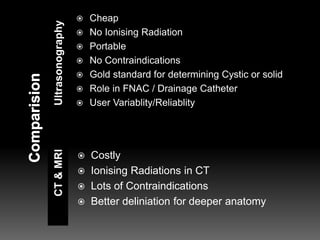
Ultrasound uses sound waves with frequencies above 20 kHz to produce images of tissues and structures. Piezoelectric materials are used to generate ultrasound, and images are formed by detecting reflected sound waves. Echogenicity refers to a tissue's ability to reflect sound waves, with more echogenic tissues appearing lighter on images. Ultrasound is used to evaluate thyroid disorders, lymph nodes, salivary glands, and other neck structures. It is a valuable tool for diagnosis and guidance of procedures due to its low cost, lack of radiation, and portability.