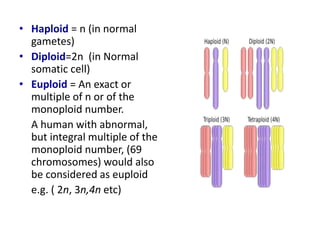
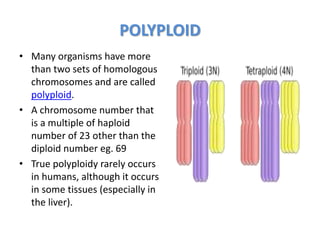
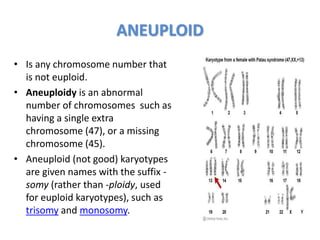
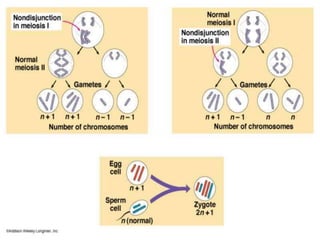
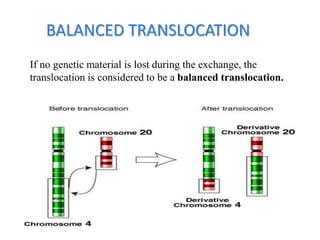
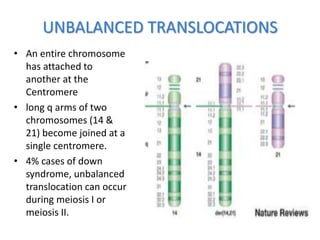
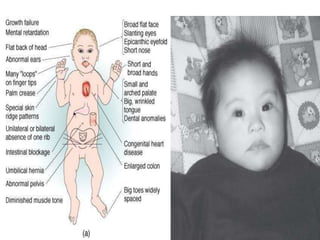
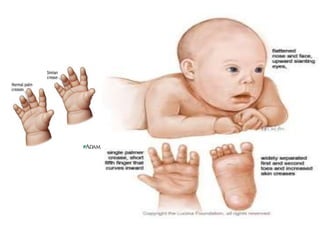
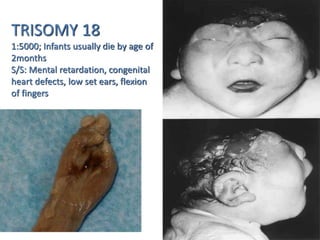
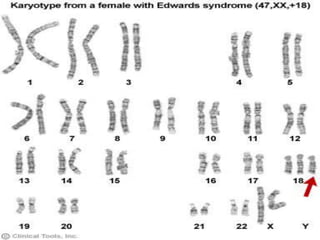
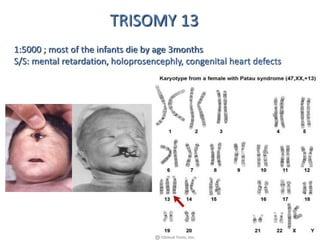
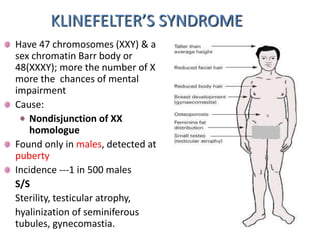
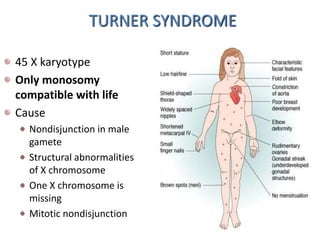
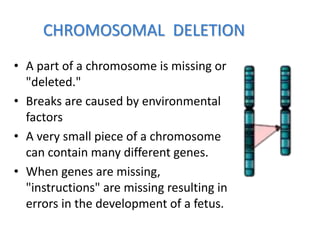
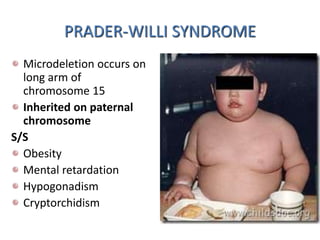
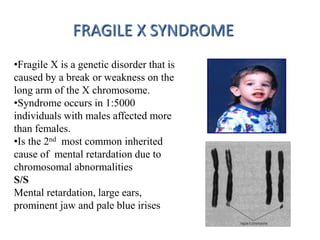
Chromosomal abnormalities can be caused by numerical or structural changes to chromosomes. Numerical abnormalities include aneuploidy, where there is an extra or missing chromosome, and polyploidy, where there are multiple sets of chromosomes. They can occur through meiotic or mitotic nondisjunction. Specific aneuploid syndromes include Down syndrome, Klinefelter syndrome, and Turner syndrome. Structural abnormalities involve changes in chromosome structure like translocations, deletions, or duplications. Specific syndromes caused by structural abnormalities include Cri-du-chat syndrome and Fragile X syndrome. Both numerical and structural chromosomal abnormalities can cause birth defects, miscarriages, and genetic disorders.