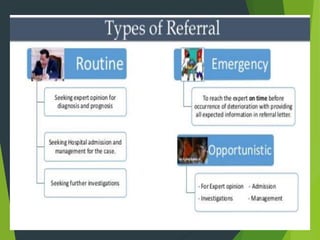
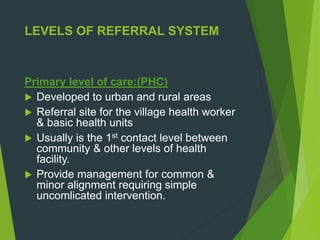
This document discusses the referral system for delivering community health services. It defines a referral system as a mechanism that enables a patient's health needs to be comprehensively managed using resources beyond the facility they initially accessed care from. The objectives, definition, reasons for referral, characteristics, rationale, levels, types, components, perspectives, and issues of a referral system are described. The levels include primary, secondary and tertiary care facilities. The responsibilities of nurses in the referral process are also outlined.