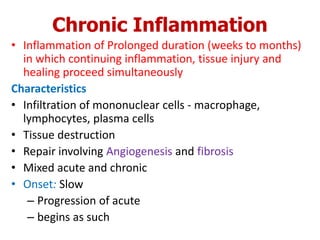
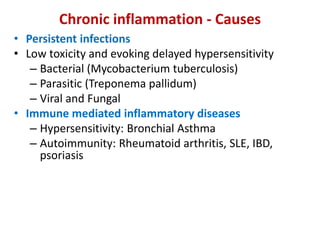
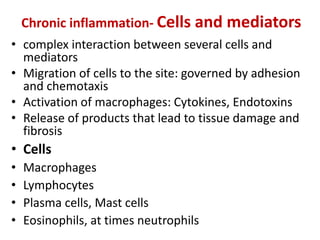
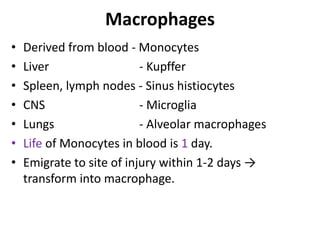
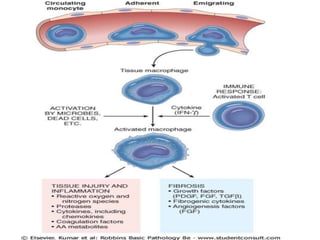
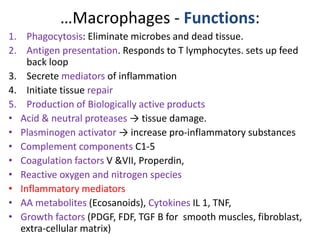
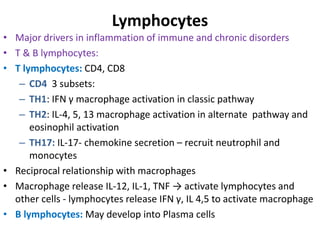
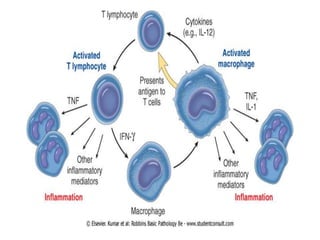
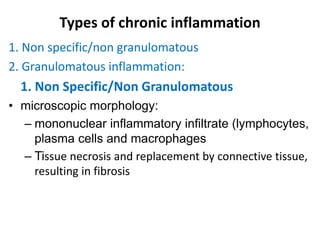
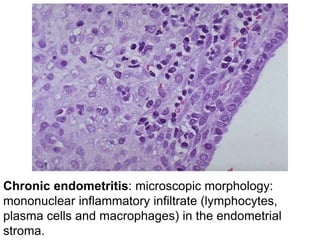
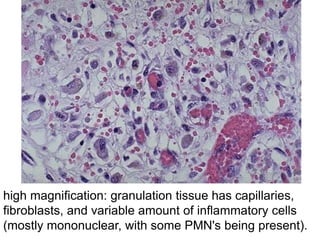
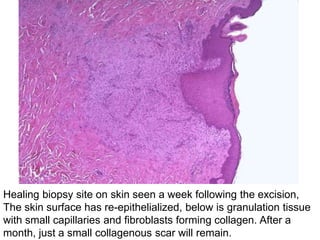
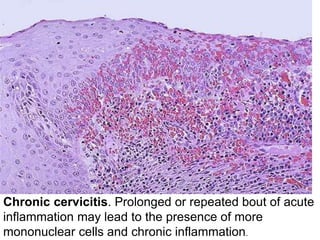
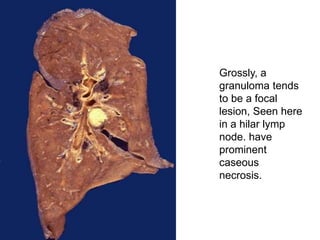
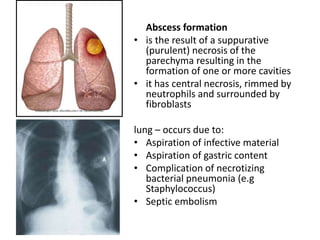
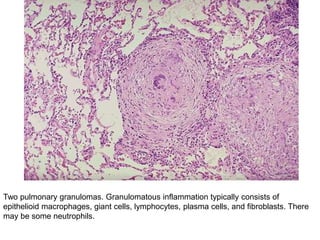
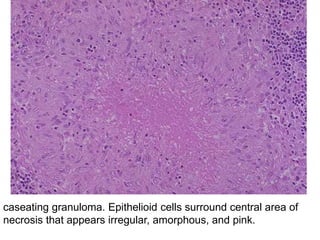
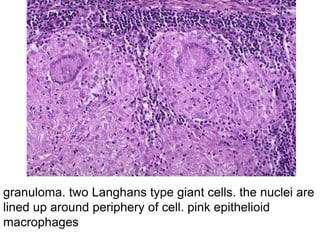
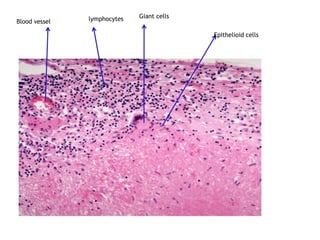
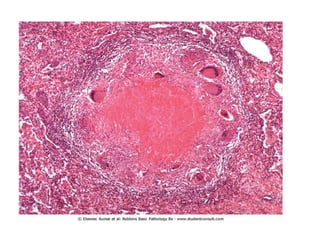
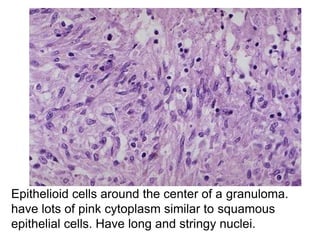
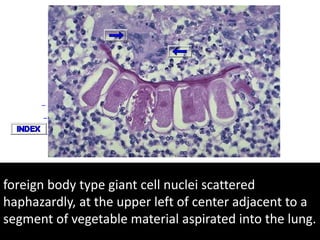
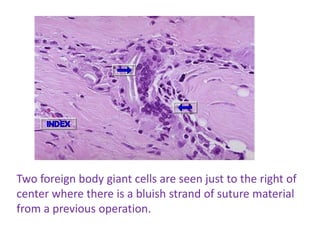
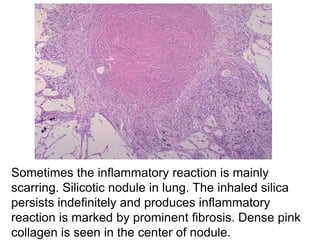
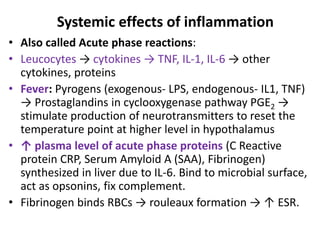
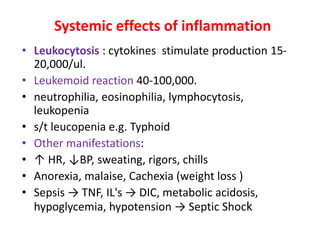
Chronic inflammation is inflammation of prolonged duration, lasting weeks to months. It is characterized by infiltration of mononuclear cells like macrophages, lymphocytes, and plasma cells; ongoing tissue destruction and repair; and both acute and chronic features. It can be caused by persistent infections, immune-mediated diseases, prolonged toxic exposures, or unknown factors. The main cells involved are macrophages, lymphocytes, and plasma cells. Macrophages play a key role through classical and alternative activation pathways and release of inflammatory mediators. Chronic inflammation can be non-granulomatous or granulomatous, and causes systemic effects like fever, increased acute phase proteins, and changes in white blood cell counts.