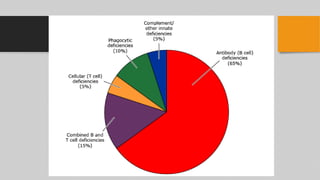
This document provides an overview of the approach to evaluating primary immunodeficiency. It discusses the importance of differentiating primary from secondary immunodeficiency. The most common presentations of primary immunodeficiency are recurrent infections, especially of the ear, sinus, lungs and gastrointestinal tract. A thorough history and physical exam can provide clues to the underlying immunodeficiency. Initial screening tests include a complete blood count, immunoglobulin levels and lymphocyte subset analysis. Further specialized testing helps characterize the specific immune deficiency.