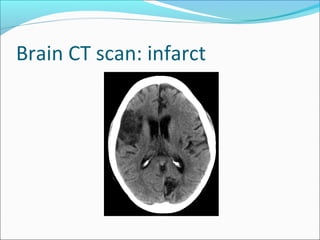
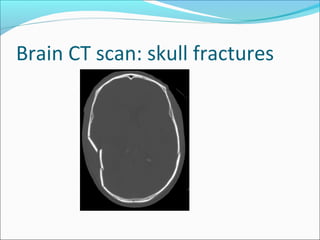
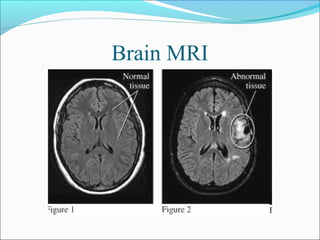
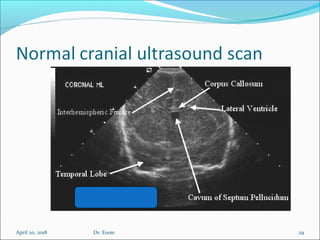
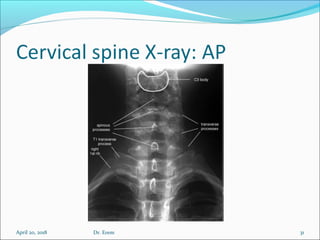
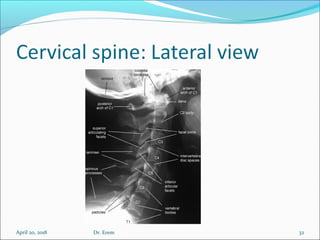
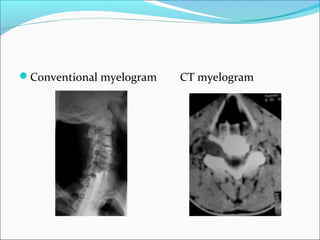
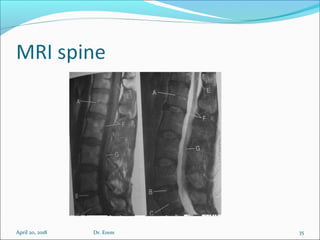
The document covers central nervous system (CNS) pathology, focusing on radiological findings and imaging modalities. It details terminologies for X-ray, CT, ultrasound, and MRI, along with their respective indications for investigating CNS conditions. Additionally, it highlights common pathologies and emergencies identifiable through radiological imaging.