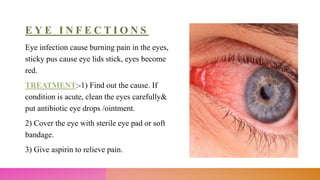
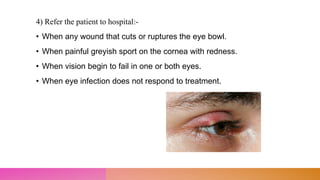
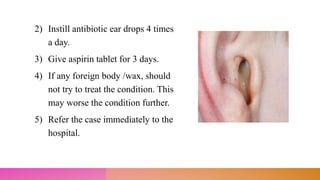
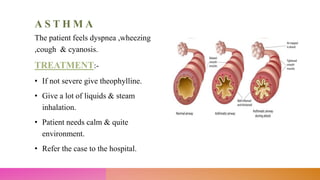
This document discusses minor ailments that may be encountered by community health nurses. It defines minor ailments as health complaints that can typically be managed by patients themselves through simple actions and do not require a doctor's care. The document outlines principles for managing minor ailments, such as ensuring a safe environment and providing health education. It then describes the management of specific minor conditions like fever, cough, sore throat, eye infections, earache, sinusitis, common cold, asthma, high blood pressure, anemia, toothache, diarrhea, indigestion, constipation, fractures, skin rashes, and wounds.