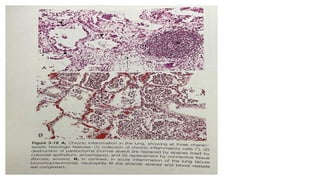
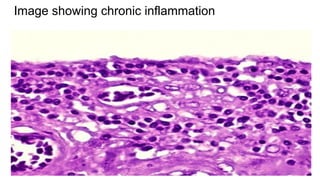
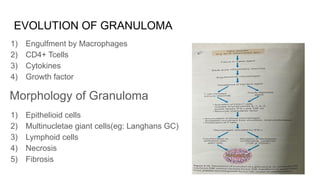
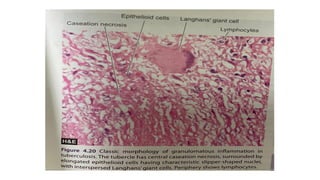
The document discusses chronic inflammation, its causes, effects, and the role of giant cells, particularly in the context of tuberculosis. Chronic inflammation is defined as a prolonged response, often resulting from persistent infection, exposure to toxic agents, or autoimmunity, and is characterized by histological features such as mononuclear infiltration and tissue destruction. Granulomas, a type of chronic inflammation response, consist of epithelioid cells and multinucleate giant cells and are formed due to type IV hypersensitivity reactions.