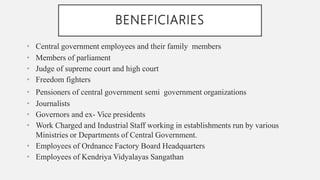
The ESI scheme provides cash and medical benefits to industrial employees in case of sickness, maternity, and employment injury. It covers factories, shops, hotels, cinemas, transport, and some private institutions employing over a certain number of people. Benefits include medical care, sickness pay, maternity benefits, disability compensation, dependent benefits, and funeral expenses. The CGHS provides comprehensive medical care to central government employees and pensioners and their families through outdoor treatment, medicines, tests, home care, and specialist consultations in government facilities. It aims to provide extensive healthcare and reduce medical expenses refund costs for the government.